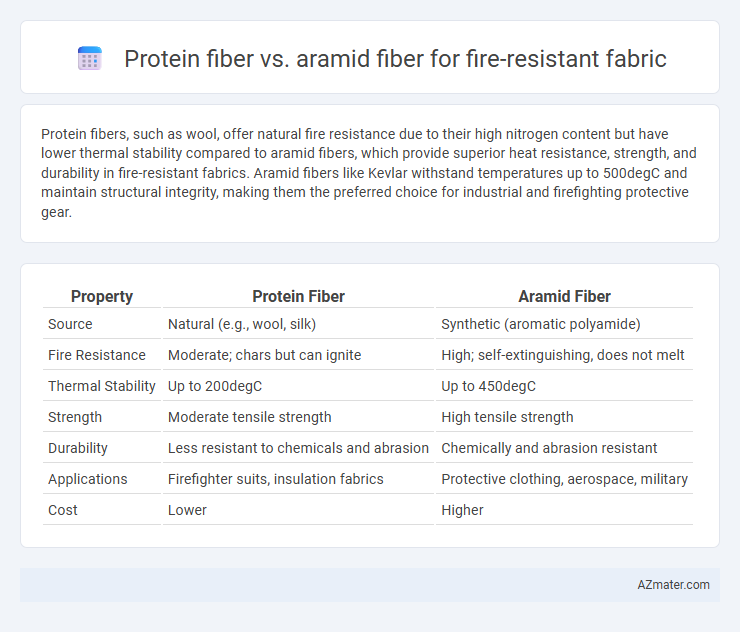
Protein fibers, such as wool, offer natural fire resistance due to their high nitrogen content but have lower thermal stability compared to aramid fibers, which provide superior heat resistance, strength, and durability in fire-resistant fabrics. Aramid fibers like Kevlar withstand temperatures up to 500degC and maintain structural integrity, making them the preferred choice for industrial and firefighting protective gear.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Protein Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural (e.g., wool, silk) | Synthetic (aromatic polyamide) |
| Fire Resistance | Moderate; chars but can ignite | High; self-extinguishing, does not melt |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 200degC | Up to 450degC |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength |
| Durability | Less resistant to chemicals and abrasion | Chemically and abrasion resistant |
| Applications | Firefighter suits, insulation fabrics | Protective clothing, aerospace, military |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Fire-Resistant Fabrics
Fire-resistant fabrics are engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent ignition, making them essential for protective clothing and industrial applications. Protein fibers, such as wool, offer natural flame resistance due to their complex keratin structure and moisture retention, which slows combustion. Aramid fibers, like Kevlar and Nomex, provide superior thermal stability and mechanical strength, maintaining integrity and protecting wearers in extreme heat conditions.
Overview of Protein Fibers
Protein fibers such as wool and silk, derived from natural animal sources, exhibit inherent flame resistance due to their nitrogen-containing amino acid structures, which promote charring rather than melting upon exposure to fire. These fibers demonstrate lower heat release rates and better thermal insulation properties compared to many synthetic fibers, making them suitable for fire-resistant fabrics. However, their moisture absorption can affect durability and comfort in high-performance safety applications compared to aramid fibers.
Overview of Aramid Fibers
Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional strength and heat resistance, are synthetic fibers widely used in fire-resistant fabrics due to their superior thermal stability and durability compared to protein fibers like wool. These fibers maintain integrity at temperatures above 400degC, making them ideal for protective clothing in firefighting and industrial applications. Aramid fibers also offer excellent resistance to abrasion and chemical exposure, enhancing the longevity and safety of fire-resistant materials.
Fire Resistance Mechanisms: Protein vs. Aramid
Protein fibers such as wool exhibit fire resistance through their high nitrogen and water content, which promotes charring and slows ignition by releasing non-flammable gases during combustion. Aramid fibers, including Kevlar and Nomex, resist fire due to their aromatic polyamide molecular structure, providing inherent thermal stability and high char formation without melting or dripping. The fire resistance mechanism in protein fibers relies on chemical decomposition and moisture release, while aramid fibers depend on molecular stability and structural integrity under high temperatures.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Protein fibers such as wool exhibit inherent flame resistance with char formation and limited heat release, maintaining structural integrity under moderate thermal exposure. Aramid fibers, including Kevlar and Nomex, demonstrate superior thermal stability with high decomposition temperatures above 400degC and excellent resistance to thermal degradation, making them ideal for extreme fire-resistant applications. The thermal performance of aramid fibers surpasses protein fibers due to their ability to withstand higher heat flux and prolonged exposure without melting or dripping.
Durability and Longevity
Protein fibers such as wool offer moderate fire resistance but tend to degrade faster under high heat exposure compared to aramid fibers like Nomex, which exhibit exceptional durability and longevity in fire-resistant applications. Aramid fibers maintain structural integrity and resist thermal degradation, making them ideal for demanding environments requiring prolonged fire protection. The superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance of aramid fibers ensure extended service life, outperforming protein fibers in fire-resistant fabric performance.
Comfort and Wearability
Protein fibers like wool offer natural breathability and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing comfort in fire-resistant fabrics. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide superior heat and flame resistance but can feel stiffer and less breathable, impacting wearability during extended use. Combining protein fibers with aramids can optimize fire protection while maintaining a balance between durability, comfort, and moisture management.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Protein fibers like wool are biodegradable and renewable, offering a lower environmental footprint compared to synthetic fibers. Aramid fibers, such as Nomex, provide superior fire resistance and durability but involve energy-intensive production and generate non-biodegradable waste. Evaluating sustainability favors protein fibers for eco-friendly disposal, while aramid fibers excel in long-term performance and chemical resistance in fire-resistant fabrics.
Common Applications in Fire-Resistant Gear
Protein fibers like wool are commonly used in fire-resistant clothing due to their natural flame-retardant properties, often found in firefighter uniforms and protective workwear. Aramid fibers, such as Nomex and Kevlar, provide superior thermal resistance and strength, making them essential in industrial safety gear, military apparel, and aerospace applications. Both fibers contribute to fire-resistant fabric technology, with protein fibers offering comfort and breathability, while aramid fibers deliver enhanced durability and flame resistance in high-risk environments.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Fire-Resistant Fabrics
Protein fibers like wool offer natural flame resistance due to their high nitrogen content and ability to char rather than melt, making them suitable for moderate fire protection. Aramid fibers such as Nomex and Kevlar provide superior thermal stability and heat resistance, maintaining strength at temperatures exceeding 400degC, ideal for high-performance fire-resistant fabrics in industrial and firefighting applications. Selecting the right fiber depends on the specific fire exposure level, desired durability, and comfort requirements, balancing natural resilience with engineered protective capabilities.
Infographic: Protein fiber vs Aramid fiber for Fire-resistant fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com