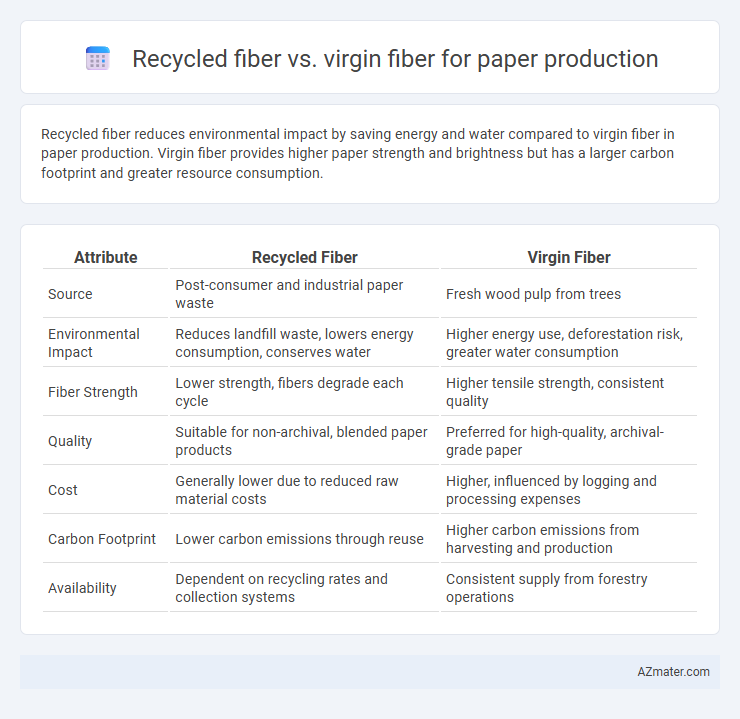
Recycled fiber reduces environmental impact by saving energy and water compared to virgin fiber in paper production. Virgin fiber provides higher paper strength and brightness but has a larger carbon footprint and greater resource consumption.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Recycled Fiber | Virgin Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Post-consumer and industrial paper waste | Fresh wood pulp from trees |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste, lowers energy consumption, conserves water | Higher energy use, deforestation risk, greater water consumption |
| Fiber Strength | Lower strength, fibers degrade each cycle | Higher tensile strength, consistent quality |
| Quality | Suitable for non-archival, blended paper products | Preferred for high-quality, archival-grade paper |
| Cost | Generally lower due to reduced raw material costs | Higher, influenced by logging and processing expenses |
| Carbon Footprint | Lower carbon emissions through reuse | Higher carbon emissions from harvesting and production |
| Availability | Dependent on recycling rates and collection systems | Consistent supply from forestry operations |
Introduction to Paper Fiber Types
Recycled fiber originates from post-consumer and post-industrial paper waste, offering sustainable benefits and reducing environmental impact by minimizing deforestation. Virgin fiber is derived directly from fresh wood pulp, providing superior strength, brightness, and uniformity essential for high-quality paper products. The choice between recycled and virgin fibers significantly influences the paper's texture, durability, and ecological footprint in various production processes.
What is Virgin Fiber?
Virgin fiber comes directly from newly harvested trees and is the primary raw material in traditional paper production, offering high strength and purity. Unlike recycled fiber, virgin fiber has not undergone previous use or processing, resulting in longer fiber lengths that contribute to superior paper quality and durability. It plays a crucial role in producing high-grade paper products such as printing paper, packaging, and specialty papers.
What is Recycled Fiber?
Recycled fiber in paper production refers to fibers recovered from used paper products that are processed and repurposed into new paper materials. This eco-friendly alternative reduces the demand for virgin fiber, which is derived directly from wood pulp, helping to conserve forests and minimize environmental impact. Utilizing recycled fiber supports sustainability efforts by lowering energy consumption and reducing landfill waste compared to virgin fiber production.
Raw Material Sources and Sustainability
Recycled fiber in paper production originates from post-consumer waste and industrial scraps, significantly reducing the need for fresh wood pulp, which is the primary raw material for virgin fiber. Utilizing recycled fibers lowers deforestation rates and minimizes environmental impacts such as greenhouse gas emissions and water usage compared to sourcing virgin fibers from trees. Sustainability metrics favor recycled fiber because it decreases landfill waste and promotes circular economy principles by reprocessing existing materials instead of continuously harvesting new ones.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Recycled fiber reduces deforestation and conserves natural resources, resulting in lower carbon emissions and less energy consumption compared to virgin fiber. Virgin fiber production typically demands extensive water usage and produces higher levels of greenhouse gases due to logging and pulping processes. Utilizing recycled fiber for paper manufacturing significantly decreases landfill waste and mitigates environmental pollutants.
Paper Quality: Virgin vs Recycled Fiber
Virgin fiber in paper production offers superior strength, brightness, and smoothness due to longer cellulose fibers, resulting in higher-quality paper ideal for premium printing and packaging. Recycled fiber contains shorter, more degraded fibers, often leading to reduced tensile strength and potential discoloration, which can affect paper durability and appearance. Advanced recycling processes and fiber blending techniques improve recycled paper quality, but virgin fiber remains the preferred choice for applications where optimal paper performance is critical.
Economic Considerations in Paper Production
Recycled fiber significantly reduces raw material costs compared to virgin fiber by utilizing waste paper, lowering expenses associated with logging, transportation, and pulp processing. Virgin fiber requires higher energy input and chemical treatments for pulping, increasing production costs, especially in regions with stringent environmental regulations. Incorporating recycled fiber enhances sustainability credentials and can attract eco-conscious consumers, potentially increasing market share and profitability for paper producers.
Energy and Water Consumption
Recycled fiber significantly reduces energy consumption in paper production, using up to 40% less energy compared to virgin fiber processes. Water usage is also lower with recycled fiber, as it requires approximately 50% less water during pulping and bleaching stages. These reductions contribute to a smaller environmental footprint and more sustainable manufacturing practices in the paper industry.
Common Applications for Each Fiber Type
Recycled fiber is predominantly used in packaging materials, newsprint, and tissue products due to its cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits. Virgin fiber is favored in high-quality printing paper, currency, and premium packaging where strength and purity are critical. Each fiber type supports specific applications based on durability requirements and production costs.
Future Trends in Sustainable Paper Production
Future trends in sustainable paper production emphasize increasing the use of recycled fiber to reduce environmental impact and conserve natural resources. Advances in fiber recovery technologies and improved recycling processes enhance the quality and durability of recycled paper, making it competitive with virgin fiber products. Innovations in bio-based additives and closed-loop water systems support a circular economy, driving greater adoption of recycled fiber in the paper industry.
Infographic: Recycled fiber vs Virgin fiber for Paper production
 azmater.com
azmater.com