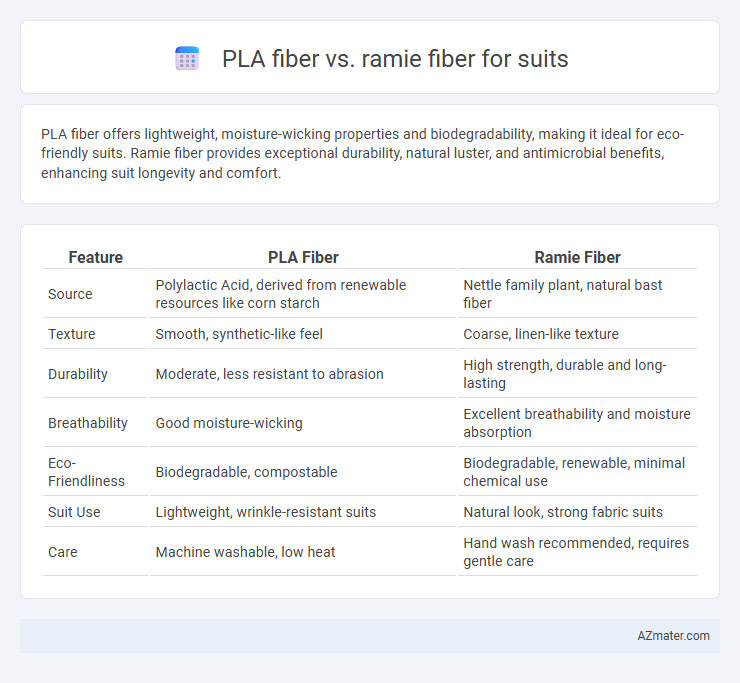
PLA fiber offers lightweight, moisture-wicking properties and biodegradability, making it ideal for eco-friendly suits. Ramie fiber provides exceptional durability, natural luster, and antimicrobial benefits, enhancing suit longevity and comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | PLA Fiber | Ramie Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Polylactic Acid, derived from renewable resources like corn starch | Nettle family plant, natural bast fiber |
| Texture | Smooth, synthetic-like feel | Coarse, linen-like texture |
| Durability | Moderate, less resistant to abrasion | High strength, durable and long-lasting |
| Breathability | Good moisture-wicking | Excellent breathability and moisture absorption |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, compostable | Biodegradable, renewable, minimal chemical use |
| Suit Use | Lightweight, wrinkle-resistant suits | Natural look, strong fabric suits |
| Care | Machine washable, low heat | Hand wash recommended, requires gentle care |
Overview of PLA Fiber and Ramie Fiber
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, is a biodegradable, lightweight, and moisture-wicking textile ideal for eco-friendly suits. Ramie fiber, a natural bast fiber extracted from the stalks of the Ramie plant, offers exceptional strength, breathability, and a silky luster, making it suitable for durable, breathable suit fabrics. Both fibers provide sustainable alternatives to traditional materials with PLA emphasizing biodegradability and Ramie highlighting natural durability and comfort.
Key Differences in Fiber Origins
PLA fiber, derived from renewable corn starch or sugarcane, is a biodegradable biopolymer known for its eco-friendly production process and lightweight texture. Ramie fiber, sourced from the stalks of the Chinese nettle plant, is a natural vegetable fiber prized for its strength, luster, and moisture-wicking properties. The key difference lies in PLA's synthetic bioplastic nature versus ramie's traditional plant-based origin, influencing durability, breathability, and sustainability in suit fabrics.
Production Processes: PLA vs Ramie
PLA fiber is produced through a fermentation process of renewable resources like corn starch, where lactic acid is polymerized into polylactic acid and then spun into fibers using extrusion techniques, emphasizing sustainability and biodegradability. Ramie fiber, derived from the stalks of the Ramie plant, undergoes mechanical scraping, degumming to remove gum and lignin, and subsequent spinning, which preserves its traditional natural fiber qualities such as strength and breathability. The production of PLA fiber involves synthetic polymerization, whereas Ramie fiber production relies on natural fiber extraction and treatment, leading to differences in environmental impact and textile performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers significant biodegradability and lower carbon emissions compared to conventional synthetic fibers, making it an environmentally friendly choice for sustainable suits. Ramie fiber, a natural bast fiber extracted from the stalks of the Ramie plant, is biodegradable, requires minimal pesticides, and supports soil health through its low-impact cultivation process. When comparing PLA and Ramie fibers in suit production, Ramie holds an edge in renewable resource management and traditional biodegradability, while PLA stands out for its potential in reducing fossil fuel dependence and enhancing circular economy practices.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
PLA fiber offers excellent tensile strength and good durability, making it a strong candidate for suit fabrics that require resilience and long-lasting wear. Ramie fiber also boasts high tensile strength, but its natural stiffness and lower elasticity may affect comfort and flexibility in garments. While PLA fiber provides consistent performance under mechanical stress, ramie tends to be more prone to moisture-related degradation, impacting its overall durability in suit applications.
Comfort and Breathability in Suits
PLA fiber offers excellent moisture-wicking properties and lightweight comfort, making suits breathable and ideal for warm climates. Ramie fiber provides natural breathability and a smooth texture, enhancing airflow and reducing heat retention in suits. Both fibers contribute to comfortable, breathable suits, with PLA excelling in moisture management and Ramie in durability and ventilation.
Dyeing and Color Retention
PLA fiber exhibits superior dye absorption due to its hydrophilic nature, resulting in vibrant and uniform colors on suits, while Ramie fiber, being more crystalline and less absorbent, often requires specialized mordants for effective dyeing. Color retention in PLA fiber suits is enhanced by its synthetic composition, which resists fading under UV exposure and washing, whereas Ramie fiber suits tend to lose brightness over time due to their natural cellulose structure. Both fibers can achieve desirable aesthetic qualities, but PLA fiber offers longer-lasting vibrancy and more consistent color fastness in suit applications.
Cost Comparison for Suit Manufacturing
PLA fiber offers a cost-effective alternative to Ramie fiber for suit manufacturing, with lower raw material expenses due to its bio-based polymer source derived from renewable resources like corn starch. Ramie fiber, although valued for its natural luster and durability, generally incurs higher production costs related to its labor-intensive retting and fiber extraction processes. Factoring in economies of scale, PLA fiber suits can achieve competitive pricing while maintaining eco-friendly credentials, making them a financially attractive option compared to traditional Ramie fiber suits.
Suit Care and Maintenance
PLA fiber suits require gentle washing at low temperatures and should be air-dried to maintain shape and avoid heat damage, as they are sensitive to high temperatures and moisture. Ramie fiber suits benefit from dry cleaning and should be stored in a cool, dry place to prevent mildew and fiber weakening, given ramie's natural absorbency and tendency to wrinkle. Proper care routines extend the longevity of both PLA and Ramie fiber suits by preserving fabric integrity and appearance.
Suit Applications: PLA vs Ramie Fiber Choices
PLA fiber offers excellent moisture-wicking and biodegradability, making suits comfortable and eco-friendly for everyday wear. Ramie fiber provides superior strength, breathability, and a natural luster, ideal for durable, lightweight suits with a luxurious feel. Suit designers often choose PLA fiber for sustainability and softness, while Ramie suits excel in formal settings requiring durability and crisp appearance.
Infographic: PLA fiber vs Ramie fiber for Suit
 azmater.com
azmater.com