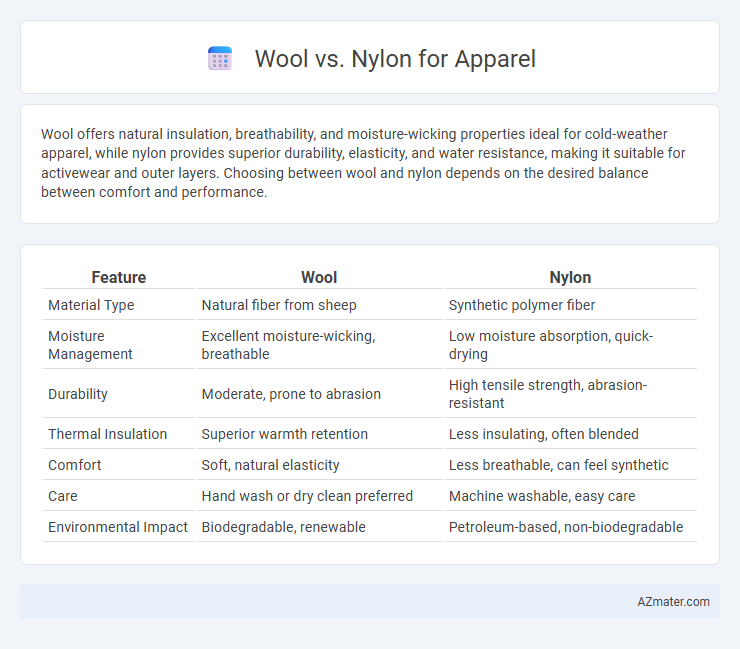
Wool offers natural insulation, breathability, and moisture-wicking properties ideal for cold-weather apparel, while nylon provides superior durability, elasticity, and water resistance, making it suitable for activewear and outer layers. Choosing between wool and nylon depends on the desired balance between comfort and performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wool | Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural fiber from sheep | Synthetic polymer fiber |
| Moisture Management | Excellent moisture-wicking, breathable | Low moisture absorption, quick-drying |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to abrasion | High tensile strength, abrasion-resistant |
| Thermal Insulation | Superior warmth retention | Less insulating, often blended |
| Comfort | Soft, natural elasticity | Less breathable, can feel synthetic |
| Care | Hand wash or dry clean preferred | Machine washable, easy care |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable | Petroleum-based, non-biodegradable |
Introduction to Wool and Nylon in Apparel
Wool, a natural fiber sourced primarily from sheep, offers exceptional insulation, moisture-wicking, and breathability, making it a popular choice for cold-weather apparel. Nylon, a synthetic polymer, is valued for its strength, elasticity, and quick-drying properties, often used in activewear and outerwear for enhanced durability. Both fibers contribute distinct performance benefits, with wool excelling in temperature regulation and nylon providing superior abrasion resistance and lightweight comfort.
Key Differences Between Wool and Nylon Fibers
Wool fibers, derived from sheep, are natural, renewable, and possess excellent moisture-wicking and insulating properties, making them ideal for breathable, temperature-regulating apparel. Nylon fibers are synthetic, made from petrochemicals, known for high durability, elasticity, and quick-drying capabilities, often used to enhance strength in blended fabrics. Key differences include wool's superior thermal insulation and biodegradability versus nylon's abrasion resistance and resistance to mildew and wrinkles.
Comfort and Wearability: Wool vs Nylon
Wool excels in comfort and wearability due to its natural moisture-wicking, breathability, and temperature-regulating properties, making it ideal for varied climates and extended wear. Nylon offers lightweight durability and quick-drying features but can trap heat and moisture, leading to less comfortable prolonged wear. Wool's natural elasticity and softness provide superior comfort compared to the synthetic feel and potential irritation from nylon fabrics.
Durability and Longevity of Wool vs Nylon
Wool offers natural durability with fibers that resist wear and retain shape over time, making it ideal for long-lasting apparel. Nylon excels in abrasion resistance and tensile strength, providing superior durability in high-stress areas and activewear. Combining wool's resilience with nylon's robustness often results in garments that balance longevity and performance effectively.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Wool excels in moisture management by naturally wicking sweat away from the skin, allowing it to absorb up to 30% of its weight in moisture without feeling damp, which enhances breathability and comfort. Nylon, while durable and quick-drying, tends to trap moisture and lacks the natural breathability of wool, making it less effective for regulating body temperature during intense activities. Apparel combining wool's moisture-wicking properties with nylon's strength often provides an optimal balance for moisture management and breathability.
Insulation and Thermal Properties Compared
Wool provides superior insulation due to its natural crimp, which traps air and retains body heat even when damp, offering excellent thermal regulation for cold weather apparel. Nylon, a synthetic fiber, excels in durability and moisture-wicking but lacks the inherent warming properties of wool, making it less effective for insulation in low temperatures. Combining wool with nylon blends can enhance fabric strength while maintaining optimal thermal performance in outdoor and activewear.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Wool, a natural fiber sourced from sheep, offers biodegradability and renewable qualities, making it a sustainable choice for apparel with lower environmental impact compared to synthetic fibers. Nylon, derived from petrochemicals, is energy-intensive to produce and contributes to microplastic pollution during washing, raising concerns about long-term environmental sustainability. Advances in recycled nylon aim to reduce its carbon footprint, yet wool remains preferred for eco-conscious consumers prioritizing renewable and biodegradable textile options.
Care, Maintenance, and Ease of Cleaning
Wool requires gentle care, including hand washing or dry cleaning, to maintain its natural fibers and prevent shrinkage, while nylon offers greater ease of cleaning due to its machine-washable and quick-drying properties. Wool's lanolin content provides natural stain resistance but demands careful handling to avoid felting, whereas nylon resists moisture and abrasion, making it ideal for activewear and frequent use. Choosing between wool and nylon for apparel depends on balancing the desire for luxury and insulation with practical maintenance needs and cleaning convenience.
Cost Factors: Affordability of Wool and Nylon
Wool typically has a higher price point due to its natural sourcing, labor-intensive processing, and superior insulation properties, making it a premium choice for apparel. Nylon, being a synthetic fiber, is generally more affordable due to mass production, lower raw material costs, and greater durability, which reduces replacement frequency. Consumers seeking budget-friendly activewear or outerwear often prefer nylon, while those prioritizing warmth and natural fiber appeal may invest more in wool despite the cost difference.
Best Use Cases: Choosing Wool or Nylon for Apparel
Wool excels in cold-weather apparel due to its natural insulation, moisture-wicking, and odor-resistant properties, making it ideal for sweaters, thermal base layers, and winter coats. Nylon is best suited for activewear and outerwear requiring durability, water resistance, and lightweight performance, such as rain jackets, windbreakers, and athletic leggings. Selecting between wool and nylon depends on the intended use, with wool preferred for warmth and comfort and nylon chosen for abrasion resistance and weather protection.
Infographic: Wool vs Nylon for Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com