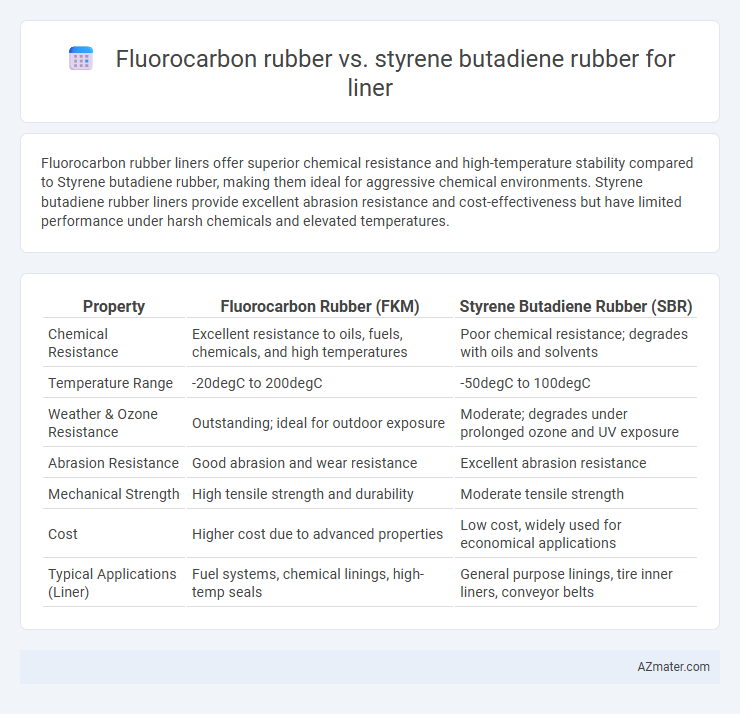
Fluorocarbon rubber liners offer superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability compared to Styrene butadiene rubber, making them ideal for aggressive chemical environments. Styrene butadiene rubber liners provide excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness but have limited performance under harsh chemicals and elevated temperatures.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, chemicals, and high temperatures | Poor chemical resistance; degrades with oils and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -20degC to 200degC | -50degC to 100degC |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Outstanding; ideal for outdoor exposure | Moderate; degrades under prolonged ozone and UV exposure |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good abrasion and wear resistance | Excellent abrasion resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and durability | Moderate tensile strength |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Low cost, widely used for economical applications |
| Typical Applications (Liner) | Fuel systems, chemical linings, high-temp seals | General purpose linings, tire inner liners, conveyor belts |
Introduction to Rubber Liners
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) offers exceptional chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 200degC, and excellent durability, making it ideal for aggressive chemical environments in rubber liners. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides cost-effective abrasion resistance and flexibility but lacks the chemical and heat resistance of FKM, limiting its use in harsh or high-temperature applications. Selecting between FKM and SBR for rubber liners depends on the operational environment's chemical exposure, temperature demands, and longevity requirements.
Overview of Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM)
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) offers exceptional chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 200-250degC, and excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents, making it ideal for critical liner applications in harsh environments. Its low permeability and strong mechanical properties ensure superior durability and longevity compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), which is more prone to swelling and degradation in aggressive chemicals and high temperatures. FKM's compatibility with a wide range of fluids and resistance to ozone and weathering significantly enhance liner performance in automotive, aerospace, and industrial seals.
Overview of Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a synthetic rubber widely used as a liner material due to its excellent abrasion resistance, good tensile strength, and cost-effectiveness. It offers superior performance in applications requiring flexibility and durability but has limited chemical resistance compared to Fluorocarbon rubber, especially against oils and solvents. SBR's balance of mechanical properties and affordability makes it suitable for industries such as automotive, conveyor belts, and general sealing applications.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), maintaining stability against a wide array of solvents, oils, acids, and alkalis at elevated temperatures. SBR shows limited resistance, particularly vulnerable to ozone, weathering, and various hydrocarbons, making it less suitable for aggressive chemical environments. The enhanced molecular structure of fluorocarbon rubber provides exceptional durability and longevity in harsh chemical applications, outperforming SBR in liner sealing and protective coatings.
Temperature Performance Differences
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits superior temperature resistance, maintaining stability and elasticity from -26degC up to 204degC, making it ideal for high-temperature liner applications. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) typically performs well within a narrower range of -50degC to 100degC but degrades faster under continuous heat exposure. This temperature performance gap significantly impacts liner durability and application suitability in demanding thermal environments.
Mechanical Properties: Durability and Flexibility
Fluorocarbon rubber exhibits superior durability with excellent resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion, making it ideal for liners exposed to harsh environments. Styrene butadiene rubber offers greater flexibility and impact resistance but has lower resistance to oils and high temperatures compared to fluorocarbon rubber. The combination of fluorocarbon rubber's mechanical strength and styrene butadiene's elasticity determines liner performance based on operational demands.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits superior chemical resistance and durability but comes with significantly higher production costs and limited availability compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR). SBR offers a cost-effective solution with widespread availability and adequate performance for less demanding liner applications. The choice between FKM and SBR hinges on balancing budget constraints with specific operational requirements, where SBR supports mass production at lower costs while FKM ensures long-term reliability in harsh environments.
Applications and Industry Usage
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) liners excel in high-temperature resistance, chemical inertness, and fuel and oil resistance, making them ideal for aerospace, automotive fuel systems, and chemical processing industries. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) liners offer superior abrasion resistance and cost-efficiency, commonly used in water treatment, conveyor belts, and general industrial sealing applications. The choice between FKM and SBR liners depends on operational environments, with FKM preferred for aggressive chemical and thermal conditions and SBR favored for abrasive, low-cost applications.
Lifespan and Maintenance Considerations
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) liners offer superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, resulting in a longer lifespan compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) liners, which are more prone to wear and degradation under harsh conditions. Maintenance requirements for FKM liners are typically lower due to their enhanced durability and resistance to solvents, acids, and high temperatures, reducing downtime and replacement frequency. In contrast, SBR liners require more frequent inspections and replacements, especially in environments involving abrasive materials or elevated heat.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Liners
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance, heat stability, and durability, making it ideal for liners exposed to aggressive chemicals and high-temperature environments. Styrene butadiene rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, suitable for applications requiring flexibility and impact absorption at lower temperatures. Selecting the right liner material depends on the specific operational conditions and performance requirements, with fluorocarbon rubber favored for harsh chemical exposure and styrene butadiene rubber preferred for mechanical wear and budget-conscious projects.
Infographic: Fluorocarbon rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Liner
 azmater.com
azmater.com