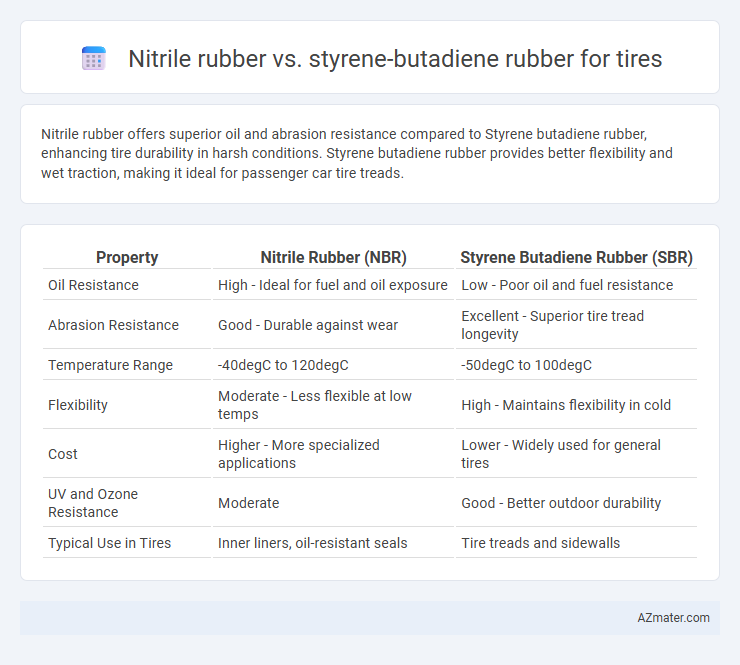
Nitrile rubber offers superior oil and abrasion resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber, enhancing tire durability in harsh conditions. Styrene butadiene rubber provides better flexibility and wet traction, making it ideal for passenger car tire treads.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Resistance | High - Ideal for fuel and oil exposure | Low - Poor oil and fuel resistance |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good - Durable against wear | Excellent - Superior tire tread longevity |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -50degC to 100degC |
| Flexibility | Moderate - Less flexible at low temps | High - Maintains flexibility in cold |
| Cost | Higher - More specialized applications | Lower - Widely used for general tires |
| UV and Ozone Resistance | Moderate | Good - Better outdoor durability |
| Typical Use in Tires | Inner liners, oil-resistant seals | Tire treads and sidewalls |
Introduction to Nitrile Rubber and Styrene Butadiene Rubber
Nitrile rubber (NBR) and styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) are widely used synthetic elastomers in tire manufacturing, valued for their distinct chemical compositions and performance characteristics. Nitrile rubber is a copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, notable for its excellent oil, fuel, and heat resistance, making it ideal for tires exposed to harsh environments. Styrene-butadiene rubber, a copolymer of styrene and butadiene, offers superior abrasion resistance and aging stability, resulting in durable and cost-effective tire applications.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Nitrile rubber (NBR) consists of copolymers of acrylonitrile and butadiene, offering high resistance to oils and fuels due to its polar nitrile groups, while Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) is a copolymer of styrene and butadiene with a nonpolar structure that provides superior abrasion and aging resistance. NBR's nitrile content typically ranges from 18% to 50%, influencing its mechanical and chemical properties, whereas SBR's styrene content varies between 15% and 25%, balancing flexibility and strength. Structurally, NBR has a heterogeneous distribution of nitrile groups leading to increased polarity and less crystallinity compared to the more uniform, semi-crystalline structure of SBR, affecting their performance in tire applications.
Physical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Durability
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior oil resistance and tensile strength compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), making it highly durable under harsh conditions. SBR exhibits better abrasion resistance and flexibility, providing enhanced grip and elasticity for tire performance. Both materials balance strength and durability, but NBR excels in chemical resistance while SBR is preferred for wear and weather resistance in tires.
Resistance to Oils, Chemicals, and Abrasion
Nitrile rubber exhibits superior resistance to oils, fuels, and many chemicals, making it ideal for tire applications where exposure to hydrocarbon-based substances is common. Styrene butadiene rubber offers good abrasion resistance and aging stability but falls short compared to nitrile rubber in chemical resistance, particularly against oils and solvents. For tire durability in harsh chemical environments, nitrile rubber provides enhanced protection and longer service life.
Performance in Different Temperature Ranges
Nitrile rubber (NBR) exhibits superior resistance to abrasion and oil at elevated temperatures, maintaining elasticity from -40degC to 120degC, making it ideal for high-heat tire applications. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) performs well in moderate temperatures between -30degC and 100degC, offering excellent wear resistance and wet traction in standard driving conditions. NBR's enhanced thermal stability and low-temperature flexibility give it an edge for tires requiring durability across a wider temperature spectrum.
Tread Life and Wear Performance in Tires
Nitrile rubber exhibits superior tread life and wear performance in tires due to its enhanced resistance to abrasion and oil degradation compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR). Tires utilizing nitrile rubber compounds demonstrate improved durability in harsh road conditions, resulting in longer tread longevity and reduced maintenance costs. SBR, while cost-effective and offering good traction, tends to wear faster under heavy stress and high-temperature environments, limiting its effectiveness in high-performance tire applications.
Rolling Resistance and Fuel Efficiency
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior oil and heat resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), but SBR provides better abrasion resistance and flexibility, which contributes to lower rolling resistance in tire applications. Lower rolling resistance in SBR tires directly improves fuel efficiency by reducing the energy required to maintain tire rotation. Consequently, tires formulated with SBR generally deliver enhanced fuel economy due to optimized rolling resistance characteristics.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers higher oil resistance and durability but comes at a higher cost compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), which is more affordable and widely available for tire manufacturing. SBR dominates the market due to its cost-effectiveness and ample supply, making it the preferred choice for most passenger and commercial vehicle tires. The balance between performance and price ensures SBR maintains a competitive edge, while NBR is reserved for specialized tire applications requiring enhanced chemical resistance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nitrile rubber (NBR) and styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability, with NBR offering better resistance to oils and chemicals, which can extend tire life and reduce waste. SBR, being derived primarily from petrochemical sources, has a higher carbon footprint, but ongoing developments in bio-based SBR aim to improve its sustainability profile. Sustainable tire production increasingly favors materials that balance performance with lower ecological impact, making advancements in both NBR and SBR critical for future eco-friendly tire technologies.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Tire Applications
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, and abrasion, making it ideal for tire applications requiring enhanced durability and chemical resistance. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability, often used in passenger car tires for balanced performance and cost efficiency. Selecting between NBR and SBR depends on specific tire requirements such as exposure to chemicals, abrasion levels, and desired lifespan.
Infographic: Nitrile rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com