Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, offers greater sustainability and biodegradability compared to Rayon fiber, which is chemically processed from wood pulp. Ingeo fiber provides superior moisture-wicking and durability for apparel, enhancing comfort and eco-friendly performance.
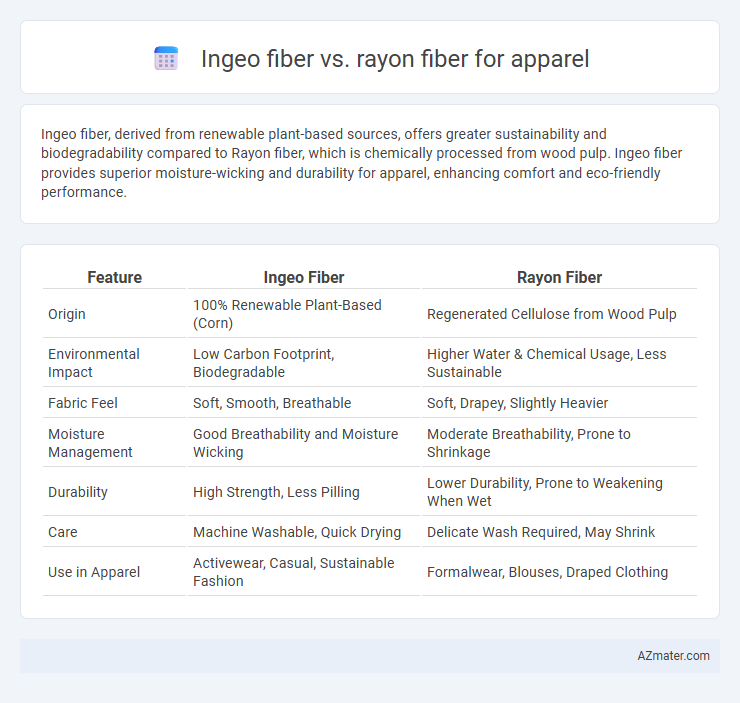
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ingeo Fiber | Rayon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | 100% Renewable Plant-Based (Corn) | Regenerated Cellulose from Wood Pulp |
| Environmental Impact | Low Carbon Footprint, Biodegradable | Higher Water & Chemical Usage, Less Sustainable |
| Fabric Feel | Soft, Smooth, Breathable | Soft, Drapey, Slightly Heavier |
| Moisture Management | Good Breathability and Moisture Wicking | Moderate Breathability, Prone to Shrinkage |
| Durability | High Strength, Less Pilling | Lower Durability, Prone to Weakening When Wet |
| Care | Machine Washable, Quick Drying | Delicate Wash Required, May Shrink |
| Use in Apparel | Activewear, Casual, Sustainable Fashion | Formalwear, Blouses, Draped Clothing |
Introduction to Ingeo and Rayon Fibers
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based resources like corn starch, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional fibers with its biodegradable properties and low carbon footprint. Rayon fiber, made from regenerated cellulose typically extracted from wood pulp, is prized for its softness and drape but involves more chemical processing and environmental concerns compared to Ingeo. Both fibers serve the apparel industry by providing versatile, breathable, and comfortable fabrics, yet Ingeo stands out for its eco-friendly lifecycle and renewable sourcing.
Origin and Production Processes
Ingeo fiber is derived from renewable plant-based sources, primarily corn, using a fermentation process to create polylactic acid (PLA) biopolymer, which is then spun into fiber, emphasizing sustainability and lower environmental impact. Rayon fiber originates from cellulose extracted from wood pulp through chemically intensive processes such as viscose or lyocell methods, often involving hazardous solvents and higher water consumption. The production of Ingeo fiber features closed-loop systems that recycle solvents and reduce carbon emissions, contrasting with traditional rayon manufacturing which can contribute to deforestation and pollution.
Fiber Structure and Composition
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based polylactic acid (PLA), exhibits a crystalline structure that offers high tensile strength and moisture-wicking properties, making it breathable and durable for apparel. Rayon fiber, made from regenerated cellulose, has a more amorphous structure that provides softness and flexibility but tends to absorb moisture more readily, affecting durability and drying time. The molecular composition of Ingeo promotes biodegradability and sustainability, whereas rayon's cellulose origin involves chemical-intensive processing, impacting environmental considerations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable corn starch, offers a significantly lower carbon footprint and reduced water consumption compared to rayon fiber, which is typically manufactured from chemically treated wood pulp causing deforestation and high water pollution. The biodegradability of Ingeo and its production process minimize environmental toxins, whereas rayon production often involves toxic chemicals like carbon disulfide, leading to harmful ecological effects. Choosing Ingeo fiber for apparel supports sustainability by promoting renewable resources, reducing chemical use, and enhancing circular economy practices over rayon's resource-intensive and pollutive manufacturing.
Physical Properties Comparison
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials, offers superior tensile strength and wrinkle resistance compared to rayon fiber, which is produced from regenerated cellulose with lower durability and higher moisture absorption. Ingeo fibers demonstrate enhanced breathability and natural moisture-wicking properties, making them ideal for activewear and sustainable apparel, whereas rayon fibers tend to retain more moisture, leading to longer drying times and potential loss of shape. The biodegradability of both fibers supports eco-friendly fashion, but Ingeo fiber maintains its physical integrity better under repeated wear and washing cycles than rayon.
Comfort and Wearability in Apparel
Ingeo fiber offers superior moisture-wicking and breathability compared to Rayon fiber, enhancing comfort during prolonged wear. Its natural origin and biodegradability appeal to eco-conscious consumers seeking sustainable apparel options without compromising softness. Rayon provides a smooth texture but tends to retain moisture, which can reduce wearability in humid conditions.
Dyeability and Color Retention
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, offers superior dyeability compared to rayon fiber, enabling vibrant and long-lasting colors in apparel. Its unique molecular structure enhances color absorption and retention, reducing fading even after multiple washes. Rayon fiber, while soft and breathable, tends to lose color intensity faster due to its semi-synthetic composition and lower affinity for certain dye types.
Cost Differences in Manufacturing
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources like corn, generally incurs higher manufacturing costs compared to rayon fiber due to its bio-based production process and proprietary technology requirements. Rayon fiber, produced from cellulose through chemical-intensive methods, benefits from established, large-scale manufacturing infrastructure that drives lower expenses. These cost differences impact final apparel pricing, with Ingeo offering sustainable benefits at a premium, while rayon remains a cost-effective choice despite environmental concerns.
Popular Apparel Uses and Applications
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, is increasingly popular in sustainable activewear and casual apparel due to its biodegradability and soft, breathable texture. Rayon fiber, produced from regenerated cellulose, is widely used in fashion apparel such as dresses, blouses, and linings for its smooth finish and excellent drape. Both fibers serve versatile roles, with Ingeo favored in eco-conscious brands and Rayon valued for its affordability and versatility in mainstream clothing lines.
Future Trends and Innovations
Ingeo fiber leverages polylactic acid derived from renewable resources, offering superior sustainability compared to traditional Rayon fibers made from chemically processed wood pulp. Future trends emphasize Ingeo's biodegradability and lower carbon footprint, aligning with growing consumer demand for eco-friendly apparel. Innovations focus on enhancing Ingeo's moisture-wicking properties and durability, positioning it as a viable alternative to Rayon in performance and comfort.
Infographic: Ingeo fiber vs Rayon fiber for Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com