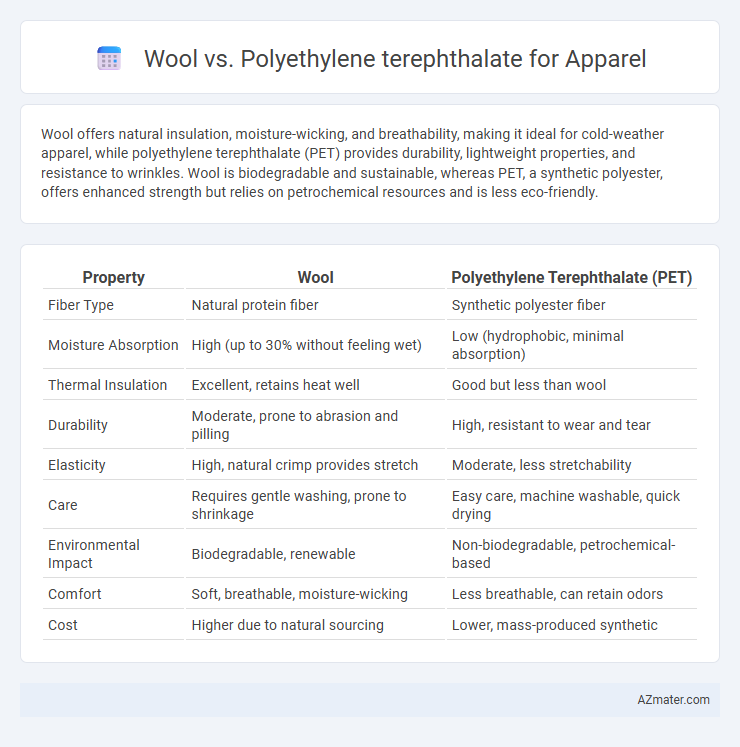
Wool offers natural insulation, moisture-wicking, and breathability, making it ideal for cold-weather apparel, while polyethylene terephthalate (PET) provides durability, lightweight properties, and resistance to wrinkles. Wool is biodegradable and sustainable, whereas PET, a synthetic polyester, offers enhanced strength but relies on petrochemical resources and is less eco-friendly.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Wool | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Type | Natural protein fiber | Synthetic polyester fiber |
| Moisture Absorption | High (up to 30% without feeling wet) | Low (hydrophobic, minimal absorption) |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, retains heat well | Good but less than wool |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to abrasion and pilling | High, resistant to wear and tear |
| Elasticity | High, natural crimp provides stretch | Moderate, less stretchability |
| Care | Requires gentle washing, prone to shrinkage | Easy care, machine washable, quick drying |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable | Non-biodegradable, petrochemical-based |
| Comfort | Soft, breathable, moisture-wicking | Less breathable, can retain odors |
| Cost | Higher due to natural sourcing | Lower, mass-produced synthetic |
Introduction to Wool and Polyethylene Terephthalate in Apparel
Wool, a natural fiber derived from sheep, offers excellent insulation, breathability, and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for high-performance apparel and cold-weather clothing. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a synthetic polyester fiber, is known for its strength, durability, wrinkle resistance, and quick-drying capabilities, commonly used in activewear and affordable fashion. Both fibers serve distinct purposes in apparel, with wool favored for warmth and sustainability, while PET provides versatility and cost-effective manufacturing options.
Fiber Composition and Structure Comparison
Wool fibers consist primarily of keratin protein with a natural crimped structure, providing excellent insulation, moisture-wicking, and elasticity, ideal for thermal apparel. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a synthetic polyester fiber composed of long-chain polymers derived from petroleum, featuring a smooth, non-porous surface that offers high durability, quick-drying properties, and resistance to wrinkles. The intrinsic difference between the natural, breathable scales of wool and the engineered, hydrophobic PET fibers dictates their suitability for diverse clothing applications based on performance and comfort needs.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Wool is a biodegradable, renewable fiber that naturally regulates temperature and requires fewer chemical treatments during production, making it a sustainable choice for apparel. In contrast, polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a synthetic plastic derived from petroleum, contributes to microplastic pollution and relies heavily on non-renewable resources, although recycled PET (rPET) reduces some environmental burden. Wool's ability to decompose and its lower carbon footprint during production provide significant ecological advantages over conventional PET fabrics in sustainable fashion.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
Wool offers superior breathability, natural moisture-wicking, and excellent temperature regulation, making it highly comfortable for various weather conditions in apparel. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) provides durability and quick-drying properties but can lack the softness and breathability of wool, sometimes causing discomfort during prolonged wear. The choice between wool and PET in clothing largely depends on desired comfort, with wool preferred for natural warmth and wearability, while PET excels in lightweight, moisture-resistant applications.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Wool naturally excels in moisture management by absorbing up to 30% of its weight in moisture while maintaining warmth, making it highly breathable and comfortable for apparel. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a synthetic fiber, offers moisture-wicking properties but tends to retain less moisture, which can result in lower breathability compared to wool. Wool's unique fiber structure enhances air circulation and odor resistance, outperforming PET in overall moisture regulation and comfort during extended wear.
Durability and Longevity in Clothing
Wool offers exceptional durability due to its natural elasticity and resilience, allowing garments to maintain shape and resist wear over time. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), or polyester, excels in longevity with strong resistance to stretching, shrinking, and abrasion, making it ideal for activewear and frequent washing. Both fibers provide long-lasting apparel options, but wool's natural moisture-wicking properties complement polyester's synthetic toughness for varied use cases.
Thermal Insulation and Weather Resistance
Wool offers superior thermal insulation due to its natural crimped fibers that trap heat effectively, making it ideal for cold weather apparel. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a synthetic fiber, provides excellent weather resistance with moisture-wicking and quick-drying properties, enhancing comfort in wet or humid conditions. While wool excels at warmth retention and breathability, PET's durability and resistance to wind and water make it a practical choice for versatile activewear.
Care, Maintenance, and Washing
Wool requires gentle care with cold water washing and mild detergents to prevent shrinking and maintain fiber integrity, while polyethylene terephthalate (PET) demands low-heat washing and drying to avoid melting or deformation. Wool garments benefit from natural lanolin properties, offering some water resistance and reducing odor buildup, whereas PET fibers are highly resistant to wrinkles, stains, and stretching, making them easier to maintain long-term. Proper storage of wool involves avoiding moth exposure and allowing adequate drying, while PET fabrics are more durable under frequent washing and can be machine dried with minimal risk.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Wool generally commands a higher price than polyethylene terephthalate (PET) due to natural sourcing and labor-intensive processing, impacting apparel production costs. PET, a synthetic polyester, offers more affordable pricing and widespread market availability, benefiting from large-scale manufacturing and recycling initiatives. The choice between wool and PET balances cost efficiency and material performance, with PET leading in budget-conscious and sustainable apparel markets.
Choosing the Right Fabric for Your Apparel Needs
Wool offers superior insulation, moisture-wicking, and natural breathability, making it ideal for cold-weather apparel and activities requiring temperature regulation and comfort. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a synthetic polyester, excels in durability, wrinkle resistance, and quick drying, which suits activewear and budget-friendly fashion requiring low maintenance. Selecting between wool and PET depends on the desired balance of warmth, moisture management, longevity, and care requirements for your apparel needs.
Infographic: Wool vs Polyethylene terephthalate for Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com