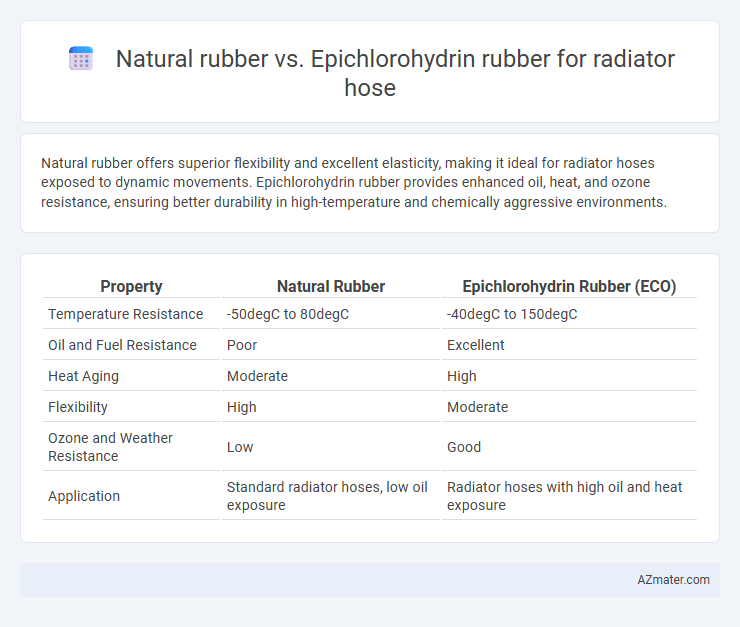
Natural rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent elasticity, making it ideal for radiator hoses exposed to dynamic movements. Epichlorohydrin rubber provides enhanced oil, heat, and ozone resistance, ensuring better durability in high-temperature and chemically aggressive environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Natural Rubber | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | -50degC to 80degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Oil and Fuel Resistance | Poor | Excellent |
| Heat Aging | Moderate | High |
| Flexibility | High | Moderate |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Low | Good |
| Application | Standard radiator hoses, low oil exposure | Radiator hoses with high oil and heat exposure |
Introduction to Radiator Hose Materials
Natural rubber offers excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for radiator hoses exposed to moderate temperatures and pressures. Epichlorohydrin rubber provides superior resistance to oil, coolant chemicals, and ozone, with higher thermal stability ideal for harsher automotive environments. Selecting between these materials depends on operating temperature ranges, exposure to automotive fluids, and durability requirements for radiator hose performance.
Overview of Natural Rubber
Natural rubber is a biopolymer derived from latex of the Hevea brasiliensis tree, known for its excellent elasticity, abrasion resistance, and high tensile strength. It offers superior flexibility and resilience under varying temperatures, making it suitable for radiator hoses exposed to mechanical stress and vibration. While natural rubber provides excellent sealing and cushioning properties, it is less resistant to oils and chemicals compared to epichlorohydrin rubber, which limits its use in certain automotive fluid environments.
Overview of Epichlorohydrin Rubber
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent heat, oil, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for radiator hose applications in automotive and industrial settings. Compared to natural rubber, ECO offers superior durability against coolant fluids and ozone, with service temperature ranges typically from -40degC to 120degC. Its resistance to swelling and cracking under harsh environmental conditions ensures longer hose life and reduced maintenance.
Performance in High Temperature Environments
Natural rubber exhibits excellent elasticity and flexibility but tends to degrade rapidly when exposed to high temperatures above 80degC, making it less suitable for radiator hoses in high-temperature environments. Epichlorohydrin rubber, by contrast, offers superior heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity and chemical stability in temperatures up to 150degC, which ensures reliable performance in demanding radiator applications. The enhanced thermal durability and oil resistance of epichlorohydrin rubber result in extended service life and reduced risk of hose failure under continuous engine heat exposure.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Natural rubber exhibits excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance but has limited chemical resistance, particularly to oils, fuels, and ozone, making it less suitable for radiator hoses exposed to aggressive fluids. Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior chemical resistance against oils, antifreeze, and weathering, maintaining integrity under harsh conditions commonly found in automotive cooling systems. The enhanced resistance of epichlorohydrin rubber to hydrocarbons and oxidation makes it the preferred material for radiator hoses requiring durability and longevity in chemically demanding environments.
Flexibility and Mechanical Properties
Natural rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for radiator hoses operating under varying temperatures and mechanical stress. Epichlorohydrin rubber provides enhanced oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, combined with good mechanical strength and moderate flexibility suitable for harsh automotive environments. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing maximum elasticity and resilience (natural rubber) or superior chemical durability with balanced mechanical performance (epichlorohydrin rubber).
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Natural rubber offers excellent flexibility and resilience, making it suitable for radiator hoses exposed to moderate temperatures but tends to degrade faster under prolonged heat and ozone exposure. Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior resistance to heat, ozone, and oil, significantly extending the durability and lifespan of radiator hoses in high-temperature engine environments. The enhanced chemical stability of epichlorohydrin rubber results in fewer cracks and leaks, ensuring longer service intervals compared to natural rubber hoses.
Cost Implications and Availability
Natural rubber offers cost advantages due to its wide availability and lower raw material prices, making it a budget-friendly choice for radiator hoses. Epichlorohydrin rubber, although more expensive, provides superior oil, heat, and chemical resistance, which can reduce long-term replacement costs despite higher initial expenses. Market availability of natural rubber is generally more stable, while epichlorohydrin rubber may face supply constraints and price fluctuations linked to synthetic production processes.
Environmental Impact Considerations
Natural rubber radiators hoses offer superior biodegradability due to their renewable origin, minimizing long-term environmental pollution. Epichlorohydrin rubber, a synthetic material derived from petrochemicals, poses challenges related to non-biodegradability and potential release of volatile organic compounds during manufacturing. Sustainable sourcing and lifecycle emissions are critical factors favoring natural rubber in eco-conscious radiator hose applications.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Radiator Hoses
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and ozone compared to natural rubber, making it the best choice for radiator hoses in high-performance and long-lasting applications. Natural rubber provides excellent flexibility and cost-effectiveness but lacks the chemical and thermal resistance required for modern engine environments. For maximum durability and reliability in radiator hoses, epichlorohydrin rubber outperforms natural rubber by maintaining integrity under extreme conditions.
Infographic: Natural rubber vs Epichlorohydrin rubber for Radiator hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com