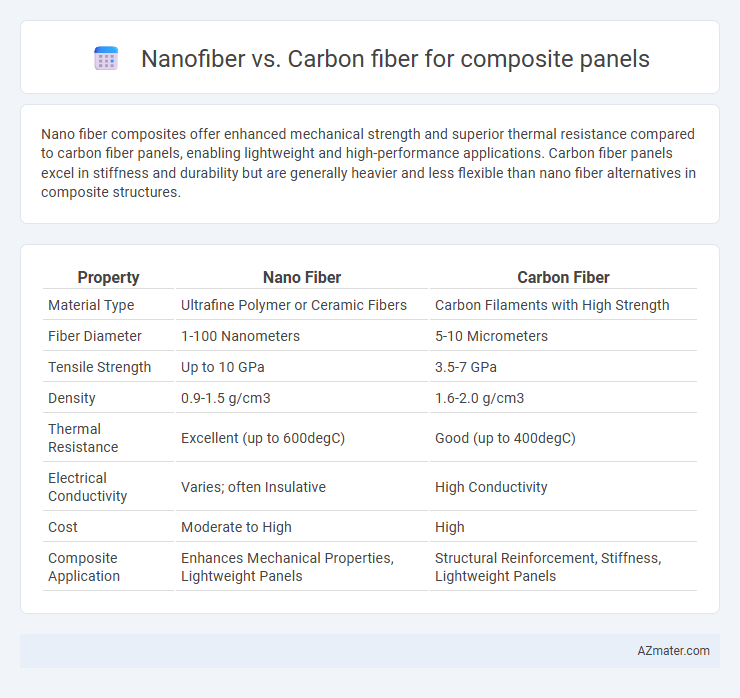
Nano fiber composites offer enhanced mechanical strength and superior thermal resistance compared to carbon fiber panels, enabling lightweight and high-performance applications. Carbon fiber panels excel in stiffness and durability but are generally heavier and less flexible than nano fiber alternatives in composite structures.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nano Fiber | Carbon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ultrafine Polymer or Ceramic Fibers | Carbon Filaments with High Strength |
| Fiber Diameter | 1-100 Nanometers | 5-10 Micrometers |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 10 GPa | 3.5-7 GPa |
| Density | 0.9-1.5 g/cm3 | 1.6-2.0 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent (up to 600degC) | Good (up to 400degC) |
| Electrical Conductivity | Varies; often Insulative | High Conductivity |
| Cost | Moderate to High | High |
| Composite Application | Enhances Mechanical Properties, Lightweight Panels | Structural Reinforcement, Stiffness, Lightweight Panels |
Introduction to Composite Panels
Composite panels combine multiple materials to achieve superior strength-to-weight ratios, with nano fibers and carbon fibers being key reinforcements. Nano fibers enhance mechanical properties at the nanoscale, improving toughness and durability without significantly increasing weight. Carbon fibers contribute exceptional stiffness and tensile strength, making them ideal for high-performance composite panels used in aerospace and automotive industries.
Overview of Nano Fiber Technology
Nano fiber technology utilizes ultra-fine fibers with diameters typically less than 100 nanometers, providing exceptional surface area and strength-to-weight ratio for composite panels. These nano fibers enhance mechanical properties such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and thermal stability through improved fiber-matrix bonding and crack inhibition. Compared to carbon fiber, nano fibers offer superior flexibility and can be engineered for multifunctional applications, including enhanced electrical conductivity and filtration capabilities within composite materials.
Understanding Carbon Fiber Composition
Carbon fiber for composite panels primarily consists of tightly woven strands of carbon atoms bonded in a crystal structure, providing exceptional tensile strength and stiffness while maintaining lightweight properties. In contrast, nano fibers, often made from materials like carbon nanotubes or polymer nanofibers, offer enhanced surface area and superior mechanical reinforcement at the nanoscale but typically require integration with carbon fiber matrices to maximize structural performance. Understanding carbon fiber composition reveals its dominance in high-strength applications due to its crystalline graphitic plane alignment, which delivers unmatched durability and resistance to deformation compared to nano fibers alone.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Nano fiber composites exhibit exceptional mechanical strength and enhanced durability due to their high surface area and superior load transfer capabilities, making them ideal for lightweight, high-performance panels. Carbon fiber composites provide outstanding tensile strength and rigidity, with excellent fatigue resistance and stability under cyclic loading conditions. Both materials significantly improve composite panel durability, but nano fiber composites excel in toughness and impact resistance, while carbon fibers dominate in stiffness and long-term structural integrity.
Weight Comparison: Nano Fiber vs Carbon Fiber
Nano fiber composite panels exhibit significantly lower weight compared to carbon fiber panels due to their ultra-fine fiber diameter and high surface area, which allow for enhanced mechanical properties with minimal material usage. While carbon fiber panels typically weigh around 1.6 g/cm3, nano fiber composites can reduce density by approximately 10-20%, improving lightness without sacrificing strength. This weight advantage makes nano fiber composites highly suitable for aerospace and automotive applications where every gram matters.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Carbon fiber composite panels typically exhibit higher initial costs due to expensive raw materials and energy-intensive manufacturing processes compared to nano fiber composites, which utilize smaller-scale materials with potentially lower production expenses. Nano fiber composites offer enhanced affordability by enabling cost-effective production techniques and reducing material usage, making them suitable for applications requiring lightweight panels with budget constraints. Evaluating total lifecycle costs, including durability and maintenance, remains essential, but nano fiber composites often provide a more accessible alternative in cost-sensitive composite panel markets.
Manufacturing Processes and Scalability
Nanofiber production for composite panels typically involves electrospinning, allowing for precise control of fiber diameter and alignment but facing challenges in large-scale manufacturing due to slower production rates and higher costs. Carbon fiber manufacturing utilizes processes such as PAN (polyacrylonitrile) precursor oxidation, carbonization, and surface treatment, enabling mass production with well-established industrial scalability and consistent mechanical properties. While nanofibers offer superior surface area and potential for enhanced mechanical or functional properties, carbon fibers remain the preferred choice for large-scale composite panels due to mature manufacturing technologies and cost-effectiveness.
Applications in Aerospace and Automotive Industries
Nano fiber composites offer enhanced mechanical properties, heat resistance, and lightweight features, making them ideal for aerospace components such as thermal insulation and structural reinforcement panels. Carbon fiber composites provide superior strength-to-weight ratios and stiffness, extensively used in automotive body panels, chassis, and aerospace structural parts. The choice between nano fiber and carbon fiber composites depends on specific application requirements like durability, flexibility, and thermal stability in high-performance aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nanofiber composites exhibit greater environmental sustainability due to their potential for biodegradability and lower energy consumption during production compared to carbon fiber panels, which require high energy processes and generate significant CO2 emissions. Carbon fiber composites often rely on non-renewable precursors and pose challenges in recycling, while nanofiber materials, derived from natural or bio-based sources, offer enhanced recyclability and reduced ecological footprints. The shift towards nanofiber composites supports circular economy principles by minimizing waste and promoting resource-efficient manufacturing in sustainable composite panel applications.
Future Trends in Composite Materials
Nano fiber technology is rapidly advancing in composite panels, offering enhanced mechanical properties and improved durability at a nanoscale level, which outperforms traditional carbon fiber in some applications. Research focuses on hybrid composites combining nano fibers and carbon fibers to achieve superior strength-to-weight ratios and multifunctional capabilities in aerospace and automotive sectors. Future trends emphasize sustainable production methods and the integration of smart sensing nano fibers for real-time structural health monitoring in next-generation composite materials.
Infographic: Nano fiber vs Carbon fiber for Composite panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com