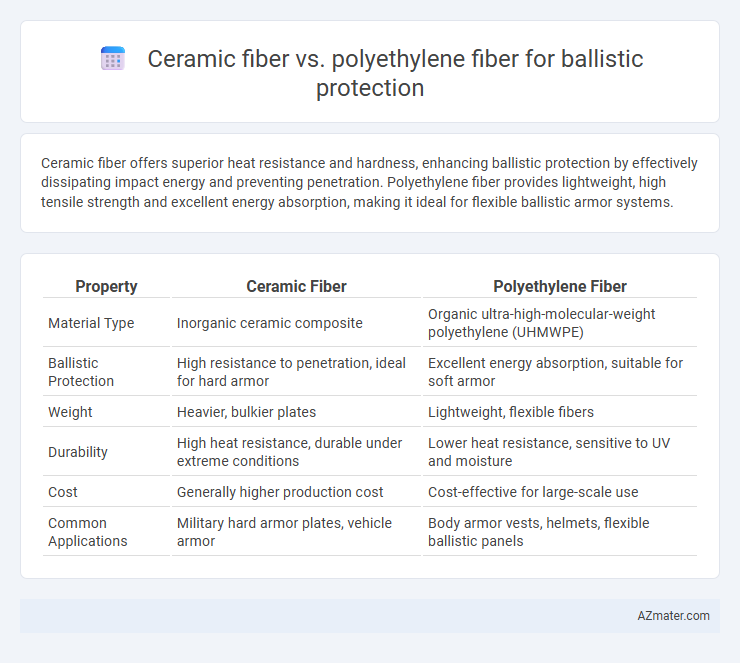
Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance and hardness, enhancing ballistic protection by effectively dissipating impact energy and preventing penetration. Polyethylene fiber provides lightweight, high tensile strength and excellent energy absorption, making it ideal for flexible ballistic armor systems.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Fiber | Polyethylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Inorganic ceramic composite | Organic ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) |
| Ballistic Protection | High resistance to penetration, ideal for hard armor | Excellent energy absorption, suitable for soft armor |
| Weight | Heavier, bulkier plates | Lightweight, flexible fibers |
| Durability | High heat resistance, durable under extreme conditions | Lower heat resistance, sensitive to UV and moisture |
| Cost | Generally higher production cost | Cost-effective for large-scale use |
| Common Applications | Military hard armor plates, vehicle armor | Body armor vests, helmets, flexible ballistic panels |
Introduction to Ballistic Protection Materials
Ceramic fiber and polyethylene fiber represent two distinct categories of ballistic protection materials, each offering unique advantages in impact resistance and weight. Ceramic fibers provide superior hardness and are effective at dissipating high-velocity projectiles through shattering, making them essential for hard armor plates. Polyethylene fibers excel in flexibility and lightweight ballistic vests, delivering high tensile strength and energy absorption for efficient blunt force mitigation.
Overview of Ceramic Fiber in Ballistic Applications
Ceramic fiber is widely used in ballistic protection due to its high hardness, low density, and excellent thermal stability, making it ideal for dissipating kinetic energy from projectiles. Its brittle nature allows ceramic fibers to fracture upon impact, absorbing and deflecting energy, which reduces penetration and enhances protective performance. Ceramic fiber composites are commonly integrated into armor systems to provide a lightweight yet effective solution against high-velocity ballistic threats.
Polyethylene Fiber: Properties and Uses in Ballistics
Polyethylene fiber, specifically Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), offers exceptional ballistic protection due to its high tensile strength-to-weight ratio, chemical resistance, and energy absorption capabilities. It provides lightweight armor solutions commonly used in soft body armor, helmets, and vehicle panels, enhancing mobility without compromising protection. Its ability to disperse impact energy efficiently makes it ideal for multi-hit scenarios and flexible ballisticwear.
Comparative Ballistic Performance: Ceramic vs Polyethylene Fiber
Ceramic fibers, such as alumina and silicon carbide, provide superior hardness and high compressive strength, enabling them to shatter and erode incoming projectiles effectively during ballistic impacts. Polyethylene fibers like ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) offer high tensile strength and energy absorption through fiber deformation and delamination, resulting in lighter weight ballistic solutions but generally lower ballistic resistance against high-velocity threats. In comparison, ceramic fiber armor excels in stopping armor-piercing rounds due to its hardness, while polyethylene fiber armor provides better multi-hit performance and flexibility, making the choice dependent on threat type and application requirements.
Weight and Flexibility Analysis
Ceramic fiber offers superior ballistic protection due to its high hardness and ability to dissipate impact energy, but it tends to be heavier and less flexible compared to polyethylene fiber. Polyethylene fiber, known for its lightweight properties and excellent flexibility, provides effective ballistic resistance while significantly reducing the overall weight of protective gear. Weight analysis reveals that polyethylene fiber-based materials can be up to 30-50% lighter than ceramic fiber composites, enhancing mobility and comfort without compromising safety.
Durability and Longevity in Field Conditions
Ceramic fiber offers superior durability and longevity in ballistic protection, maintaining structural integrity under high-impact and extreme environmental conditions like heat, moisture, and abrasion. Polyethylene fiber, while lightweight and flexible, tends to degrade faster when exposed to UV radiation, moisture, and abrasive wear, limiting its lifespan in harsh field environments. Field data indicate ceramic fiber systems can sustain effectiveness over extended deployments, whereas polyethylene-based gear often requires more frequent replacement to ensure reliable ballistic performance.
Cost-Effectiveness of Ceramic vs Polyethylene Fiber
Ceramic fiber offers superior ballistic protection at a higher initial cost due to its hardness and ability to dissipate impact energy, making it cost-effective for high-threat environments where maximum protection is essential. Polyethylene fiber provides a more affordable alternative with lighter weight and ease of integration, suitable for moderate threat levels but may require more frequent replacement, increasing long-term expenses. Evaluating lifecycle costs and threat requirements is critical to determine the optimal balance between upfront investment and durability in ballistic protection solutions.
Multi-Threat Protection Capabilities
Ceramic fiber offers superior multi-threat ballistic protection due to its high hardness and ability to dissipate impact energy from rifle rounds and fragments, while polyethylene fiber provides excellent lightweight resistance against stab and blunt force trauma with effectiveness against certain ballistic threats. The combination of ceramic fiber's rigidity and polyethylene fiber's tensile strength creates a hybrid solution that enhances multi-threat protection without compromising mobility. Advanced body armor systems integrating both materials deliver balanced defense against bullets, sharp objects, and explosive fragments in diverse combat scenarios.
Environmental Resistance and Maintenance
Ceramic fiber offers superior environmental resistance for ballistic protection, with excellent stability against high temperatures, moisture, and chemical exposure, making it ideal for extreme conditions. Polyethylene fiber provides good resistance to moisture but degrades under UV exposure and high heat, requiring more frequent maintenance to retain ballistic integrity. Maintenance for ceramic fiber involves minimal cleaning and inspection, while polyethylene fiber demands regular checks for wear and environmental damage to ensure consistent protection.
Choosing the Right Fiber: Application-Specific Recommendations
Ceramic fibers exhibit superior hardness and heat resistance, making them ideal for high-impact ballistic applications requiring rigid armor solutions. Polyethylene fibers provide lightweight, flexible alternatives suitable for soft body armor where mobility and comfort are critical factors. Selecting the correct fiber depends on balancing protection level, weight constraints, and intended use environment for optimal ballistic performance.
Infographic: Ceramic fiber vs Polyethylene fiber for Ballistic protection
 azmater.com
azmater.com