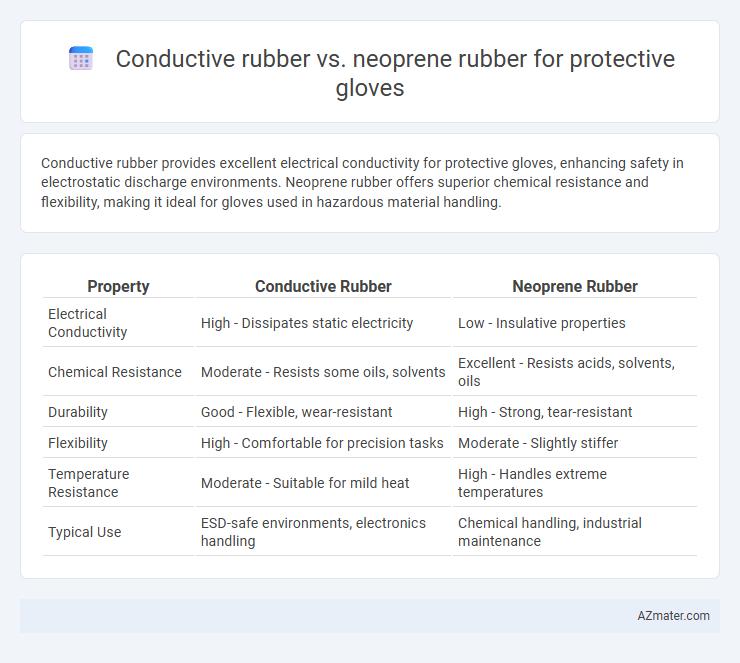
Conductive rubber provides excellent electrical conductivity for protective gloves, enhancing safety in electrostatic discharge environments. Neoprene rubber offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for gloves used in hazardous material handling.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Conductive Rubber | Neoprene Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High - Dissipates static electricity | Low - Insulative properties |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate - Resists some oils, solvents | Excellent - Resists acids, solvents, oils |
| Durability | Good - Flexible, wear-resistant | High - Strong, tear-resistant |
| Flexibility | High - Comfortable for precision tasks | Moderate - Slightly stiffer |
| Temperature Resistance | Moderate - Suitable for mild heat | High - Handles extreme temperatures |
| Typical Use | ESD-safe environments, electronics handling | Chemical handling, industrial maintenance |
Introduction to Protective Glove Materials
Conductive rubber and neoprene rubber are essential materials used in protective gloves, each offering unique properties that enhance safety and functionality. Conductive rubber provides superior electrical conductivity, making it ideal for applications requiring static discharge protection and electronics handling. Neoprene rubber excels in chemical resistance and flexibility, offering robust protection against oils, acids, and environmental hazards in industrial and medical glove applications.
What is Conductive Rubber?
Conductive rubber is a type of elastomer embedded with conductive fillers like carbon or metal particles, enabling it to dissipate static electricity effectively in protective glove applications. It offers enhanced electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection compared to neoprene rubber, which is primarily valued for its chemical resistance and flexibility but lacks intrinsic conductivity. Using conductive rubber in gloves ensures safety in ESD-sensitive environments by preventing static buildup, crucial for handling electronic components and volatile substances.
What is Neoprene Rubber?
Neoprene rubber is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and durability, making it ideal for protective gloves in various industrial applications. It provides outstanding protection against oils, acids, and extreme temperatures, ensuring safety and comfort in harsh environments. Unlike conductive rubber, neoprene offers superior insulation properties, preventing electrical conductivity while maintaining high mechanical strength.
Key Differences: Conductive vs Neoprene Rubber
Conductive rubber in protective gloves offers enhanced electrical conductivity suitable for preventing static build-up and enabling precise electronic handling, while neoprene rubber excels in chemical resistance, flexibility, and durability against harsh environments. Conductive rubber typically incorporates carbon or metal fillers to achieve conductivity, whereas neoprene relies on its synthetic polymer structure for insulation and resistance to oils, acids, and weathering. Choosing between conductive and neoprene rubber depends on the specific protection requirements--electrical conductivity versus chemical and environmental resistance--for optimal glove performance.
Electrical Properties and Applications
Conductive rubber offers superior electrical conductivity due to embedded conductive materials like carbon or metal particles, making it ideal for applications requiring static dissipation and electrical safety gloves. Neoprene rubber provides excellent insulation, chemical resistance, and durability, suitable for gloves used in hazardous environments where electrical conductivity is not desired. Choosing between conductive rubber and neoprene depends on the specific requirement for either electrical conduction or insulation in protective glove applications.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Conductive rubber exhibits moderate chemical resistance, performing well against oils, solvents, and some acids, making it suitable for environments requiring static dissipation along with protection. Neoprene rubber offers superior chemical resistance, especially against a wide range of acids, alkalis, oils, and solvents, providing enhanced durability and protection in harsh chemical handling applications. When selecting protective gloves, neoprene's broader chemical resistance spectrum generally makes it a more reliable choice for comprehensive chemical exposure scenarios.
Mechanical Durability & Flexibility
Conductive rubber offers superior mechanical durability with excellent resistance to abrasion and tearing, making it ideal for protective gloves used in demanding environments. Neoprene rubber exhibits enhanced flexibility and elasticity, providing comfortable fit and dexterity crucial for precision tasks. Both materials balance protection and comfort, but conductive rubber is preferred where durability and long-term wear resistance are critical.
Comfort and Ergonomics for Glove Wearers
Conductive rubber offers superior flexibility and breathability, enhancing comfort and reducing hand fatigue during prolonged glove use compared to neoprene rubber. Neoprene rubber provides excellent chemical resistance but tends to be stiffer and less breathable, potentially compromising ergonomic fit and wearer dexterity. Prioritizing conductive rubber in protective gloves supports better tactile sensitivity and ergonomic performance, crucial for tasks requiring fine motor skills and extended wear.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Conductive rubber gloves generally have higher costs due to specialized materials and manufacturing processes compared to neoprene rubber gloves, which are more widely produced and readily available. Neoprene gloves offer a cost-effective option with extensive market availability, making them suitable for general protective applications. Conductive rubber gloves are typically reserved for niche uses requiring static dissipation, limiting their mass-market accessibility and increasing overall expense.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Protective Gloves
Conductive rubber offers excellent electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection, making it ideal for protective gloves used in electronics and sensitive equipment handling. Neoprene rubber provides superior chemical resistance, durability, and flexibility, suited for gloves in industrial, chemical, and medical environments. Choosing the right rubber depends on the specific application requirements, including conductivity needs, chemical exposure, and mechanical protection.
Infographic: Conductive rubber vs Neoprene rubber for Protective glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com