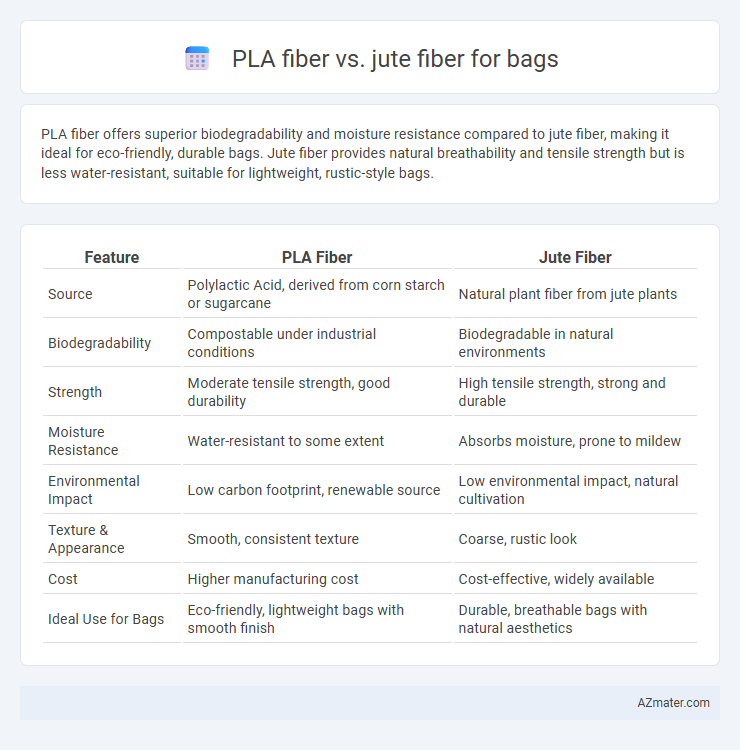
PLA fiber offers superior biodegradability and moisture resistance compared to jute fiber, making it ideal for eco-friendly, durable bags. Jute fiber provides natural breathability and tensile strength but is less water-resistant, suitable for lightweight, rustic-style bags.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | PLA Fiber | Jute Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Polylactic Acid, derived from corn starch or sugarcane | Natural plant fiber from jute plants |
| Biodegradability | Compostable under industrial conditions | Biodegradable in natural environments |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength, good durability | High tensile strength, strong and durable |
| Moisture Resistance | Water-resistant to some extent | Absorbs moisture, prone to mildew |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, renewable source | Low environmental impact, natural cultivation |
| Texture & Appearance | Smooth, consistent texture | Coarse, rustic look |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Cost-effective, widely available |
| Ideal Use for Bags | Eco-friendly, lightweight bags with smooth finish | Durable, breathable bags with natural aesthetics |
Introduction to PLA Fiber and Jute Fiber
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers biodegradable and eco-friendly properties ideal for sustainable bag production. Jute fiber, a natural plant fiber obtained from the jute plant, is known for its strength, durability, and biodegradability, making it a popular choice for eco-conscious packaging. Both fibers contribute to reducing plastic waste, but PLA provides a synthetic alternative with flexibility, whereas jute emphasizes natural texture and robustness.
Origins and Production Processes
PLA fiber originates from renewable resources like cornstarch or sugarcane through a fermentation process that produces polylactic acid, which is then spun into fibers, emphasizing sustainability and biodegradability. Jute fiber is derived from the bark of the Corchorus plant, primarily cultivated in India and Bangladesh, where the harvested stalks undergo retting, stripping, and drying before being processed into coarse, strong fibers ideal for bags. The production of PLA fiber involves industrial biopolymer synthesis and extrusion, while jute fiber relies on traditional agricultural and mechanical processes, reflecting distinct ecological and economic impacts.
Environmental Impact Comparison
PLA fiber, derived from renewable corn starch, offers biodegradability and compostability within industrial facilities, reducing long-term environmental pollution compared to synthetic fibers. Jute fiber, a natural plant-based material, is biodegradable and requires minimal pesticides and fertilizers during cultivation, contributing to soil health and lower carbon emissions. While PLA fiber production depends on agricultural inputs and industrial composting infrastructure, jute fiber's cultivation supports sustainable farming practices and natural decomposition in the environment, making it a favored choice for eco-friendly bag manufacturing.
Biodegradability and Sustainability
PLA fiber is derived from renewable resources like corn starch and offers excellent biodegradability, breaking down fully within months under industrial composting conditions. Jute fiber, a natural plant fiber, biodegrades naturally in soil within one to two years without releasing toxic substances, making it highly sustainable. Both fibers provide eco-friendly alternatives for bags, with PLA suited for controlled composting environments and jute excelling in soil biodegradability and sustainable cultivation.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
PLA fiber demonstrates higher tensile strength and resistance to abrasion compared to traditional jute fiber, making PLA-based bags more robust for heavy loads. Jute fiber offers good flexibility and natural biodegradability but generally exhibits lower mechanical strength and faster wear under stress. The enhanced durability of PLA fiber ensures longer-lasting bags suitable for repeated use and harsh conditions.
Aesthetic Qualities: Texture and Appearance
PLA fiber offers a smooth, consistent texture with a slightly glossy finish, enhancing the bag's modern and polished look. Jute fiber features a coarse, natural texture with a matte, earthy appearance that provides a rustic and organic aesthetic. Bags made from PLA fiber often appear sleek and uniform, while jute bags stand out with their distinctive, natural weave patterns.
Cost and Market Availability
PLA fiber offers a higher production cost compared to jute fiber due to its bio-based polymer manufacturing process, making it less competitive for budget-conscious bag markets. Jute fiber remains widely available and economically advantageous, benefiting from established cultivation and supply chains in countries like India and Bangladesh. Market availability favors jute fiber for large-scale bag production, while PLA fiber serves niche markets prioritizing biodegradability despite limited cost efficiency.
Usability in Bag Manufacturing
PLA fiber offers excellent biodegradability and strength, making it ideal for eco-friendly bag manufacturing with consistent durability and resistance to moisture. Jute fiber, known for its natural coarse texture and breathability, provides a rustic aesthetic but may require treatment to enhance wear resistance and reduce water absorption in bags. Manufacturers favor PLA fiber for lightweight, flexible designs, while jute is preferred for heavy-duty, natural-textured bags with a traditional appeal.
Consumer Preferences and Trends
PLA fiber offers consumers a sustainable and biodegradable alternative to traditional jute fiber, appealing to eco-conscious buyers prioritizing environmental impact. Jute fiber remains popular for its natural texture, durability, and affordability, aligning with trends favoring rustic and organic aesthetics in bag design. Consumer preferences are increasingly shifting towards PLA fiber due to its innovative nature and compatibility with circular economy initiatives, while jute maintains strong appeal in markets valuing traditional craftsmanship and cost-efficiency.
Conclusion: Which Fiber is Better for Bags?
PLA fiber offers superior biodegradability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for eco-friendly, durable bags. Jute fiber excels in breathability and natural strength, providing a sustainable option with a rustic aesthetic. For long-lasting, water-resistant bags, PLA fiber is better, while jute suits biodegradable, breathable products with a natural texture.
Infographic: PLA fiber vs Jute fiber for Bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com