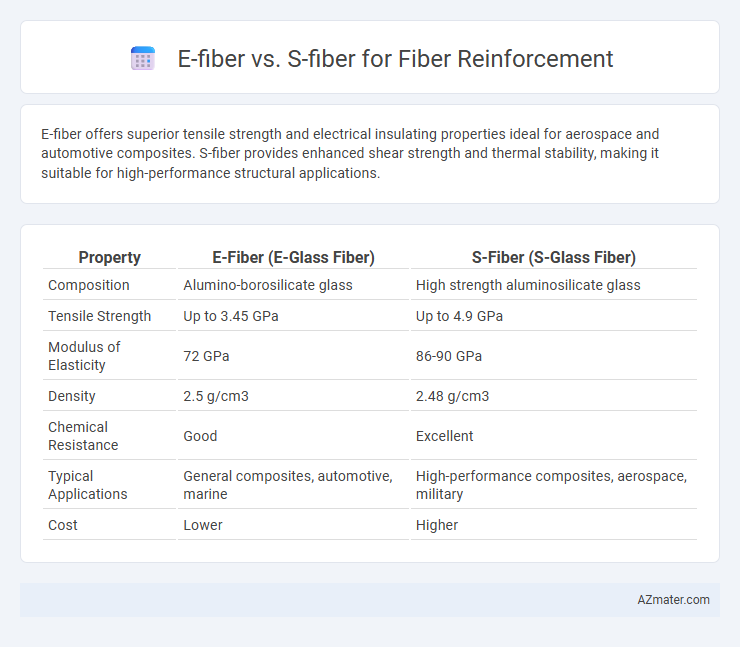
E-fiber offers superior tensile strength and electrical insulating properties ideal for aerospace and automotive composites. S-fiber provides enhanced shear strength and thermal stability, making it suitable for high-performance structural applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | E-Fiber (E-Glass Fiber) | S-Fiber (S-Glass Fiber) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Alumino-borosilicate glass | High strength aluminosilicate glass |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 3.45 GPa | Up to 4.9 GPa |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 72 GPa | 86-90 GPa |
| Density | 2.5 g/cm3 | 2.48 g/cm3 |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Typical Applications | General composites, automotive, marine | High-performance composites, aerospace, military |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Fiber Reinforcement: E-Fiber vs S-Fiber
E-fiber and S-fiber are two primary types of glass fibers used in fiber reinforcement, each offering distinct mechanical properties. E-fiber, or electrical fiber, is known for its high tensile strength, electrical insulating capabilities, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for general reinforcement applications in composites and construction materials. S-fiber, or structural fiber, provides superior mechanical strength, higher stiffness, and excellent resistance to heat and chemicals, often preferred in aerospace and high-performance industrial components.
Chemical Composition and Structure Differences
E-fiber, primarily composed of alumino-borosilicate glass, features a chemical composition rich in silica (SiO2), alumina (Al2O3), and boron oxide (B2O3), which provides excellent electrical insulation and corrosion resistance. S-fiber, or high-strength silica fiber, contains higher amounts of silica with reduced alkali content, enhancing tensile strength and thermal stability compared to E-fiber. Structurally, E-fiber's amorphous glass network facilitates flexibility and electrical insulating properties, whereas S-fiber's optimized silica structure delivers superior mechanical durability and resistance to high temperatures for advanced composite applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
E-fiber and S-fiber differ significantly in mechanical properties for fiber reinforcement applications; E-fiber offers high tensile strength around 3.45 GPa and a tensile modulus near 72 GPa, making it suitable for general structural composites. S-fiber exhibits superior mechanical performance with tensile strength exceeding 4.8 GPa and a tensile modulus up to 86 GPa, providing enhanced stiffness and strength for high-performance composites. The choice between E-fiber and S-fiber depends on specific application requirements where S-fiber is preferred for demanding load-bearing roles due to its notable mechanical advantages.
Tensile Strength and Modulus Analysis
E-fiber, composed primarily of alumino-borosilicate glass, offers high tensile strength typically around 3400 MPa and a moderate tensile modulus approximately 72 GPa, making it suitable for general composite reinforcement. S-fiber, made from high-purity silica and alumina, significantly surpasses E-fiber with tensile strength reaching up to 4800 MPa and a tensile modulus near 86 GPa, providing superior stiffness and load-bearing capacity. The enhanced mechanical properties of S-fiber result from its optimized microstructure and higher crystallinity, making it the preferred choice in high-performance fiber-reinforced composites where strength and rigidity are critical.
Thermal Stability and Performance
E-fiber exhibits superior thermal stability compared to S-fiber due to its higher temperature tolerance, typically maintaining structural integrity up to 1100degC, while S-fiber withstands temperatures around 700degC. E-fiber's enhanced thermal resistance makes it ideal for applications requiring prolonged exposure to high heat, offering consistent performance and durability under thermal stress. In contrast, S-fiber provides greater mechanical strength at moderate temperatures but may degrade faster in extreme thermal environments, limiting its use in high-temperature reinforcement scenarios.
Resistance to Moisture and Corrosion
E-fiber exhibits superior resistance to moisture and corrosion compared to S-fiber, making it more suitable for environments exposed to high humidity or corrosive substances. The high aluminum content in E-fiber enhances its ability to resist chemical degradation, whereas S-fiber's high silicon content increases its susceptibility to moisture-induced corrosion. This difference in chemical composition directly impacts the long-term durability of fiber-reinforced composites in moist or corrosive conditions.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
E-fiber offers a lower cost and wider availability compared to S-fiber, making it a more cost-effective choice for general fiber reinforcement applications. However, while S-fiber provides superior mechanical and thermal properties, its higher price and limited supply restrict usage to specialized applications requiring enhanced performance. Selecting between E-fiber and S-fiber depends on balancing budget constraints with the required material properties for specific reinforcement needs.
Application Suitability in Construction and Composites
E-fiber (E-glass fiber) offers high tensile strength and excellent electrical insulation, making it ideal for applications in construction materials like concrete reinforcement and structural composites where durability and resistance to moisture are critical. S-fiber (S-glass fiber) provides superior tensile strength and higher stiffness compared to E-fiber, making it suitable for high-performance composite applications such as aerospace components, sporting goods, and military armor where enhanced mechanical properties are required. Both fibers improve the toughness and impact resistance of composites, but the choice depends on balancing cost, mechanical demands, and environmental exposure specific to the construction or composite application.
Durability and Long-Term Performance
E-fiber offers excellent tensile strength and cost-effectiveness but is more susceptible to alkaline environments, impacting its durability in concrete applications. S-fiber provides superior chemical resistance and enhanced long-term performance due to its stable silicon-based composition, making it ideal for harsh environmental conditions. For fiber reinforcement requiring extended lifespan and resilience, S-fiber typically outperforms E-fiber in terms of durability and sustained structural integrity.
Conclusion: Choosing Between E-Fiber and S-Fiber
E-fiber offers high electrical insulation and cost-effective mechanical strength, making it suitable for general-purpose fiber reinforcement applications. S-fiber provides superior tensile strength, higher modulus, and better resistance to heat and chemicals, ideal for advanced, high-performance composites in aerospace and automotive industries. Selecting between E-fiber and S-fiber hinges on balancing budget constraints with performance requirements such as stiffness, strength, and environmental durability.
Infographic: E-fiber vs S-fiber for Fiber Reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com