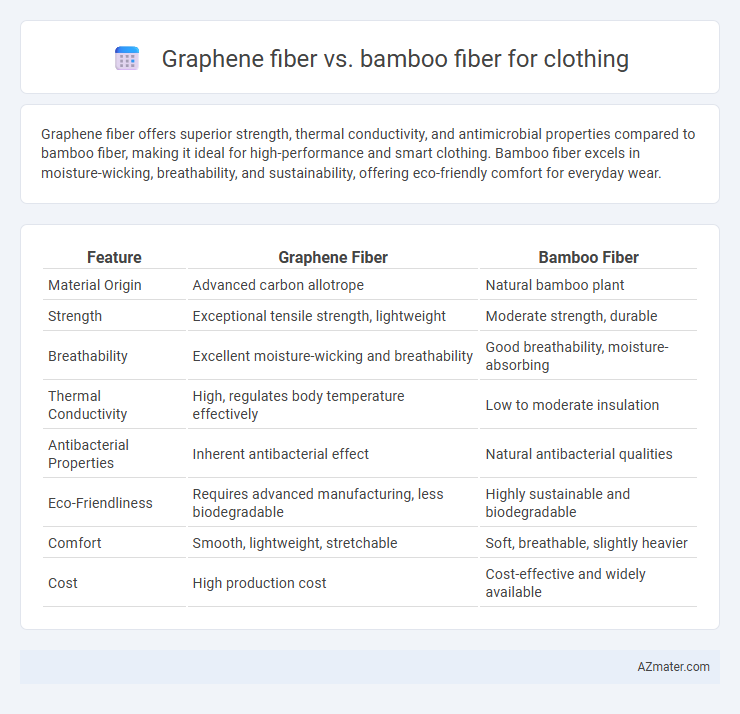
Graphene fiber offers superior strength, thermal conductivity, and antimicrobial properties compared to bamboo fiber, making it ideal for high-performance and smart clothing. Bamboo fiber excels in moisture-wicking, breathability, and sustainability, offering eco-friendly comfort for everyday wear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Graphene Fiber | Bamboo Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Origin | Advanced carbon allotrope | Natural bamboo plant |
| Strength | Exceptional tensile strength, lightweight | Moderate strength, durable |
| Breathability | Excellent moisture-wicking and breathability | Good breathability, moisture-absorbing |
| Thermal Conductivity | High, regulates body temperature effectively | Low to moderate insulation |
| Antibacterial Properties | Inherent antibacterial effect | Natural antibacterial qualities |
| Eco-Friendliness | Requires advanced manufacturing, less biodegradable | Highly sustainable and biodegradable |
| Comfort | Smooth, lightweight, stretchable | Soft, breathable, slightly heavier |
| Cost | High production cost | Cost-effective and widely available |
Introduction to Graphene and Bamboo Fibers
Graphene fiber, derived from a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, offers exceptional strength, flexibility, and conductivity, making it a cutting-edge material for advanced clothing applications. Bamboo fiber, sourced from the pulp of bamboo plants, is renowned for its natural breathability, moisture-wicking properties, and eco-friendly biodegradability, appealing to sustainable fashion markets. Both fibers provide unique benefits in textiles, with graphene enhancing durability and performance, while bamboo emphasizes comfort and environmental sustainability.
Material Origins: Graphene vs Bamboo
Graphene fiber is derived from carbon atoms arranged in a two-dimensional lattice, offering exceptional strength, conductivity, and lightweight properties. Bamboo fiber originates from the cellulose-rich pulp of bamboo plants, known for its natural softness, breathability, and eco-friendly cultivation. The synthetic nature of graphene allows for advanced performance in technical apparel, while bamboo fiber's renewable plant source supports sustainability and biodegradability in textile production.
Production Processes Compared
Graphene fiber production involves advanced chemical vapor deposition and nanomaterial integration, resulting in high conductivity and strength for technical textiles. Bamboo fiber is produced through mechanical crushing or chemical processing of bamboo pulp, offering eco-friendly and biodegradable fabric properties. The graphene process is more complex and costly but yields superior performance, whereas bamboo fiber is valued for sustainability and softness in clothing manufacturing.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Graphene fiber exhibits exceptional mechanical strength with tensile strength exceeding 130 GPa, making it one of the strongest materials for clothing applications, far outperforming bamboo fiber which typically has tensile strength around 250-500 MPa. The durability of graphene fiber is superior due to its resistance to wear, tear, and environmental degradation, ensuring long-lasting performance in garments. Bamboo fiber, while sustainable and biodegradable, offers moderate durability and mechanical resilience, prone to faster wear under high-stress conditions compared to graphene fiber.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Graphene fiber offers superior breathability and moisture management due to its enhanced thermal conductivity and antimicrobial properties, which help regulate body temperature and reduce odor. Bamboo fiber naturally excels in moisture-wicking and breathability through its porous structure, providing a soft and comfortable feel. Compared to bamboo, graphene fiber delivers faster sweat evaporation and improved temperature control, making it ideal for high-performance athletic clothing.
Comfort and Skin Compatibility
Graphene fiber offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it exceptionally comfortable and ideal for sensitive skin due to its hypoallergenic nature and antimicrobial benefits. Bamboo fiber, known for its natural softness and excellent moisture absorption, provides a gentle touch and natural antibacterial qualities that enhance skin compatibility. Both fibers promote comfort, but graphene fiber excels in thermal regulation and durability, while bamboo fiber stands out for sustainable softness and eco-friendliness.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Graphene fiber offers exceptional durability and thermal regulation with minimal environmental footprint due to its efficient production process involving carbon atoms, whereas bamboo fiber is biodegradable and renewable but often requires chemically intensive treatments that can impact ecosystems. Bamboo cultivation demands less water and pesticides compared to conventional cotton, promoting soil health and reducing deforestation, while graphene manufacturing relies on advanced technologies with potential energy consumption concerns. Sustainable clothing choices should weigh the low biodegradability of graphene fiber against the ecological benefits and processing challenges associated with bamboo fiber.
Cost and Market Availability
Graphene fiber remains significantly more expensive than bamboo fiber due to its complex manufacturing processes and limited large-scale production facilities. Bamboo fiber is widely available in the market, benefiting from established supply chains and more affordable raw material costs, making it a cost-effective choice for clothing. The cost difference and accessibility strongly influence consumer adoption, with bamboo fiber dominating budget-conscious segments while graphene fiber targets niche, high-performance apparel markets.
Performance in Athletic and Everyday Wear
Graphene fiber offers superior thermal conductivity and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing temperature regulation and breathability in athletic and everyday wear. Bamboo fiber provides natural antibacterial qualities and softness, promoting comfort and odor resistance for prolonged use. Graphene's durability and strength outperform bamboo, making it ideal for high-performance athletic clothing demanding resilience and flexibility.
Future Prospects in Textile Innovation
Graphene fiber offers exceptional strength, conductivity, and flexibility, positioning it as a groundbreaking material for smart textiles and wearable technology in the future of clothing. Bamboo fiber's natural sustainability, biodegradability, and antimicrobial properties make it a leading candidate for eco-friendly and comfortable apparel. Innovations combining graphene's advanced performance with bamboo's environmental benefits highlight a promising frontier for sustainable, high-performance textiles.
Infographic: Graphene fiber vs Bamboo fiber for Clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com