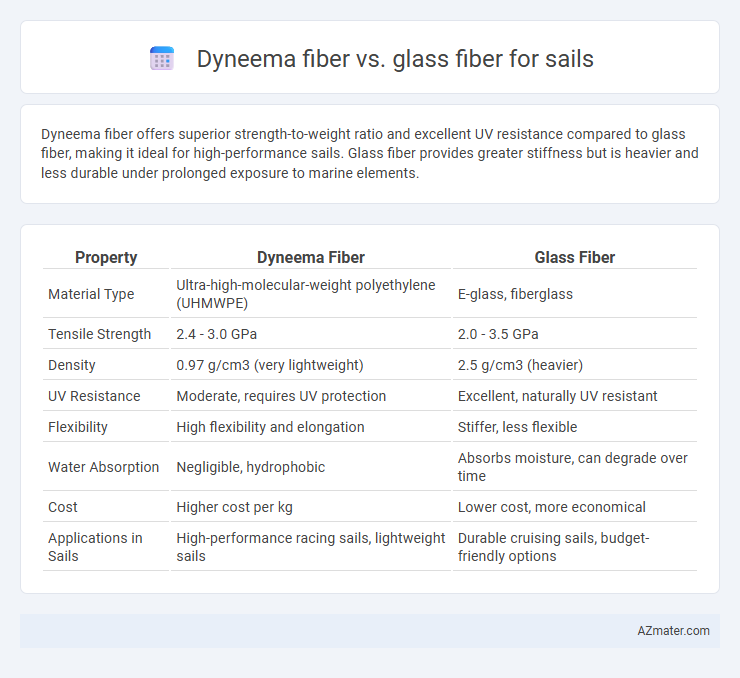
Dyneema fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent UV resistance compared to glass fiber, making it ideal for high-performance sails. Glass fiber provides greater stiffness but is heavier and less durable under prolonged exposure to marine elements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Dyneema Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) | E-glass, fiberglass |
| Tensile Strength | 2.4 - 3.0 GPa | 2.0 - 3.5 GPa |
| Density | 0.97 g/cm3 (very lightweight) | 2.5 g/cm3 (heavier) |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, requires UV protection | Excellent, naturally UV resistant |
| Flexibility | High flexibility and elongation | Stiffer, less flexible |
| Water Absorption | Negligible, hydrophobic | Absorbs moisture, can degrade over time |
| Cost | Higher cost per kg | Lower cost, more economical |
| Applications in Sails | High-performance racing sails, lightweight sails | Durable cruising sails, budget-friendly options |
Introduction to Sail Fiber Materials
Dyneema fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional durability compared to traditional glass fiber, making it ideal for high-performance sails. Unlike glass fiber, Dyneema provides enhanced resistance to UV damage and fatigue, ensuring longer sail lifespan and reduced maintenance. These properties contribute to improved sail efficiency and agility in various wind conditions.
What is Dyneema Fiber?
Dyneema fiber, also known as ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), is a lightweight, high-strength synthetic fiber renowned for its exceptional tensile strength and durability, making it ideal for sails requiring superior performance and longevity. Compared to glass fiber, Dyneema offers increased flexibility, higher strength-to-weight ratio, and enhanced resistance to UV damage, moisture, and abrasion. This results in sails that are lighter, more durable, and able to maintain shape and performance under extreme sailing conditions.
What is Glass Fiber?
Glass fiber is a material made from fine strands of glass spun into threads, widely used in sailmaking for its high tensile strength and resistance to stretching. Unlike Dyneema fiber, which is a lightweight ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene, glass fiber provides excellent durability and fire resistance but tends to be heavier and less flexible. Its stiff structure allows sails to maintain shape better under load, making it a traditional choice for performance and cruising sails.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Dyneema fiber offers exceptional tensile strength, outperforming glass fiber by a factor of 15 to 20 while maintaining lightweight properties essential for high-performance sails. Its resistance to UV degradation and moisture absorption ensures superior durability and longevity compared to glass fiber, which tends to stiffen and weaken under prolonged environmental exposure. The superior strength-to-weight ratio of Dyneema significantly enhances sail performance, making it the preferred choice for racing and endurance sailing applications.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Dyneema fiber is significantly lighter than glass fiber, offering superior weight reduction critical for sail performance and handling. Its exceptional flexibility allows sails to maintain shape and resist fatigue under variable wind conditions, unlike the stiffer glass fiber which can be prone to brittleness over time. The combination of low weight and high flexibility makes Dyneema an optimal choice for high-performance sailing applications where durability and agility are crucial.
UV and Weather Resistance
Dyneema fiber exhibits superior UV and weather resistance compared to glass fiber, maintaining strength and flexibility under prolonged sun exposure and harsh marine environments. Unlike glass fiber, which can degrade and become brittle when exposed to UV radiation, Dyneema's ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene structure provides excellent durability and resistance to moisture and saltwater corrosion. This makes Dyneema ideal for sails requiring long-term performance and minimal maintenance in challenging outdoor conditions.
Performance Under Stress
Dyneema fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and superior resistance to elongation under stress, outperforming glass fiber in durability and load-bearing capacity for sails. Its lightweight nature ensures enhanced sail shape retention and improved overall vessel speed compared to the heavier and more brittle glass fiber. Dyneema's high modulus and fatigue resistance provide long-lasting performance in demanding sailing conditions, making it a preferred choice for high-performance racing sails.
Cost and Availability
Dyneema fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio for sails but comes at a higher cost compared to glass fiber, making it less accessible for budget-conscious projects. Glass fiber remains widely available and more affordable, making it a common choice for mass production and recreational sailing. Manufacturers often choose glass fiber for its cost-effectiveness, while Dyneema is preferred in high-performance or professional sailing applications where durability and weight savings justify the expense.
Common Applications in Sailing
Dyneema fiber is widely used in high-performance sails for racing yachts due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and low stretch properties, enhancing sail shape and speed. Glass fiber is commonly utilized in cruising sails for its durability and resistance to UV damage, making it suitable for long-term use and offshore conditions. Both fibers serve distinct roles in sailing, with Dyneema preferred for competitive racing and glass fiber favored for recreational and endurance applications.
Choosing the Best Fiber for Your Sail
Dyneema fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and superior resistance to UV damage, making it ideal for high-performance sails requiring durability and lightness. Glass fiber provides excellent stiffness and cost-effectiveness, but its heavier weight and susceptibility to UV degradation may limit sail efficiency over time. Choosing the best fiber depends on balancing factors like performance demands, budget constraints, and environmental exposure for optimized sail longevity and handling.
Infographic: Dyneema fiber vs Glass fiber for Sail
 azmater.com
azmater.com