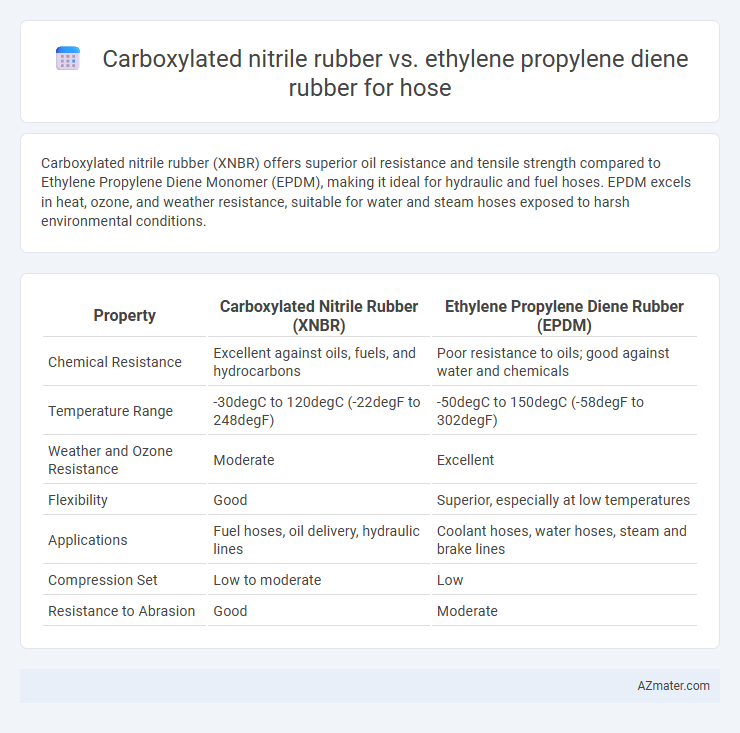
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance and tensile strength compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM), making it ideal for hydraulic and fuel hoses. EPDM excels in heat, ozone, and weather resistance, suitable for water and steam hoses exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons | Poor resistance to oils; good against water and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 120degC (-22degF to 248degF) | -50degC to 150degC (-58degF to 302degF) |
| Weather and Ozone Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Flexibility | Good | Superior, especially at low temperatures |
| Applications | Fuel hoses, oil delivery, hydraulic lines | Coolant hoses, water hoses, steam and brake lines |
| Compression Set | Low to moderate | Low |
| Resistance to Abrasion | Good | Moderate |
Introduction to Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber and EPDM
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its enhanced oil resistance, improved mechanical properties, and superior abrasion resistance compared to standard nitrile rubber, making it suitable for demanding hose applications exposed to fuels and oils. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, heat, and water, with outstanding flexibility at low temperatures, which makes it ideal for hoses used in outdoor and automotive environments. Both materials serve distinct performance needs in hose manufacturing, with XNBR preferred for hydrocarbon exposure and EPDM favored for environmental durability and thermal stability.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) features polar carboxyl groups attached to nitrile butadiene rubber chains, enhancing hydrogen bonding and chemical resistance, which improves abrasion durability in hoses. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) consists of saturated ethylene-propylene copolymer chains with diene monomers, providing excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering but lower solvent resistance compared to XNBR. The presence of polar carboxyl groups in XNBR results in superior mechanical strength and fuel resistance, whereas EPDM excels in environmental aging stability for hose applications.
Key Physical Properties
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior oil resistance, tensile strength up to 25 MPa, and excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for high-performance hose applications in harsh environments. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers outstanding resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering with tensile strength typically around 15 MPa, suitable for water and steam hoses. XNBR's higher hardness (60-75 Shore A) contrasts with EPDM's softer profile (50-70 Shore A), influencing flexibility and durability based on specific hose requirements.
Resistance to Oils and Fuels
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior resistance to oils and fuels compared to ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) due to its polar nature and enhanced cross-linking density, which minimizes swelling and degradation in hydrocarbon environments. EPDM generally has poor compatibility with oils and fuels, leading to rapid deterioration and loss of mechanical properties when exposed to petroleum-based fluids. Consequently, XNBR is the preferred elastomer for hoses requiring long-term durability and chemical resistance in oil and fuel applications.
Weather and Ozone Resistance
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior weather and ozone resistance compared to ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM), making it more suitable for hoses exposed to harsh outdoor conditions. XNBR's enhanced resistance to ozone prevents crack formation and degradation, extending hose durability in environments with high ozone levels. EPDM also offers excellent weather resistance, particularly against UV radiation and moisture, but it is generally less effective than XNBR in resisting ozone-induced damage in long-term applications.
Temperature Performance Range
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits a temperature performance range from approximately -40degC to 120degC, making it suitable for applications requiring resistance to oils, fuels, and abrasion at moderate temperatures. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber withstands a broader temperature range, typically from -50degC up to 150degC, offering superior heat, ozone, and weather resistance, ideal for high-temperature hose applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Selecting between XNBR and EPDM for hose manufacturing depends on the specific temperature requirements and chemical exposure, with EPDM favored for higher thermal stability and XNBR optimal for hydrocarbon resistance.
Abrasion and Wear Characteristics
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior abrasion resistance and wear characteristics compared to ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber, making it highly suitable for high-friction hose applications. XNBR's tightly cross-linked molecular structure enhances its durability against mechanical stress and abrasive environments, while EPDM, though excellent in weather and chemical resistance, shows lower performance under continuous abrasive conditions. Consequently, XNBR hoses provide longer service life and reduced maintenance in industrial settings requiring high wear resistance.
Typical Hose Applications
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance and tensile strength, making it ideal for hoses used in automotive fuel lines, hydraulic systems, and oil transfer applications. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in heat, ozone, and weather resistance, commonly applied in water hoses, steam hoses, and industrial chemical transport where environmental durability is crucial. Selecting between XNBR and EPDM depends on the hose's exposure to oils, chemicals, temperature ranges, and environmental conditions.
Cost and Availability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) generally offers higher abrasion resistance and chemical resistance but comes at a higher cost compared to ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM). EPDM is more widely available and cost-effective, making it a preferred choice for hoses requiring excellent weather, ozone, and heat resistance in less demanding chemical environments. Cost considerations often drive the selection, with EPDM hoses offering a more economical solution for large-volume applications.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Hose Solutions
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for hoses in automotive and industrial fluid transfer applications. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in heat, ozone, and weather resistance, suitable for hoses exposed to harsh environmental conditions or steam. Selecting the right rubber depends on the hose's exposure to chemicals, temperature ranges, and mechanical stress requirements to ensure optimal durability and performance.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com