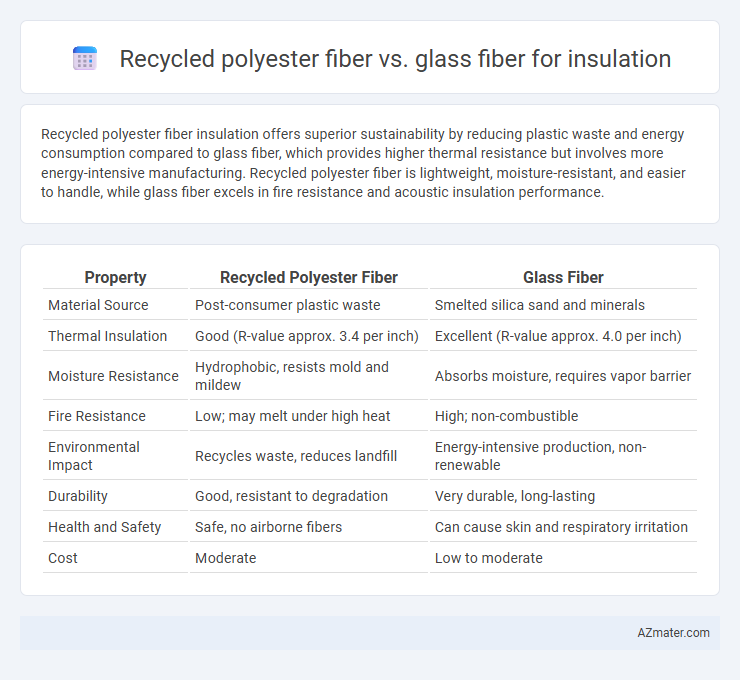
Recycled polyester fiber insulation offers superior sustainability by reducing plastic waste and energy consumption compared to glass fiber, which provides higher thermal resistance but involves more energy-intensive manufacturing. Recycled polyester fiber is lightweight, moisture-resistant, and easier to handle, while glass fiber excels in fire resistance and acoustic insulation performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Polyester Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Post-consumer plastic waste | Smelted silica sand and minerals |
| Thermal Insulation | Good (R-value approx. 3.4 per inch) | Excellent (R-value approx. 4.0 per inch) |
| Moisture Resistance | Hydrophobic, resists mold and mildew | Absorbs moisture, requires vapor barrier |
| Fire Resistance | Low; may melt under high heat | High; non-combustible |
| Environmental Impact | Recycles waste, reduces landfill | Energy-intensive production, non-renewable |
| Durability | Good, resistant to degradation | Very durable, long-lasting |
| Health and Safety | Safe, no airborne fibers | Can cause skin and respiratory irritation |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Insulation Materials
Recycled polyester fiber and glass fiber are widely used insulation materials known for their thermal performance and sustainability profiles. Recycled polyester fiber offers excellent moisture resistance, flexibility, and eco-friendly attributes due to its origin from post-consumer plastics, making it a preferred choice in green building projects. Glass fiber insulation provides high thermal resistance, fire retardance, and soundproofing capabilities, maintaining effectiveness in a broad temperature range often utilized in industrial and residential applications.
What is Recycled Polyester Fiber Insulation?
Recycled polyester fiber insulation is a sustainable material made from post-consumer plastic bottles, melted and spun into fibers that trap air for thermal efficiency. It offers excellent moisture resistance, lightweight properties, and sound absorption compared to traditional glass fiber insulation. The fiber's eco-friendly origin reduces landfill waste and carbon footprint, making it a favored choice for green building projects.
Understanding Glass Fiber Insulation
Glass fiber insulation consists of fine glass strands spun into a durable material with high thermal and sound insulating properties, commonly used in residential and commercial buildings. It offers excellent fire resistance, moisture tolerance, and maintains performance over time, making it a reliable choice for energy efficiency and noise reduction. Compared to recycled polyester fiber, glass fiber insulation provides superior heat resistance and structural stability but tends to be less flexible and heavier.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Recycled polyester fiber offers superior thermal insulation performance with lower thermal conductivity (around 0.035 W/mK) compared to glass fiber, which typically ranges between 0.040 and 0.045 W/mK. The porous structure of recycled polyester fiber traps air more effectively, enhancing heat retention and reducing energy consumption in buildings. Glass fiber, while cost-effective and fire-resistant, often requires thicker layers to match the thermal efficiency of recycled polyester fiber insulation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Recycled polyester fiber significantly reduces landfill waste and decreases reliance on virgin petroleum resources compared to glass fiber, which is energy-intensive to produce and difficult to recycle. The production of recycled polyester fiber emits lower greenhouse gases and consumes less water, enhancing its environmental sustainability. Conversely, glass fiber insulation has longer durability but poses challenges in end-of-life disposal and contributes to higher embodied energy throughout its lifecycle.
Health and Safety Considerations
Recycled polyester fiber insulation offers enhanced health and safety benefits due to its non-toxic, hypoallergenic properties and low respiratory irritant potential, making it suitable for sensitive environments. In contrast, glass fiber insulation can release airborne glass particles that pose inhalation risks and cause skin and eye irritation, requiring protective measures during installation. Choosing recycled polyester fiber reduces long-term health hazards and improves indoor air quality compared to traditional glass fiber insulation materials.
Installation Process and Ease
Recycled polyester fiber insulation offers superior ease of installation due to its lightweight, flexible nature and fewer associated health hazards compared to glass fiber. Glass fiber requires careful handling with protective gear to avoid skin irritation and respiratory issues, complicating the installation process. The pliability of recycled polyester fibers allows for quicker fitting in irregular spaces, reducing labor time and improving overall efficiency on site.
Cost Analysis: Polyester vs Glass Fiber
Recycled polyester fiber insulation typically costs less than glass fiber due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses, making it a more budget-friendly option for eco-conscious projects. Glass fiber insulation, while generally pricier, offers superior thermal resistance and durability, contributing to long-term savings despite higher upfront investment. Cost analysis must balance initial price differences with performance benefits, considering factors like installation complexity and lifespan for optimal insulation value.
Durability and Maintenance
Recycled polyester fiber offers excellent durability with resistance to moisture, mold, and mildew, reducing the need for frequent maintenance in insulation applications. Glass fiber, while providing strong thermal resistance, is prone to damage from moisture and physical wear, requiring regular inspections and maintenance to maintain performance. The synthetic resilience of recycled polyester fiber ensures longer-lasting insulation with lower upkeep demands compared to the more fragile and maintenance-intensive glass fiber.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Insulation
Recycled polyester fiber offers superior thermal insulation, moisture resistance, and eco-friendliness compared to glass fiber, making it ideal for sustainable building projects. Glass fiber excels in fire resistance and durability but may pose health risks during installation due to airborne particles. Selecting the right insulation depends on balancing environmental impact, safety requirements, and specific thermal performance needs.
Infographic: Recycled polyester fiber vs Glass fiber for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com