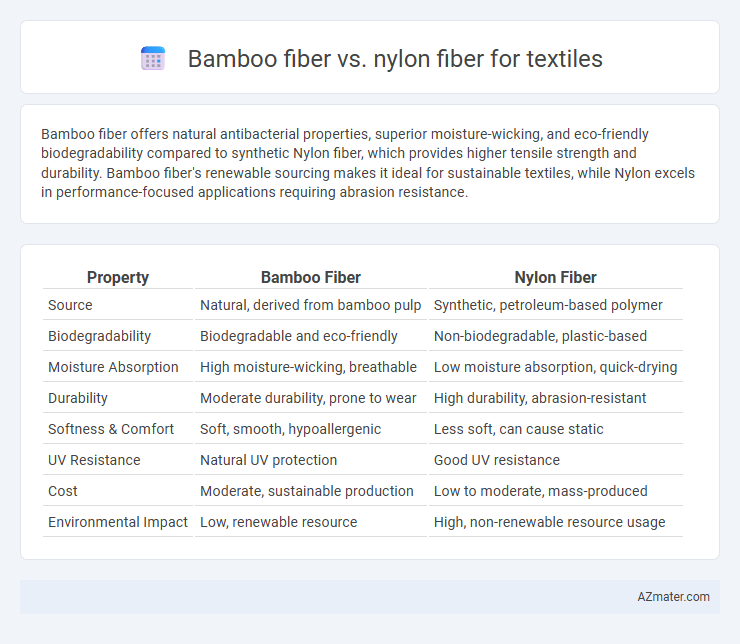
Bamboo fiber offers natural antibacterial properties, superior moisture-wicking, and eco-friendly biodegradability compared to synthetic Nylon fiber, which provides higher tensile strength and durability. Bamboo fiber's renewable sourcing makes it ideal for sustainable textiles, while Nylon excels in performance-focused applications requiring abrasion resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bamboo Fiber | Nylon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural, derived from bamboo pulp | Synthetic, petroleum-based polymer |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, plastic-based |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture-wicking, breathable | Low moisture absorption, quick-drying |
| Durability | Moderate durability, prone to wear | High durability, abrasion-resistant |
| Softness & Comfort | Soft, smooth, hypoallergenic | Less soft, can cause static |
| UV Resistance | Natural UV protection | Good UV resistance |
| Cost | Moderate, sustainable production | Low to moderate, mass-produced |
| Environmental Impact | Low, renewable resource | High, non-renewable resource usage |
Introduction to Bamboo and Nylon Fibers
Bamboo fiber, derived from natural bamboo plants, offers eco-friendly, biodegradable, and moisture-wicking properties ideal for sustainable textiles. Nylon fiber, a synthetic polymer made from petrochemicals, provides exceptional strength, elasticity, and durability widely used in performance and industrial fabrics. Comparing bamboo and nylon fibers highlights the contrast between renewable, breathable materials and long-lasting, resilient synthetics in textile applications.
Origin and Production Processes
Bamboo fiber is derived from the cellulose of bamboo plants through mechanical crushing and enzymatic treatment or chemical processing, making it a sustainable and biodegradable textile option. Nylon fiber, a synthetic polymer made from petrochemicals, is produced through a complex chemical process called polymerization, involving hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid. The natural origin of bamboo and its eco-friendly extraction contrasts with nylon's energy-intensive, non-renewable petroleum-based production.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Bamboo fiber offers a significantly lower environmental footprint than nylon fiber due to its natural biodegradability and renewable growth cycle, requiring minimal water and pesticides compared to conventional textile crops. Nylon production relies heavily on fossil fuels, generating considerable greenhouse gas emissions and non-biodegradable microplastics that contribute to ocean pollution. Sustainable textile manufacturing increasingly favors bamboo fibers for reducing carbon emissions, conserving water resources, and minimizing ecological harm compared to synthetic nylon alternatives.
Durability and Strength
Bamboo fiber offers moderate strength and durability, making it suitable for lightweight textile applications but less resistant to abrasion compared to nylon. Nylon fiber is renowned for its exceptional tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and long-lasting durability, often outperforming natural fibers in heavy-duty and high-stress environments. Textile products utilizing nylon exhibit superior lifespan and resilience, especially in activewear and industrial fabrics, while bamboo fiber garments prioritize sustainability and softness over extreme durability.
Moisture Absorption and Breathability
Bamboo fiber exhibits superior moisture absorption and breathability compared to nylon fiber, absorbing up to 40% more moisture while remaining dry to the touch. Its natural micro-gaps and porous structure enhance airflow, promoting better ventilation and comfort in textiles. Nylon fiber, being synthetic, tends to trap heat and moisture, resulting in lower breathability and slower drying times.
Comfort and Skin Sensitivity
Bamboo fiber offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it highly comfortable and ideal for sensitive skin due to its natural anti-bacterial and hypoallergenic qualities. Nylon fiber, while durable and elastic, tends to retain heat and moisture, potentially causing discomfort and irritation for individuals with sensitive skin. Choosing bamboo fiber textiles enhances skin comfort and reduces the risk of allergic reactions compared to nylon-based fabrics.
Color Retention and Dyeing Properties
Bamboo fiber exhibits excellent dye absorption due to its natural cellulose structure, resulting in vibrant colors with superior color retention even after multiple washes. Nylon fiber, a synthetic polymer, demonstrates strong affinity for disperse dyes, allowing bright and consistent hues but may experience faster color fading under UV exposure. The moisture-wicking properties of bamboo enhance dye fixation, while nylon's hydrophobic nature requires specialized dyeing techniques to optimize colorfastness.
Cost and Market Availability
Bamboo fiber is generally more cost-effective than nylon fiber due to its renewable sourcing and lower production energy requirements, making it an attractive option for eco-conscious textile manufacturers. Nylon fiber, however, benefits from widespread market availability and well-established supply chains, ensuring consistent quality and bulk purchasing options. While bamboo fiber offers sustainability advantages, nylon remains dominant in sectors demanding high durability and performance at scale.
Popular Applications in Textiles
Bamboo fiber is favored in textiles for its natural antibacterial properties, breathability, and moisture-wicking abilities, making it ideal for activewear, eco-friendly apparel, and baby clothing. Nylon fiber is widely used in textiles requiring high durability, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, such as sportswear, hosiery, and outdoor gear. Both fibers serve specific market demands, with bamboo appealing to sustainable and comfort-focused products, while nylon dominates performance-oriented applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber
Bamboo fiber offers superior breathability, natural antibacterial properties, and eco-friendliness, making it ideal for sustainable and comfortable textiles. Nylon fiber excels in durability, elasticity, and moisture-wicking performance, suitable for high-performance and long-lasting fabrics. Selecting the right fiber depends on prioritizing sustainability and softness with bamboo or resilience and strength with nylon for specific textile applications.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber vs Nylon fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com