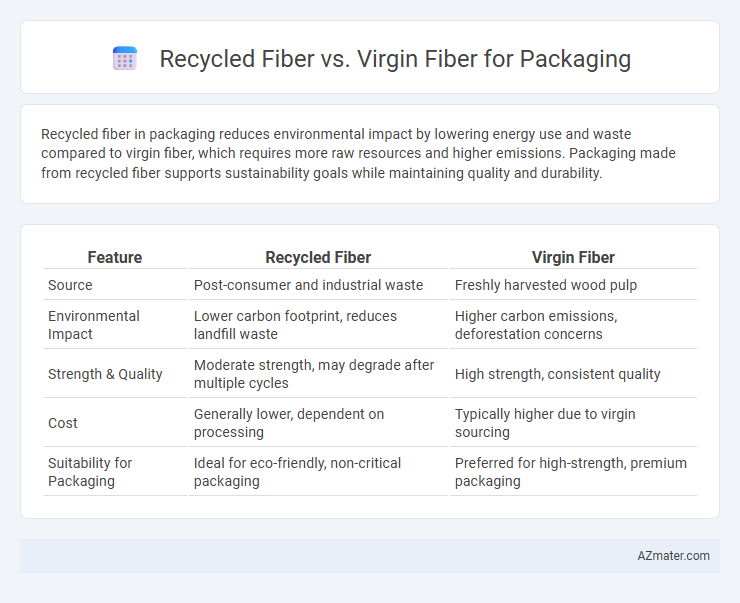
Recycled fiber in packaging reduces environmental impact by lowering energy use and waste compared to virgin fiber, which requires more raw resources and higher emissions. Packaging made from recycled fiber supports sustainability goals while maintaining quality and durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Fiber | Virgin Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Post-consumer and industrial waste | Freshly harvested wood pulp |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, reduces landfill waste | Higher carbon emissions, deforestation concerns |
| Strength & Quality | Moderate strength, may degrade after multiple cycles | High strength, consistent quality |
| Cost | Generally lower, dependent on processing | Typically higher due to virgin sourcing |
| Suitability for Packaging | Ideal for eco-friendly, non-critical packaging | Preferred for high-strength, premium packaging |
Introduction to Fiber Types in Packaging
Recycled fiber in packaging is derived from post-consumer or post-industrial paper waste, offering sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives that reduce environmental impact and conserve natural resources. Virgin fiber originates from freshly harvested wood pulp, providing higher strength, brightness, and consistent quality, which is essential for certain packaging applications requiring durability and premium appearance. Choosing between recycled and virgin fibers depends on balancing sustainability goals, product protection requirements, and cost-effectiveness in packaging design.
What Are Recycled Fibers?
Recycled fibers are materials derived from post-consumer or post-industrial waste, reprocessed to create new packaging products, reducing the demand for virgin fiber from fresh wood pulp. These fibers undergo thorough cleaning and de-inking processes to eliminate contaminants, ensuring quality suitable for various packaging applications. Utilizing recycled fibers in packaging helps lower environmental impact by conserving natural resources, reducing energy consumption, and minimizing landfill waste compared to virgin fiber production.
Understanding Virgin Fibers
Virgin fibers originate directly from natural sources such as trees, offering superior strength, purity, and consistency compared to recycled fibers. These fibers provide enhanced durability and printable surfaces, which are critical for high-quality packaging applications requiring structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. Understanding the performance benefits of virgin fibers helps manufacturers optimize packaging that meets strict safety standards and consumer expectations.
Environmental Impact: Recycled vs Virgin Fiber
Recycled fiber significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to virgin fiber, which requires extensive logging and chemical processing. Utilizing recycled fiber conserves natural resources, decreases landfill waste, and reduces water usage during production. In packaging, opting for recycled fiber supports sustainable supply chains and mitigates deforestation, making it a more eco-friendly choice over virgin fiber.
Performance and Quality Comparison
Recycled fiber in packaging offers environmental benefits but may exhibit lower strength, reduced brightness, and less uniformity compared to virgin fiber, potentially impacting print quality and durability. Virgin fiber provides superior tensile strength, consistent fiber length, and higher purity, resulting in enhanced packaging performance, better print clarity, and improved barrier properties. Advances in recycling technology are narrowing these gaps, yet virgin fiber remains the preferred choice for applications demanding optimal structural integrity and premium quality.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Recycled fiber in packaging significantly reduces raw material costs by lowering reliance on virgin pulp, which is typically 20-30% more expensive due to intensive processing and resource extraction. Economic considerations highlight that although recycled fibers may incur additional sorting and cleaning expenses, their overall lifecycle cost benefits include reduced energy consumption and waste management fees, contributing to a 15-25% savings in production costs. Cost analysis also factors in market volatility of virgin fiber prices, where fluctuations increase financial risks, making recycled fiber a more stable and economically viable option for sustainable packaging solutions.
Supply Chain and Availability Issues
Recycled fiber offers environmental benefits but faces supply chain challenges due to inconsistent quality and limited availability compared to virgin fiber, which ensures a stable and high-quality supply crucial for packaging manufacturers. Virgin fiber is typically sourced from sustainable forestry practices, providing a reliable and scalable resource, whereas recycled fiber depends heavily on local collection systems and fluctuating recycling rates. Packaging companies must balance the environmental advantages of recycled fibers with the supply chain reliability of virgin fibers to meet demand and maintain production consistency.
Regulatory and Certification Aspects
Recycled fiber packaging must comply with stringent regulations such as the U.S. FDA's indirect food additive guidelines and the EU's Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive to ensure safety and sustainability. Virgin fiber packaging often benefits from certifications like FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) and PEFC (Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification), which verify responsible forest management and environmental standards. Regulatory bodies increasingly mandate transparent supply chain traceability and life cycle assessments for both recycled and virgin fibers to meet evolving environmental policies.
Industry Trends and Innovations
Recycled fiber is gaining significant traction in packaging due to rising environmental regulations and consumer demand for sustainable products, driving innovation in deinking and cleaning technologies that improve fiber quality. Virgin fiber continues to be essential for high-strength packaging applications, but industry trends show a growing hybrid approach optimizing both fiber types to balance durability with eco-friendly credentials. Advances in fiber blending techniques and automated sorting systems are enhancing the scalability of recycled fiber use, making it a competitive alternative in the packaging sector.
Making the Right Choice for Sustainable Packaging
Recycled fiber significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to virgin fiber, making it an essential component for sustainable packaging. Virgin fiber offers superior strength and print quality, which may be necessary for specific packaging applications demanding durability and aesthetic appeal. Evaluating the balance between performance requirements and environmental benefits is crucial for businesses aiming to make the right choice in eco-friendly packaging solutions.
Infographic: Recycled fiber vs Virgin fiber for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com