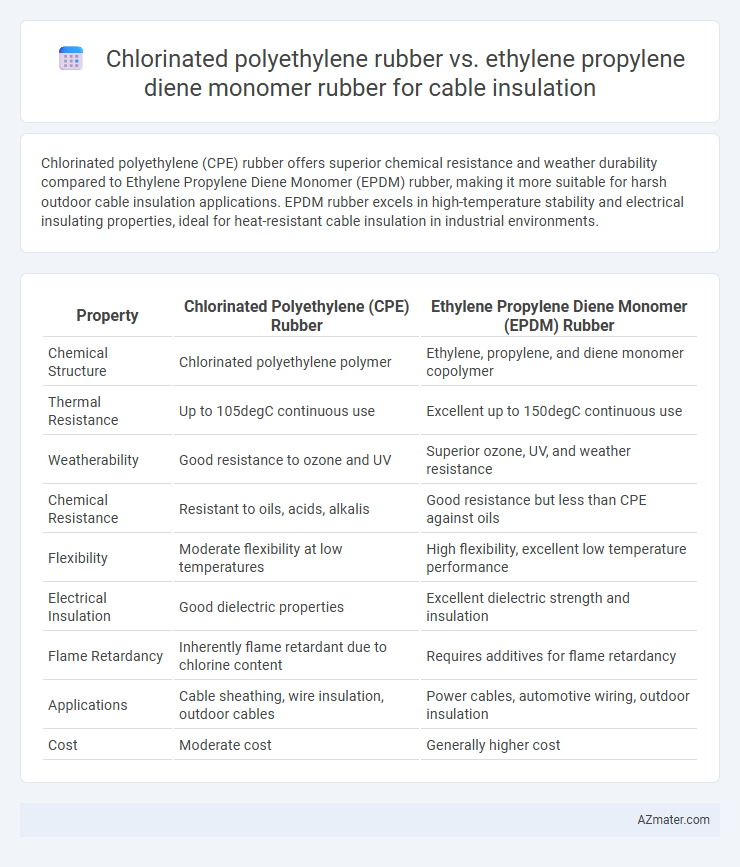
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) rubber offers superior chemical resistance and weather durability compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, making it more suitable for harsh outdoor cable insulation applications. EPDM rubber excels in high-temperature stability and electrical insulating properties, ideal for heat-resistant cable insulation in industrial environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chlorinated Polyethylene (CPE) Rubber | Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Chlorinated polyethylene polymer | Ethylene, propylene, and diene monomer copolymer |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 105degC continuous use | Excellent up to 150degC continuous use |
| Weatherability | Good resistance to ozone and UV | Superior ozone, UV, and weather resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils, acids, alkalis | Good resistance but less than CPE against oils |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility at low temperatures | High flexibility, excellent low temperature performance |
| Electrical Insulation | Good dielectric properties | Excellent dielectric strength and insulation |
| Flame Retardancy | Inherently flame retardant due to chlorine content | Requires additives for flame retardancy |
| Applications | Cable sheathing, wire insulation, outdoor cables | Power cables, automotive wiring, outdoor insulation |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Generally higher cost |
Introduction to Cable Insulation Materials
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) rubber and ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber are widely used materials for cable insulation due to their excellent chemical resistance and electrical properties. CPE offers superior resistance to oils, flames, and weathering, making it ideal for harsh environmental conditions, while EPDM provides outstanding thermal stability, ozone resistance, and flexibility across a broad temperature range. The choice between CPE and EPDM depends on specific operational requirements such as exposure to chemicals, temperature variations, and mechanical stress in cable applications.
Overview of Chlorinated Polyethylene (CPE) Rubber
Chlorinated Polyethylene (CPE) rubber is a versatile elastomer known for its excellent flame resistance, weatherability, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for cable insulation applications requiring durability and safety. CPE exhibits superior resistance to oils, acids, and alkalis, enhancing the longevity and performance of cables in harsh environments. Compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, CPE offers better resistance to fire and oil, although EPDM excels in heat and ozone resistance.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Rubber
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber is widely used for cable insulation due to its excellent weather, ozone, and heat resistance, ensuring long-term durability in harsh environments. Its superior electrical insulation properties and flexibility make it ideal for outdoor and high-voltage cable applications. Compared to Chlorinated Polyethylene (CPE) rubber, EPDM offers enhanced resistance to UV radiation and aging, providing more reliable performance in diverse conditions.
Key Physical and Chemical Properties: CPE vs EPDM
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) rubber offers excellent chemical resistance, particularly against oils, acids, and alkalis, while maintaining good flexibility and weatherability, making it suitable for harsh cable insulation environments. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber provides superior heat resistance, excellent electrical insulation properties, and strong resistance to ozone and UV exposure, ideal for outdoor and high-temperature cable applications. Both materials exhibit good mechanical strength, but EPDM generally outperforms CPE in thermal stability, whereas CPE excels in chemical resilience and flame retardancy for cable insulation.
Electrical Insulation Performance Comparison
Chlorinated polyethylene rubber (CPE) exhibits excellent electrical insulation properties, including high dielectric strength and resistance to electrical tracking, making it suitable for harsh environmental conditions in cable insulation. Ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber (EPDM) offers superior dielectric elasticity with stable permittivity and minimal dielectric loss across a broad temperature range, enhancing cable performance in fluctuating thermal environments. EPDM generally provides better long-term electrical insulation reliability under thermal and UV exposure, whereas CPE excels in chemical resistance and flame retardancy, influencing the selection based on specific application requirements.
Heat and Weather Resistance in CPE and EPDM
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) rubber offers superior heat resistance, maintaining stability in temperatures up to 125degC, while exhibiting excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and UV exposure, making it ideal for outdoor cable insulation. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in weather resistance, providing outstanding durability against ozone, UV radiation, and moisture, but its continuous operating temperature limit is generally lower, around 90degC to 120degC. Both materials provide robust insulation performance; however, CPE's enhanced thermal tolerance suits applications requiring higher heat endurance, whereas EPDM is favored for environments with severe weather exposure and flexibility demands.
Flame Retardancy and Safety Considerations
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) rubber offers excellent flame retardancy due to its high chlorine content, which slows combustion and reduces smoke generation, making it a safer choice for cable insulation in fire-prone environments. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber provides superior electrical insulation and weather resistance but generally requires additional flame-retardant additives to achieve comparable fire safety performance. In safety-critical cable applications, CPE's inherent flame retardant properties enhance compliance with strict fire safety standards, whereas EPDM's use often involves integrated fire-retardant systems to meet similar requirements.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) rubber typically offers a lower cost compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, making it a budget-friendly option for cable insulation. CPE is widely available in the market due to its extensive use in various industrial applications, ensuring consistent supply and easier procurement. EPDM, while slightly more expensive, may have limited availability in some regions, as it is specialized for high-performance insulation needs with superior weather and ozone resistance.
Typical Applications in Cable Insulation
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) rubber is widely used for cable insulation in applications requiring excellent weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial power cables. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in high-voltage cable insulation due to its superior electrical properties and resistance to heat, ozone, and aging. Both materials provide durability in harsh environments, but EPDM is preferred for high-performance electrical insulation, while CPE is favored for mechanical protection and environmental resistance.
Conclusion: Choosing Between CPE and EPDM Rubber
Chlorinated polyethylene rubber (CPE) offers excellent chemical resistance, flame retardancy, and weatherability, making it suitable for harsh environments and outdoor cable insulation. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber provides superior electrical insulation, ozone resistance, and flexibility at low temperatures, ideal for high-performance cables requiring durable thermal and weather resistance. Selecting between CPE and EPDM depends on the specific environmental conditions, electrical requirements, and mechanical stresses of the cable application.
Infographic: Chlorinated polyethylene rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber for Cable insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com