PLA fiber offers excellent biodegradability and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for eco-friendly bedding. Lyocell fiber provides superior softness, breathability, and durability, enhancing comfort and longevity in high-quality bed linens.
Table of Comparison
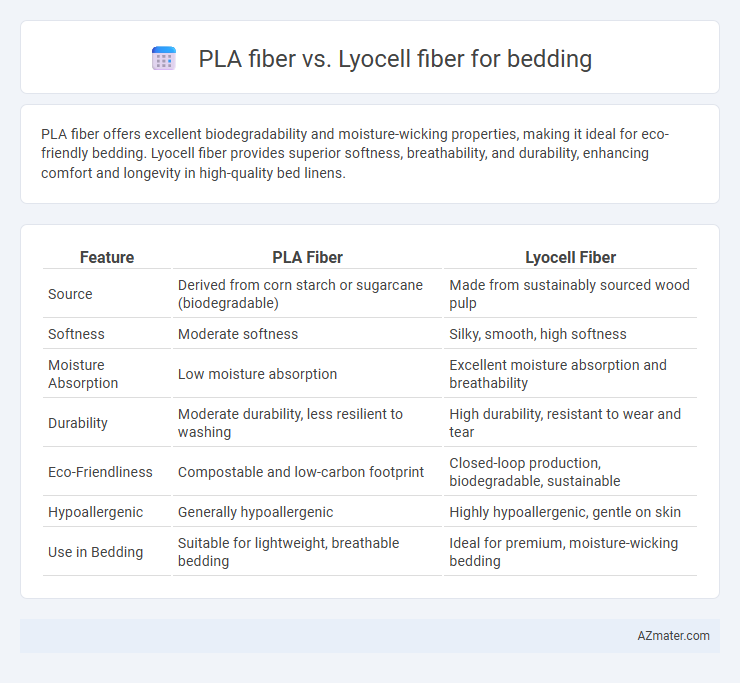
| Feature | PLA Fiber | Lyocell Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Derived from corn starch or sugarcane (biodegradable) | Made from sustainably sourced wood pulp |
| Softness | Moderate softness | Silky, smooth, high softness |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | Excellent moisture absorption and breathability |
| Durability | Moderate durability, less resilient to washing | High durability, resistant to wear and tear |
| Eco-Friendliness | Compostable and low-carbon footprint | Closed-loop production, biodegradable, sustainable |
| Hypoallergenic | Generally hypoallergenic | Highly hypoallergenic, gentle on skin |
| Use in Bedding | Suitable for lightweight, breathable bedding | Ideal for premium, moisture-wicking bedding |
Introduction to PLA Fiber and Lyocell Fiber
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers biodegradable and eco-friendly properties ideal for sustainable bedding applications. Lyocell fiber, produced from wood pulp through a closed-loop process, is renowned for its exceptional moisture-wicking, softness, and durability in bedding textiles. Both fibers provide biodegradable alternatives to traditional synthetic fibers, but PLA emphasizes compostability while Lyocell excels in comfort and breathability for enhanced sleep quality.
Origins and Production Processes
PLA fiber originates from fermented plant starches, primarily corn, undergoing a polymerization process to create biodegradable fibers ideal for eco-friendly bedding. Lyocell fiber is derived from sustainably harvested wood pulp, processed using a closed-loop solvent spinning method that recycles water and chemicals, minimizing environmental impact. Both fibers offer sustainable alternatives in bedding, with PLA focusing on renewable agricultural sources and Lyocell emphasizing forest-based raw materials and efficient solvent recovery.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers biodegradability and lower carbon emissions during production compared to conventional synthetic fibers, making it a more sustainable choice for bedding. Lyocell fiber, produced from sustainably sourced wood pulp through a closed-loop process, minimizes chemical waste and uses less water, positioning it as an eco-friendly and biodegradable alternative. Both fibers contribute to reducing environmental impact, but Lyocell's efficient manufacturing and superior biodegradability often result in a smaller ecological footprint for sustainable bedding products.
Fiber Structure and Performance Characteristics
PLA fiber, derived from renewable biomass like corn starch, features a smooth and round fiber structure that offers excellent moisture-wicking and breathability, making it ideal for bedding applications. Lyocell fiber, produced from sustainably sourced wood pulp through a closed-loop process, has a unique fibrillated surface that enhances softness, strength, and moisture absorption properties, providing superior comfort and durability in bedding. Both fibers exhibit antimicrobial characteristics and biodegradability, but Lyocell generally outperforms PLA in terms of tensile strength and resistance to pilling.
Comfort and Breathability for Bedding
PLA fiber offers excellent moisture-wicking properties and maintains a cool touch, making it ideal for breathable and comfortable bedding. Lyocell fiber excels in softness and natural moisture absorption, providing a smooth, hypoallergenic surface that enhances sleep quality. Both fibers promote airflow; however, Lyocell typically delivers superior breathability due to its fine fiber structure, while PLA ensures durability with eco-friendly characteristics.
Durability and Longevity in Everyday Use
PLA fiber offers moderate durability with good resistance to wear but may degrade faster under prolonged exposure to moisture and heat, making it less ideal for high-frequency washing in bedding. Lyocell fiber exhibits superior longevity due to its strong, smooth cellulose structure, resisting pilling and maintaining fabric integrity through frequent laundering and daily use. Bedding made from lyocell provides enhanced durability and sustained comfort, outperforming PLA fiber in long-term performance and resilience.
Allergenicity and Skin Sensitivity
PLA fiber, derived from renewable corn starch, offers hypoallergenic properties ideal for sensitive skin, as it resists dust mites and mold growth, reducing allergen exposure in bedding. Lyocell fiber, made from sustainably sourced eucalyptus wood pulp, features exceptional moisture-wicking and breathability, preventing bacterial buildup that can trigger skin irritation and allergic reactions. Both fibers provide skin-friendly alternatives to synthetic bedding, but PLA's inherent antimicrobial traits give it an edge for minimizing allergenicity and enhancing comfort for allergy-prone users.
Care, Maintenance, and Laundering
PLA fiber bedding requires gentle washing at low temperatures to prevent fiber degradation, avoiding bleach and high heat drying to maintain fabric integrity. Lyocell fiber bedding exhibits excellent moisture management and shape retention, allowing for machine washing in cool or warm water with mild detergent and low-heat tumble drying to preserve softness and durability. Both fibers benefit from air drying and minimal exposure to harsh chemicals to extend bedding lifespan and enhance comfort.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
PLA fiber offers a more cost-effective solution than Lyocell fiber for bedding, with production costs typically 20-30% lower due to its bio-based, renewable corn starch origins. Lyocell, derived from wood pulp using a more complex solvent-spinning process, commands a higher price point reflecting its superior softness and moisture-wicking properties. Market availability for PLA fiber is rapidly expanding in sustainable textile sectors, while Lyocell maintains widespread presence across premium bedding products, supported by established global supply chains.
Which Fiber Is Best for Bedding? (Summary and Recommendation)
PLA fiber offers excellent moisture-wicking and biodegradability, making it an eco-friendly choice for bedding with good durability and softness. Lyocell fiber stands out for its exceptional breathability, smooth texture, and superior moisture management, promoting a cooler and more comfortable sleep environment. For bedding that prioritizes sustainability, softness, and enhanced comfort, Lyocell fiber is generally recommended as the best option.
Infographic: PLA fiber vs Lyocell fiber for Bedding
 azmater.com
azmater.com