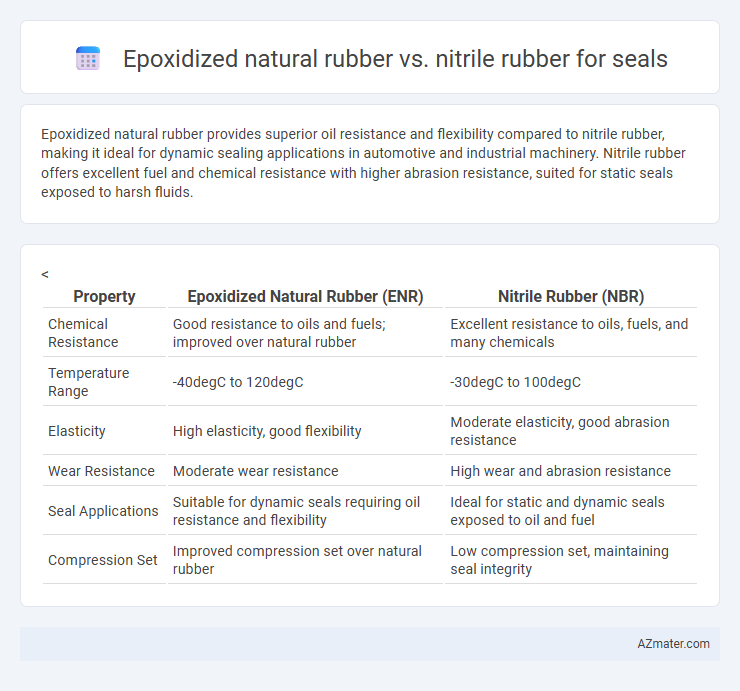
Epoxidized natural rubber provides superior oil resistance and flexibility compared to nitrile rubber, making it ideal for dynamic sealing applications in automotive and industrial machinery. Nitrile rubber offers excellent fuel and chemical resistance with higher abrasion resistance, suited for static seals exposed to harsh fluids.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and fuels; improved over natural rubber | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and many chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -30degC to 100degC |
| Elasticity | High elasticity, good flexibility | Moderate elasticity, good abrasion resistance |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate wear resistance | High wear and abrasion resistance |
| Seal Applications | Suitable for dynamic seals requiring oil resistance and flexibility | Ideal for static and dynamic seals exposed to oil and fuel |
| Compression Set | Improved compression set over natural rubber | Low compression set, maintaining seal integrity |
Introduction to Seal Materials
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced oil resistance and flexibility due to its modified polar epoxy groups, making it suitable for sealing applications exposed to moderate heat and chemicals. Nitrile rubber (NBR) is widely recognized for its superior resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and lubricants, providing durability and strong mechanical properties in seals used in automotive and industrial environments. Selecting between ENR and NBR seal materials depends on specific operating conditions such as temperature ranges, chemical exposure, and required elasticity for optimal performance and longevity.
Overview of Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR)
Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) is a chemically modified form of natural rubber with enhanced oil resistance, making it highly suitable for sealing applications exposed to oils and fuels. The epoxidation process introduces oxygen-containing epoxide groups into the polymer backbone, improving its mechanical strength and gas barrier properties compared to conventional natural rubber. ENR offers superior elasticity, resilience, and environmental resistance, positioning it as an optimal material in seals where durability and chemical resistance are critical.
Overview of Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a synthetic elastomer renowned for its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and various chemicals, making it ideal for sealing applications in harsh environments. Its superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and ability to withstand a wide temperature range from -40degC to 120degC enhance its performance in dynamic seals and gaskets. Compared to epoxidized natural rubber, NBR offers better impermeability to gases and greater durability in petroleum-based fluids, which is critical for automotive and industrial sealing components.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits excellent resistance to oxygen, ozone, and moderate chemicals, making it suitable for applications exposed to oxidative environments, while its polar epoxy groups enhance compatibility with polar substances. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, hydrocarbons, and many solvents due to its nitrile groups, which provide enhanced barrier properties against petroleum-based fluids. For seals, NBR is generally preferred in fuel and oil exposure scenarios, whereas ENR is advantageous in environments requiring improved oxidative and weathering resistance combined with moderate chemical resistance.
Temperature Tolerance: ENR vs NBR
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior temperature tolerance compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), functioning effectively in a range from -40degC up to 130degC, making it suitable for applications exposed to elevated temperatures. In contrast, nitrile rubber typically operates within -30degC to 100degC, which limits its use in high-temperature seal environments. ENR's enhanced thermal stability and resistance to oxidation provide longer-lasting performance in seals subjected to fluctuating or high thermal conditions.
Mechanical and Physical Properties
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior elasticity, resilience, and excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and aging, making it ideal for dynamic seal applications requiring flexibility and durability. Nitrile rubber (NBR) exhibits outstanding resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, with high tensile strength and abrasion resistance, suitable for seals in harsh chemical environments. While ENR provides better mechanical flexibility and environmental resistance, NBR outperforms in oil resistance and physical robustness under aggressive conditions.
Oil and Fuel Compatibility
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced oil and fuel resistance compared to traditional natural rubber due to the introduction of epoxy groups, which improve its polarity and chemical stability. Nitrile rubber (NBR) is highly regarded for excellent oil and fuel compatibility, especially with petroleum-based fluids, making it a preferred choice for sealing applications in automotive and industrial environments. While ENR provides better biodegradability and moderate fuel resistance, NBR outperforms in long-term exposure to hydrocarbons, ensuring superior durability in seals exposed to aggressive oils and fuels.
Aging and Environmental Performance
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior aging resistance compared to nitrile rubber, maintaining flexibility and tensile strength under prolonged exposure to heat, oxygen, and ozone due to its enhanced polarity and crosslinking. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in chemical and oil resistance but tends to degrade faster when exposed to UV light and ozone, leading to surface cracking and loss of mechanical properties over time. ENR demonstrates better environmental performance through higher biodegradability and renewable resource content, making it a more sustainable choice for seals in environmentally sensitive applications.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers moderate cost efficiency due to its partially bio-based origin and improved oil resistance compared to standard natural rubber, making it a cost-effective option for sealing applications in industries with moderate chemical exposure. Nitrile rubber (NBR) generally provides superior cost efficiency for heavy-duty seals requiring excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, and is widely available from numerous global suppliers, ensuring competitive pricing and consistent supply. Availability favors nitrile rubber, as it is produced on a larger industrial scale, while epoxidized natural rubber remains less common and can be more expensive depending on regional production capacity and demand.
Choosing the Best Material for Seal Applications
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers excellent resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals, making it ideal for seals in dynamic environments requiring elasticity and durability. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in oil resistance, fuel exposure, and wear, providing superior performance for seals in industrial and automotive applications where chemical exposure is frequent. Selecting the best material depends on the specific sealing environment: ENR suits applications demanding flexibility and thermal resistance, while NBR is preferable for oil-heavy conditions and abrasive wear.
Infographic: Epoxidized natural rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com