Chitosan fiber offers natural antibacterial properties, biodegradability, and excellent moisture absorption, making it ideal for eco-friendly, skin-friendly apparel. Acrylic fiber provides durability, lightweight warmth, and vibrant color retention, commonly used in affordable, synthetic clothing.
Table of Comparison
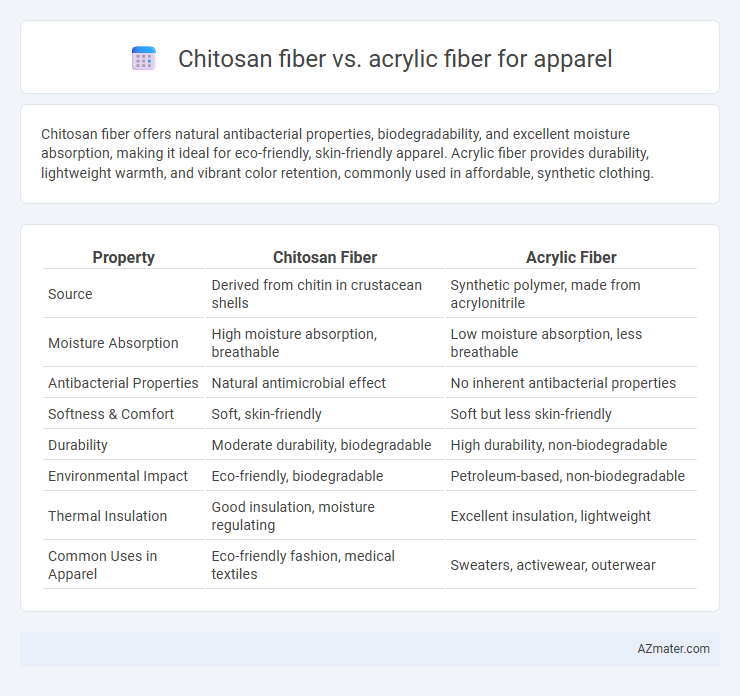
| Property | Chitosan Fiber | Acrylic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Derived from chitin in crustacean shells | Synthetic polymer, made from acrylonitrile |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture absorption, breathable | Low moisture absorption, less breathable |
| Antibacterial Properties | Natural antimicrobial effect | No inherent antibacterial properties |
| Softness & Comfort | Soft, skin-friendly | Soft but less skin-friendly |
| Durability | Moderate durability, biodegradable | High durability, non-biodegradable |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable | Petroleum-based, non-biodegradable |
| Thermal Insulation | Good insulation, moisture regulating | Excellent insulation, lightweight |
| Common Uses in Apparel | Eco-friendly fashion, medical textiles | Sweaters, activewear, outerwear |
Introduction to Chitosan and Acrylic Fibers
Chitosan fiber, derived from chitin found in crustacean shells, offers biodegradability, antimicrobial properties, and excellent moisture absorption, making it a sustainable option for eco-friendly apparel. Acrylic fiber, a synthetic polymer made from acrylonitrile, is known for its lightweight, soft texture, vibrant color retention, and resistance to wrinkles and shrinking, widely used in fashion and sportswear. The choice between chitosan and acrylic fibers depends on the desired balance of natural benefits and synthetic durability in textile applications.
Fiber Source and Manufacturing Process
Chitosan fiber is derived from chitin, primarily sourced from crustacean shells like shrimp and crab, making it a natural, biodegradable alternative to synthetic fibers. The manufacturing process involves deacetylation of chitin to produce chitosan, followed by wet spinning into fibers, preserving its antibacterial and moisture-wicking properties. Acrylic fiber originates from petroleum-based polyacrylonitrile, produced via polymerization and dry or wet spinning, offering durability and elasticity but with less environmental sustainability compared to chitosan fibers.
Physical Properties Comparison
Chitosan fiber exhibits superior moisture absorption and antibacterial properties compared to acrylic fiber, making it more suitable for comfortable and hygienic apparel. Acrylic fiber offers higher durability and better resistance to abrasion, enhancing garment longevity in active wear. Both fibers differ significantly in thermal insulation, with acrylic providing better warmth retention, while chitosan ensures breathability and softness.
Comfort and Wearability
Chitosan fiber offers superior moisture absorption and breathability compared to acrylic fiber, enhancing wearer comfort by regulating body temperature and reducing sweat accumulation. Its natural antibacterial properties prevent odor buildup, making it ideal for prolonged wear and sensitive skin, unlike acrylic fibers which may trap heat and cause irritation. The lightweight, soft texture of chitosan fiber contributes to better wearability, combining eco-friendliness with functional performance in apparel applications.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Chitosan fiber offers superior moisture management and breathability compared to acrylic fiber due to its natural hydrophilic properties and porous structure, enabling rapid sweat absorption and effective moisture evaporation. Acrylic fiber, being synthetic and hydrophobic, tends to trap heat and moisture, leading to reduced comfort and slower drying times in apparel. Selecting chitosan fiber enhances wearer comfort through improved ventilation and efficient moisture control, making it ideal for activewear and outdoor clothing.
Durability and Strength
Chitosan fiber exhibits superior durability compared to acrylic fiber due to its natural antimicrobial properties and resistance to wear and tear, making it ideal for long-lasting apparel. Acrylic fiber, while lightweight and soft, tends to have lower tensile strength and is more prone to pilling and abrasion damage. The inherent robustness of chitosan fibers provides enhanced strength retention after multiple washes, ensuring sustained garment performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Chitosan fiber, derived from natural chitin in crustacean shells, offers superior biodegradability and non-toxic properties compared to acrylic fiber, which is petroleum-based and contributes to microplastic pollution. The production of chitosan fiber consumes less energy and produces fewer greenhouse gases, supporting sustainable apparel manufacturing. In contrast, acrylic fiber's reliance on fossil fuels and its slow degradation pose significant challenges for environmental sustainability in the textile industry.
Antimicrobial and Functional Benefits
Chitosan fiber exhibits superior antimicrobial properties due to its natural biopolymer structure, effectively inhibiting bacterial and fungal growth, which enhances hygiene in apparel applications. In contrast, acrylic fibers lack inherent antimicrobial effects, often requiring chemical treatments to achieve similar benefits. The functional advantages of chitosan include biodegradability, moisture retention, and skin-friendly characteristics, making it a sustainable and health-conscious choice over synthetic acrylic fiber for performance and casual wear.
Cost and Market Availability
Chitosan fiber, derived from natural sources like shrimp shells, typically costs more than synthetic acrylic fiber due to its eco-friendly extraction process and limited large-scale production. Acrylic fiber benefits from widespread manufacturing and established supply chains, making it significantly more affordable and readily available in global apparel markets. The higher price and niche market presence of chitosan fiber restrict its use to specialty or eco-conscious apparel segments, while acrylic remains dominant for cost-effective mass-produced clothing.
Future Trends in Apparel Applications
Chitosan fiber offers biodegradable and antimicrobial properties, positioning it as a sustainable alternative to acrylic fiber in future apparel markets. Innovations in blending chitosan with synthetic fibers enhance moisture management and comfort, attracting eco-conscious consumers and sportswear brands. Advancement in green textile technologies and increasing regulatory pressure on synthetic fiber pollution drive higher adoption of chitosan fiber in sustainable fashion.
Infographic: Chitosan fiber vs Acrylic fiber for Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com