Corn fiber offers a sustainable, biodegradable alternative to polyester, which is derived from non-renewable petroleum and is less eco-friendly. Dresses made from corn fiber provide breathable comfort and reduced environmental impact compared to the durability and moisture-wicking properties of polyester.
Table of Comparison
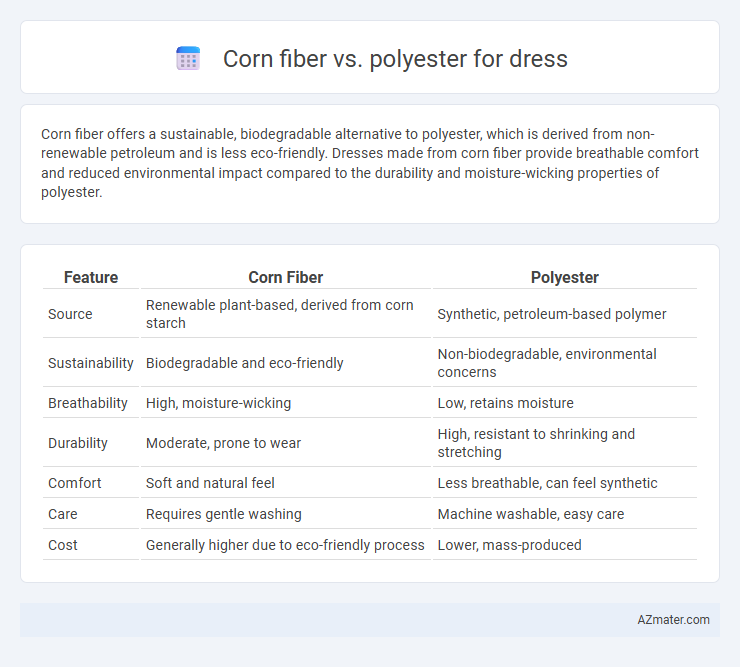
| Feature | Corn Fiber | Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable plant-based, derived from corn starch | Synthetic, petroleum-based polymer |
| Sustainability | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, environmental concerns |
| Breathability | High, moisture-wicking | Low, retains moisture |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to wear | High, resistant to shrinking and stretching |
| Comfort | Soft and natural feel | Less breathable, can feel synthetic |
| Care | Requires gentle washing | Machine washable, easy care |
| Cost | Generally higher due to eco-friendly process | Lower, mass-produced |
Introduction to Corn Fiber and Polyester
Corn fiber, derived from renewable corn starch, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional fabrics with its biodegradable and lightweight properties, making it ideal for eco-friendly dress production. Polyester, a synthetic polymer made from petroleum-based products, is known for its durability, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking abilities, commonly used in mass-produced dresses. The comparison between corn fiber and polyester highlights the balance between environmental impact and performance in textile manufacturing.
Overview of Fabric Composition
Corn fiber, also known as PLA (polylactic acid), is a biodegradable fabric derived from fermented plant starch, primarily corn, offering a renewable alternative to synthetic fibers. Polyester is a synthetic polymer made from petrochemicals, widely used in the fashion industry for its durability, wrinkle resistance, and affordability. Corn fiber provides eco-friendly breathability and moisture-wicking properties, while polyester excels in strength and elasticity but has a higher environmental impact due to fossil fuel dependency.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Corn fiber, derived from renewable corn starch, offers a biodegradable and compostable alternative to polyester, which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. The production of corn fiber consumes less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to the intensive fossil fuel extraction and chemical processing needed for polyester. While polyester excels in durability and moisture-wicking, its environmental footprint is significantly higher due to microplastic pollution and long degradation times, making corn fiber a more sustainable choice for eco-friendly dress manufacturing.
Comfort and Breathability
Corn fiber, derived from corn starch, offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to polyester, making it ideal for warm weather dresses. Polyester, a synthetic fabric, tends to trap heat and moisture, often leading to discomfort and reduced airflow during prolonged wear. Lightweight and hypoallergenic, corn fiber fabric naturally enhances comfort by allowing better air circulation and reducing skin irritation.
Durability and Longevity
Corn fiber, derived from natural corn starch, offers moderate durability but tends to degrade faster under frequent washing and prolonged exposure to sunlight compared to polyester. Polyester, a synthetic polymer, is highly durable with excellent resistance to abrasion, stretching, and environmental factors, ensuring longer garment lifespan. Dress fabrics made from polyester maintain shape and color over extended use, making them preferable for longevity-focused apparel.
Moisture-Wicking and Quick-Dry Capabilities
Corn fiber fabric exhibits superior moisture-wicking properties, drawing sweat away from the body and promoting faster evaporation to keep the skin dry during intense activities. Polyester, known for its hydrophobic nature, resists water absorption and dries quickly, making it an excellent choice for quick-dry performance in activewear. Both materials offer effective moisture management, but corn fiber adds a natural, biodegradable option with enhanced breathability compared to synthetic polyester.
Care and Maintenance
Corn fiber dresses require gentle washing with mild detergents and air drying to maintain their softness and prevent shrinkage. Polyester dresses are highly durable, allowing for machine washing and quick drying without significant risk of damage or color fading. Both materials resist wrinkles, but polyester offers superior ease of maintenance due to its synthetic resilience.
Allergenicity and Skin Sensitivity
Corn fiber, derived from natural corn starch, offers hypoallergenic properties making it suitable for sensitive skin and reducing the risk of allergic reactions. Polyester, a synthetic fabric, can sometimes cause irritation or exacerbate skin sensitivities due to its non-breathable nature and chemical processing. Choosing corn fiber dresses benefits those prone to allergies or skin sensitivities by providing better moisture absorption and minimizing skin irritation.
Cost and Accessibility
Corn fiber offers a sustainable alternative to polyester with a slightly higher production cost due to its agricultural sourcing and biodegradable properties. Polyester remains more accessible and cost-effective, benefiting from well-established global manufacturing and supply chains that lower consumer prices. Consumers seeking eco-friendly fabrics may face premium prices and limited availability for corn fiber dresses compared to the mass-market affordability and widespread availability of polyester garments.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Fabric for Dresses
Corn fiber offers a sustainable and biodegradable alternative to polyester, making it ideal for eco-conscious fashion choices. Polyester excels in durability, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking properties, suitable for long-lasting, easy-care dresses. The final verdict depends on prioritizing sustainability with corn fiber or performance and affordability with polyester when selecting fabric for dresses.
Infographic: Corn fiber vs Polyester for Dress
 azmater.com
azmater.com