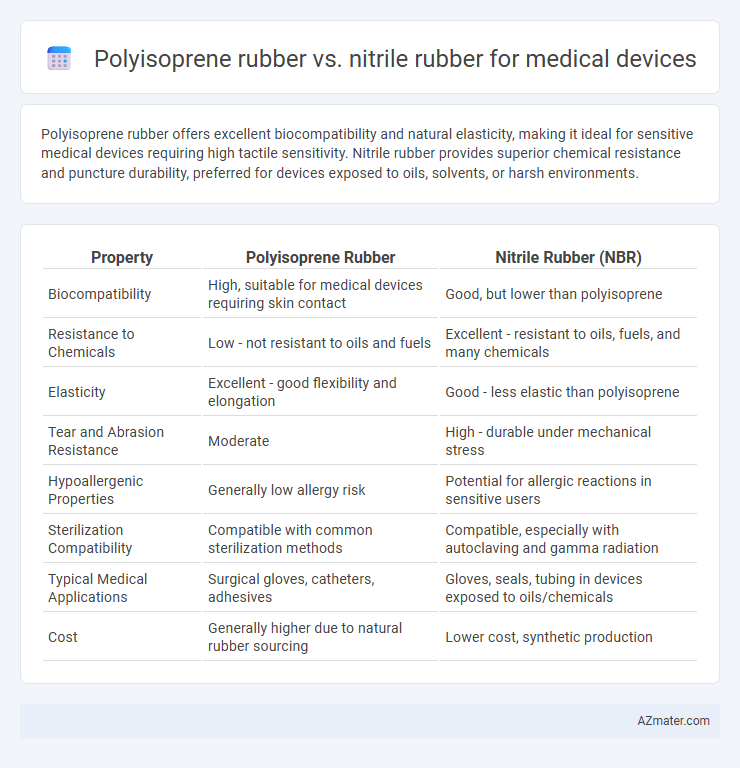
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent biocompatibility and natural elasticity, making it ideal for sensitive medical devices requiring high tactile sensitivity. Nitrile rubber provides superior chemical resistance and puncture durability, preferred for devices exposed to oils, solvents, or harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyisoprene Rubber | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Biocompatibility | High, suitable for medical devices requiring skin contact | Good, but lower than polyisoprene |
| Resistance to Chemicals | Low - not resistant to oils and fuels | Excellent - resistant to oils, fuels, and many chemicals |
| Elasticity | Excellent - good flexibility and elongation | Good - less elastic than polyisoprene |
| Tear and Abrasion Resistance | Moderate | High - durable under mechanical stress |
| Hypoallergenic Properties | Generally low allergy risk | Potential for allergic reactions in sensitive users |
| Sterilization Compatibility | Compatible with common sterilization methods | Compatible, especially with autoclaving and gamma radiation |
| Typical Medical Applications | Surgical gloves, catheters, adhesives | Gloves, seals, tubing in devices exposed to oils/chemicals |
| Cost | Generally higher due to natural rubber sourcing | Lower cost, synthetic production |
Introduction to Polyisoprene and Nitrile Rubber
Polyisoprene rubber, a natural polymer derived from the latex of rubber trees, is renowned for its excellent elasticity, biocompatibility, and tactile sensitivity, making it ideal for medical devices requiring high dexterity such as gloves and tubing. Nitrile rubber, a synthetic copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, offers superior chemical resistance and puncture protection, which is essential for medical applications exposed to oils, greases, and various solvents. Both materials fulfill critical roles in medical device manufacturing, with polyisoprene providing natural flexibility and nitrile ensuring durability and chemical resilience.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polyisoprene rubber is a natural polymer composed of repeating isoprene units with a cis-1,4 configuration, giving it excellent elasticity and biocompatibility for medical devices. Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a synthetic copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, characterized by nitrile groups that enhance chemical resistance against oils and chemicals. The distinct chemical compositions influence their suitability: polyisoprene offers superior tactile sensitivity and comfort, while nitrile provides enhanced durability and protection against solvents in medical applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits superior elasticity and tear strength, making it ideal for medical devices requiring flexibility and durability. Nitrile rubber offers higher resistance to oils, chemicals, and punctures, providing enhanced protection in environments with exposure to bodily fluids or harsh substances. Both materials maintain adequate tensile strength, but nitrile's chemical resistance and polyisoprene's natural feel determine their specific applications in medical device manufacturing.
Biocompatibility in Medical Applications
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits excellent biocompatibility due to its natural origin, making it suitable for medical devices requiring high skin compatibility and low allergenic potential. Nitrile rubber offers superior chemical resistance and durability but may cause allergic reactions in sensitive patients due to residual accelerators and additives. Medical applications demanding hypoallergenic materials often favor polyisoprene, while nitrile is preferred for devices exposed to oils, solvents, or harsh chemicals.
Allergenicity and Patient Safety
Polyisoprene rubber offers superior biocompatibility and significantly lower allergenicity compared to nitrile rubber, making it the preferred material for latex-sensitive patients in medical devices. Nitrile rubber, while resistant to oils and chemicals, contains synthetic polymers that can occasionally trigger skin irritation but generally presents fewer allergenic risks than natural latex. Ensuring patient safety, polyisoprene's hypoallergenic properties reduce the incidence of type I latex allergies, critical for devices like gloves and catheters used in sensitive healthcare environments.
Performance in Sterilization Processes
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits excellent elasticity and biocompatibility but tends to degrade when exposed to high-energy sterilization methods like gamma radiation or ethylene oxide. Nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to sterilization processes, maintaining mechanical integrity and chemical stability under steam autoclaving and gamma irradiation. The choice between polyisoprene and nitrile rubber hinges on the specific sterilization requirements and compatibility with medical device applications.
Resistance to Chemicals and Fluids
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent tactile sensitivity and biocompatibility but has limited resistance to oils, fuels, and many solvents, making it less suitable for aggressive chemical exposure in medical devices. Nitrile rubber, known for its superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including hydrocarbons, acids, and alkalis, provides robust protection against blood, alcohol, and many disinfectants commonly encountered in medical environments. For medical devices requiring rigorous chemical and fluid resistance, nitrile rubber is the preferred material due to its durability and impermeability under harsh conditions.
Durability and Mechanical Strength
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and tensile strength, making it highly durable for medical devices requiring flexibility and repeated use. Nitrile rubber excels in resistance to oils, chemicals, and puncture, providing superior mechanical strength and durability in harsh environments. Choosing between polyisoprene and nitrile rubber depends on the specific mechanical demands and chemical exposure of the medical application.
Cost-effectiveness for Manufacturers
Polyisoprene rubber offers superior elasticity and biocompatibility, making it ideal for medical devices requiring high tactile sensitivity, but it tends to be more expensive due to complex manufacturing processes. Nitrile rubber provides excellent chemical resistance and durability at a lower cost, enhancing cost-effectiveness for manufacturers focused on budget-conscious production without compromising essential performance. Manufacturers often choose nitrile rubber for disposable medical gloves to balance affordability and protective quality while reserving polyisoprene for premium applications where sensitivity and skin-friendliness justify higher expenses.
Applications in Medical Device Components
Polyisoprene rubber is widely used in medical device components requiring high elasticity and biocompatibility, such as surgical gloves and catheters, due to its latex-like properties and excellent tactile sensitivity. Nitrile rubber is preferred for medical devices exposed to oils, solvents, and harsh chemicals, including gloves, seals, and tubing, because of its superior resistance to punctures and chemical degradation. Both materials meet critical industry standards like ASTM and ISO but are selected based on specific application needs related to durability, flexibility, and chemical resistance.
Infographic: Polyisoprene rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Medical device
 azmater.com
azmater.com