Mineral fiber reinforced panels offer superior fire resistance, thermal insulation, and durability compared to plastic fiber panels, which provide lightweight and cost-effective solutions with better flexibility and moisture resistance. Choosing mineral fiber panels enhances structural integrity and safety in high-temperature applications, while plastic fiber panels are ideal for lightweight, moisture-prone environments.
Table of Comparison
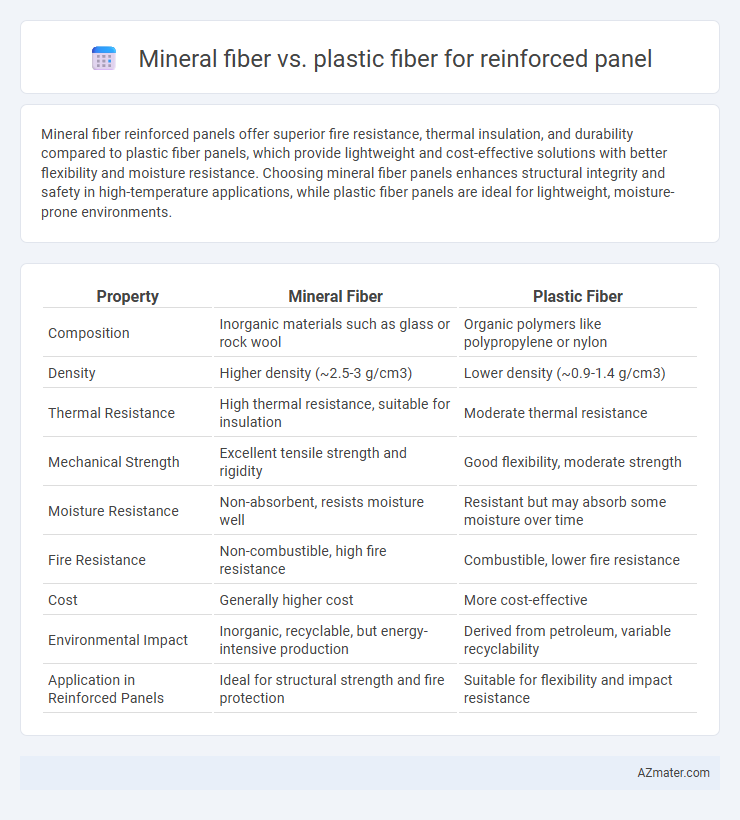
| Property | Mineral Fiber | Plastic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Inorganic materials such as glass or rock wool | Organic polymers like polypropylene or nylon |
| Density | Higher density (~2.5-3 g/cm3) | Lower density (~0.9-1.4 g/cm3) |
| Thermal Resistance | High thermal resistance, suitable for insulation | Moderate thermal resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent tensile strength and rigidity | Good flexibility, moderate strength |
| Moisture Resistance | Non-absorbent, resists moisture well | Resistant but may absorb some moisture over time |
| Fire Resistance | Non-combustible, high fire resistance | Combustible, lower fire resistance |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | More cost-effective |
| Environmental Impact | Inorganic, recyclable, but energy-intensive production | Derived from petroleum, variable recyclability |
| Application in Reinforced Panels | Ideal for structural strength and fire protection | Suitable for flexibility and impact resistance |
Introduction to Reinforced Panels
Reinforced panels benefit from the enhanced structural properties provided by mineral fibers, such as increased fire resistance, thermal stability, and sound insulation, compared to plastic fibers that mainly improve flexibility and impact resistance. Mineral fibers, often derived from glass or basalt, offer superior durability and environmental resistance, making them ideal for applications requiring long-term performance and safety. Plastic fibers, typically polypropylene or nylon, contribute to weight reduction and cost efficiency but may degrade faster under UV exposure and high temperatures.
Overview of Mineral Fiber Reinforcement
Mineral fiber reinforcement in panels consists of materials like glass, basalt, and rock wool fibers, known for their high tensile strength, thermal resistance, and excellent fire retardant properties. These fibers provide superior durability, enhanced structural integrity, and improved insulation compared to plastic fibers, making them ideal for applications requiring high-performance fire safety and mechanical strength. Mineral fiber reinforced panels are widely used in construction and industrial sectors where long-term stability and resistance to heat and chemicals are critical.
Overview of Plastic Fiber Reinforcement
Plastic fiber reinforcement in panels enhances tensile strength, impact resistance, and durability by effectively distributing stresses throughout the material. These synthetic fibers, often made from polypropylene, polyethylene, or nylon, offer superior corrosion resistance and lightweight properties compared to mineral fibers like glass or basalt. Plastic fibers improve crack control and reduce shrinkage, making them ideal for reinforced panels in construction and industrial applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Mineral fiber reinforced panels exhibit higher tensile strength and superior fire resistance compared to plastic fiber reinforced panels, making them ideal for structural applications requiring durability and thermal stability. Plastic fiber reinforced panels typically offer better flexibility and impact resistance but lower stiffness and heat tolerance. The mechanical performance differences impact choices in construction, with mineral fibers favored for load-bearing components and plastic fibers preferred for lightweight, vibration-damping panels.
Durability and Longevity
Mineral fiber reinforced panels exhibit superior durability due to their resistance to fire, moisture, and chemical degradation, resulting in longer service life compared to plastic fiber panels. Plastic fibers tend to degrade under UV exposure and high temperatures, reducing the longevity of reinforced panels in outdoor or harsh environments. Enhanced mechanical properties of mineral fiber panels provide improved structural integrity over time, making them ideal for demanding construction applications.
Fire Resistance and Safety Aspects
Mineral fiber panels exhibit superior fire resistance due to their non-combustible nature and high melting points, often exceeding 1000degC, which significantly enhances safety in fire-prone environments. Plastic fiber panels, typically made from synthetic polymers, have lower ignition temperatures and produce toxic smoke when burned, posing higher risks during fires. In reinforced panel applications, mineral fiber's fire resistance and minimal smoke generation make it a safer choice compared to plastic fiber alternatives.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Mineral fiber reinforced panels offer superior environmental benefits due to their non-toxic composition, recyclability, and resistance to fire and mold, reducing long-term ecological impact. Plastic fiber panels often rely on petroleum-based materials, leading to higher carbon footprints and challenges in recyclability, thus contributing to microplastic pollution. Choosing mineral fibers promotes sustainability in construction by minimizing harmful emissions and enabling circular material use.
Cost Analysis: Mineral vs Plastic Fiber
Mineral fiber reinforced panels typically have higher initial costs due to raw material expenses and manufacturing processes compared to plastic fiber panels, which are generally more economical and easier to produce at scale. However, long-term cost savings with mineral fiber panels can be realized through enhanced fire resistance, thermal insulation, and durability, reducing maintenance and replacement expenses. Plastic fiber panels may require more frequent repairs and have lower fire resistance, impacting overall lifecycle costs despite lower upfront investment.
Applications in Construction and Industry
Mineral fibers, such as glass wool and rock wool, excel in fire resistance and thermal insulation, making them ideal for construction applications like roofing, wall panels, and fireproofing in industrial settings. Plastic fibers, commonly polypropylene or polyester, offer superior flexibility and impact resistance, frequently used in industrial panels requiring lightweight reinforcement and enhanced durability. Both fiber types improve mechanical strength and longevity of reinforced panels, with mineral fibers favored for high-temperature environments and plastic fibers chosen for cost-effective, versatile applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Reinforced Panels
Mineral fiber offers superior fire resistance, thermal insulation, and soundproofing qualities, making it ideal for reinforced panels in construction requiring enhanced safety and durability. Plastic fiber provides greater flexibility and moisture resistance, suitable for lightweight applications and environments prone to humidity exposure. Selecting the right fiber depends on balancing performance needs, environmental conditions, and cost efficiency to optimize panel strength and longevity.
Infographic: Mineral fiber vs Plastic fiber for Reinforced panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com