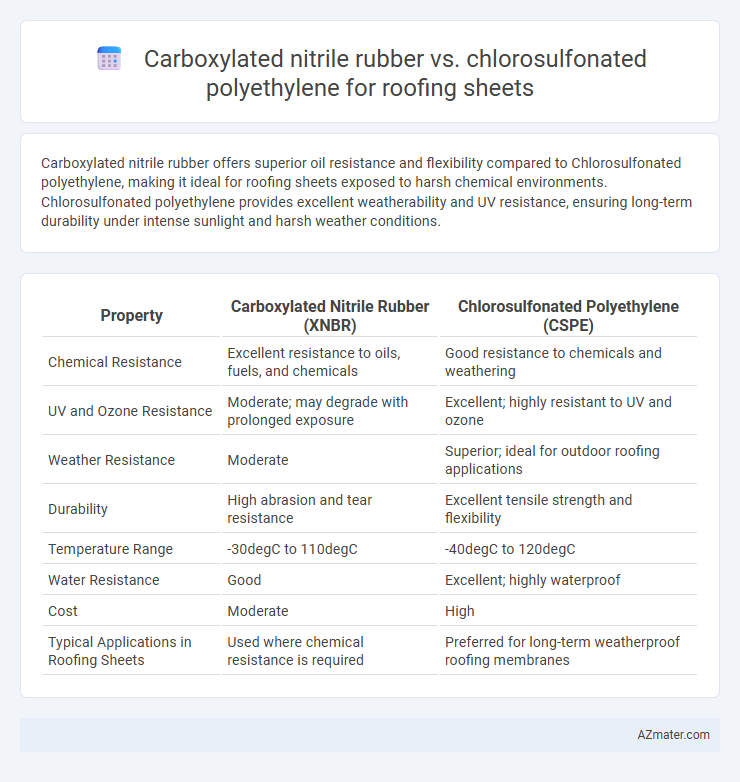
Carboxylated nitrile rubber offers superior oil resistance and flexibility compared to Chlorosulfonated polyethylene, making it ideal for roofing sheets exposed to harsh chemical environments. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene provides excellent weatherability and UV resistance, ensuring long-term durability under intense sunlight and harsh weather conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Good resistance to chemicals and weathering |
| UV and Ozone Resistance | Moderate; may degrade with prolonged exposure | Excellent; highly resistant to UV and ozone |
| Weather Resistance | Moderate | Superior; ideal for outdoor roofing applications |
| Durability | High abrasion and tear resistance | Excellent tensile strength and flexibility |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 110degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Water Resistance | Good | Excellent; highly waterproof |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Typical Applications in Roofing Sheets | Used where chemical resistance is required | Preferred for long-term weatherproof roofing membranes |
Introduction to Roofing Sheet Materials
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil and chemical resistance along with excellent tensile strength, making it durable for roofing sheet applications exposed to harsh environments. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) excels in UV resistance, weather durability, and flexibility, providing reliable waterproofing and long-term performance in roofing membranes. Both materials are widely used in roofing sheets, with XNBR preferred for industrial chemical exposure and CSPE favored for climate resilience and outdoor longevity.
Overview of Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR)
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) is a high-performance elastomer known for its superior abrasion resistance, excellent tensile strength, and enhanced oil and chemical resistance compared to conventional nitrile rubber. Its carboxyl groups improve adhesion properties and cross-linking density, resulting in increased durability and weather resistance, making it ideal for roofing sheet applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. XNBR outperforms chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) by providing better mechanical stability, higher elasticity at low temperatures, and improved resistance to ozone and UV degradation.
Overview of Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSM)
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) is a synthetic rubber known for its exceptional resistance to weathering, UV radiation, and chemical exposure, making it highly suitable for roofing sheets in harsh environments. Its chlorine and sulfonyl functional groups provide excellent durability, flexibility, and resistance to ozone and oxidation, outperforming many other elastomers including carboxylated nitrile rubber in outdoor applications. CSM roofing sheets offer robust waterproofing and long-term stability, ensuring extended service life and reduced maintenance costs in roofing systems.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE), making it more durable under mechanical stress in roofing sheets. CSPE excels in UV resistance and chemical stability, providing enhanced weathering performance and longer lifespan in harsh environmental conditions. Both materials demonstrate excellent waterproofing properties, but XNBR's higher resilience to oil and fuel exposure optimizes it for industrial roofing applications.
Chemical Resistance Differences
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior resistance to oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons due to its high nitrile content, making it ideal for roofing sheets exposed to petrochemical environments. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) demonstrates excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and UV radiation, with moderate chemical resistance but less effectiveness against petroleum-based substances. The choice between XNBR and CSPE for roofing sheets hinges on the specific chemical exposure, with XNBR favored for hydrocarbon resistance and CSPE preferred for long-term outdoor durability against oxidative agents.
Weathering and UV Resistance Performance
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior weathering and UV resistance compared to chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE), making it highly effective for roofing sheets exposed to harsh climates. XNBR's enhanced polar group structure provides excellent resistance against ozone, UV radiation, and thermal degradation, preventing cracking and material breakdown over time. In contrast, CSPE demonstrates moderate UV resistance but may require additional stabilizers to maintain long-term durability under prolonged sunlight exposure.
Durability and Lifespan in Roofing Applications
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and chemical exposure, resulting in enhanced durability and an extended lifespan for roofing sheets. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) offers excellent weathering resistance and flexibility but may experience degradation under prolonged UV exposure and chemical attack, potentially reducing its service life. In roofing applications, XNBR generally outperforms CSPE by maintaining structural integrity and performance over a longer period, making it a preferred choice for long-term durability.
Installation and Maintenance Factors
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) roofing sheets offer superior chemical resistance and enhanced flexibility, making installation easier on irregular surfaces and reducing the risk of cracking during handling. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) sheets provide excellent UV and weather resistance, which lowers maintenance frequency by preventing degradation and prolonging roof lifespan. Installation of CSPE may require specialized adhesives and tools, whereas XNBR sheets typically allow simpler adhesion methods, impacting overall labor costs and maintenance scheduling.
Cost Analysis: XNBR vs CSM
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) roofing sheets typically present a higher initial material cost compared to chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM), driven by XNBR's superior oil resistance and tensile strength. CSM offers a more cost-effective solution with excellent weathering, UV, and chemical resistance, making it a preferred option for long-term durability under harsh environmental conditions. When evaluating total cost of ownership, the balance between XNBR's enhanced mechanical properties and CSM's competitive pricing and weatherability should guide the material selection for roofing applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Roofing Sheets
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance, flexibility, and weather durability, making it ideal for roofing sheets exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) excels in UV resistance, chemical stability, and long-term performance, suitable for roofing requiring excellent protection against sunlight and ozone degradation. Selecting the right material depends on the specific roof exposure factors and performance priorities, with XNBR favored for oil resistance and CSPE preferred for UV and chemical resistance.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Chlorosulfonated polyethylene for Roofing sheet
 azmater.com
azmater.com