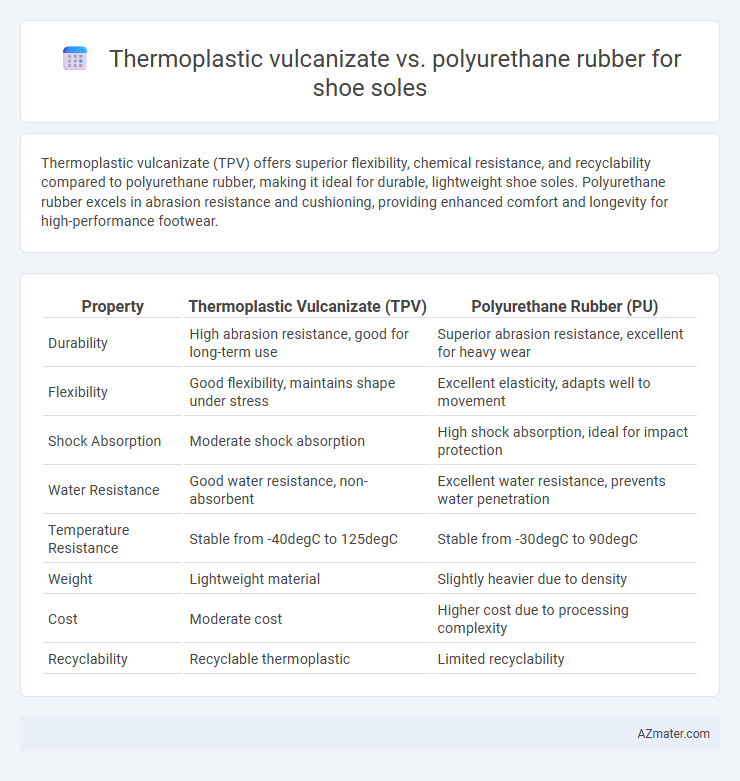
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and recyclability compared to polyurethane rubber, making it ideal for durable, lightweight shoe soles. Polyurethane rubber excels in abrasion resistance and cushioning, providing enhanced comfort and longevity for high-performance footwear.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV) | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High abrasion resistance, good for long-term use | Superior abrasion resistance, excellent for heavy wear |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility, maintains shape under stress | Excellent elasticity, adapts well to movement |
| Shock Absorption | Moderate shock absorption | High shock absorption, ideal for impact protection |
| Water Resistance | Good water resistance, non-absorbent | Excellent water resistance, prevents water penetration |
| Temperature Resistance | Stable from -40degC to 125degC | Stable from -30degC to 90degC |
| Weight | Lightweight material | Slightly heavier due to density |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost due to processing complexity |
| Recyclability | Recyclable thermoplastic | Limited recyclability |
Introduction to Thermoplastic Vulcanizate and Polyurethane Rubber
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) is a dynamic elastomer combining the processing advantages of thermoplastics with the elastic properties of vulcanized rubber, making it ideal for durable and flexible shoe soles. Polyurethane rubber offers excellent abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and superior cushioning, enhancing comfort and longevity in footwear applications. Both materials are widely used in shoe sole manufacturing, with TPV providing recyclability and ease of molding while polyurethane rubber ensures resilience and wear performance.
Composition and Material Properties
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) consists of a dynamically vulcanized blend of rubber and thermoplastic polymers, offering excellent elasticity, chemical resistance, and recyclability, which are vital for durable shoe soles. Polyurethane rubber is a versatile elastomer known for its high abrasion resistance, flexibility, and superior cushioning, making it ideal for impact absorption in footwear. TPV's composition provides better thermal stability and processing ease, whereas polyurethane excels in wear resistance and load-bearing capacity.
Manufacturing Processes: TPV vs Polyurethane Rubber
Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPV) are produced through dynamic vulcanization, combining thermoplastic polymers with crosslinked rubber particles, allowing for injection molding and efficient recycling during shoe sole manufacturing. Polyurethane rubber, typically formed via liquid casting or reaction injection molding (RIM), relies on chemical curing to create durable, abrasion-resistant soles with customizable hardness and flexibility. TPV manufacturing offers faster cycle times and easier reprocessing, while polyurethane rubber demands precise processing conditions to achieve optimal performance characteristics.
Durability and Wear Resistance Comparison
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers excellent durability and superior wear resistance, making it ideal for shoe soles subjected to high abrasion and repeated flexing. Polyurethane rubber provides outstanding wear resistance with enhanced cushioning and resilience but may show faster degradation under extreme environmental conditions. TPV's balanced hardness and elasticity result in longer-lasting soles compared to polyurethane, which excels in energy absorption but can compromise longevity in heavy-use scenarios.
Flexibility and Comfort in Shoe Soles
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior flexibility and cushioning in shoe soles, adapting well to dynamic foot movements and providing enhanced comfort during extended wear. Polyurethane rubber excels in durability and abrasion resistance but tends to be stiffer, which can reduce overall flexibility and comfort levels for all-day use. Selecting TPV enhances shock absorption and pliability, making it ideal for casual and athletic footwear focused on flexibility and ergonomic comfort.
Slip Resistance and Traction Performance
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior slip resistance and traction compared to polyurethane rubber due to its enhanced elasticity and rebound properties, which maintain grip on wet and oily surfaces. TPV's microcellular structure provides consistent contact with the ground, improving overall safety in slippery conditions, whereas polyurethane rubber tends to harden over time, reducing traction efficiency. Shoe soles made from TPV are ideal for environments requiring high slip resistance and durability under dynamic movement.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers improved recyclability compared to polyurethane rubber, as TPV can be remelted and reshaped without significant property degradation, reducing landfill waste. Polyurethane rubber, while durable and providing excellent wear resistance, is typically more challenging to recycle and often ends up in incineration or landfill, contributing to environmental pollution. TPV's production generally involves fewer hazardous chemicals and lower energy consumption, enhancing its sustainability profile for shoe sole manufacturing.
Cost Efficiency for Footwear Production
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior cost efficiency for footwear production due to its recyclability and faster molding cycle times compared to polyurethane rubber, which requires longer curing processes and generates more waste. TPV's durability and flexibility reduce material usage and lower overall production expenses, making it a preferred choice for large-scale shoe sole manufacturing. Polyurethane soles, while offering excellent abrasion resistance, typically incur higher raw material and processing costs, impacting the cost-effectiveness of mass production.
Applications in the Footwear Industry
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) and polyurethane rubber each offer distinct advantages for shoe sole applications in the footwear industry, with TPV providing excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and recyclability ideal for casual and athletic shoes requiring durability and comfort. Polyurethane rubber excels in abrasion resistance, elasticity, and cushioning, making it preferred for high-performance athletic footwear and work boots that demand superior shock absorption and wear resistance. Both materials support diverse footwear designs but are selected based on specific performance needs such as longevity, grip, and environmental conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Shoe Soles
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and easier recyclability compared to polyurethane rubber, making it ideal for environmentally-conscious and versatile shoe sole applications. Polyurethane rubber excels in abrasion resistance, cushioning, and durability, suitable for high-performance footwear demanding long-lasting comfort and wear. Selecting the right material depends on balancing factors such as flexibility, durability, environmental impact, and specific use case requirements to optimize shoe sole performance.
Infographic: Thermoplastic vulcanizate vs Polyurethane rubber for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com