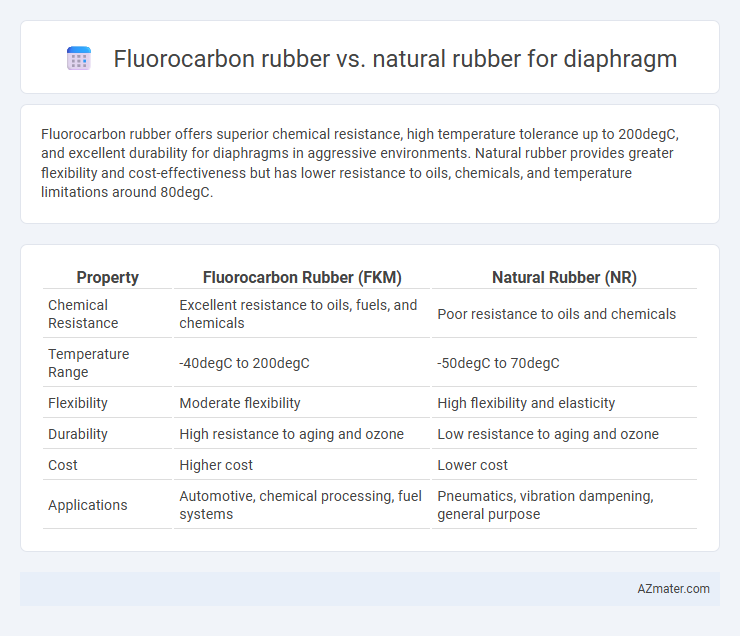
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance, high temperature tolerance up to 200degC, and excellent durability for diaphragms in aggressive environments. Natural rubber provides greater flexibility and cost-effectiveness but has lower resistance to oils, chemicals, and temperature limitations around 80degC.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM) | Natural Rubber (NR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Poor resistance to oils and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 200degC | -50degC to 70degC |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High flexibility and elasticity |
| Durability | High resistance to aging and ozone | Low resistance to aging and ozone |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Applications | Automotive, chemical processing, fuel systems | Pneumatics, vibration dampening, general purpose |
Introduction to Diaphragm Materials
Fluorocarbon rubber, known for its exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, is often preferred in diaphragm applications subjected to harsh environments and aggressive fluids. Natural rubber offers superior elasticity and flexibility, making it suitable for dynamic sealing in less chemically demanding or lower-temperature settings. Selecting between fluorocarbon and natural rubber depends on the diaphragm's exposure to chemicals, temperature range, and required mechanical properties for optimal performance.
Overview of Fluorocarbon Rubber
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) offers exceptional chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 250degC, and excellent durability compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for demanding diaphragm applications in automotive and chemical processing industries. Its superior resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents ensures long service life in harsh environments, whereas natural rubber typically exhibits stronger elasticity but lacks chemical and temperature resilience. Fluorocarbon rubber's compatibility with aggressive media and high mechanical strength enhances diaphragm performance, significantly reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
Overview of Natural Rubber
Natural rubber, derived from the latex of Hevea brasiliensis trees, offers exceptional elasticity, resilience, and tensile strength, making it an ideal diaphragm material in applications requiring flexibility and dynamic sealing. It demonstrates superior wear resistance and low compression set, essential for maintaining diaphragm integrity under cyclic loading conditions. Despite its excellent mechanical properties, natural rubber is less resistant to heat, oils, and chemical exposure compared to fluorocarbon rubber, limiting its use in harsh environments.
Comparative Chemical Resistance
Fluorocarbon rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to natural rubber, especially against acids, oils, fuels, and solvents, making it ideal for diaphragms exposed to harsh chemical environments. Natural rubber tends to degrade when in contact with ozone, petroleum products, and many chemicals, limiting its application in chemically aggressive settings. This enhanced durability of fluorocarbon rubber ensures longer diaphragm life and improved performance in industrial and automotive applications where chemical exposure is significant.
Temperature Tolerance Differences
Fluorocarbon rubber excels in temperature tolerance, maintaining stability between -20degC and 200degC, making it ideal for diaphragms exposed to extreme heat or aggressive chemicals. In contrast, natural rubber typically operates effectively within a narrower range of -40degC to 70degC but deteriorates quickly at elevated temperatures. This significant temperature performance disparity influences material selection for diaphragms in industrial applications requiring high thermal resistance.
Mechanical Properties and Flexibility
Fluorocarbon rubber exhibits superior mechanical properties such as high tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance, and outstanding chemical stability compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for demanding diaphragm applications. Its flexibility remains stable over a wide temperature range, from -20degC to 200degC, ensuring durability and performance in extreme environments. Natural rubber offers higher elasticity and softer compression set but has limited resistance to oils, solvents, and heat, which can compromise diaphragm longevity and mechanical integrity.
Applications in Industrial Environments
Fluorocarbon rubber diaphragms offer exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, making them ideal for harsh industrial environments such as chemical processing, automotive fuel systems, and oil refineries. Natural rubber diaphragms provide excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance suitable for less aggressive applications, including water treatment and pneumatic systems. Fluorocarbon rubber's superior durability enhances lifespan and performance in volatile conditions, while natural rubber maintains cost-effectiveness in moderate industrial settings.
Longevity and Maintenance Requirements
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior longevity compared to natural rubber due to its exceptional resistance to chemicals, heat, and ozone, resulting in less frequent diaphragm replacements. Its low permeability and stable physical properties under harsh conditions reduce maintenance requirements significantly. Natural rubber diaphragms, while cost-effective initially, degrade faster when exposed to oils, acids, and extreme temperatures, leading to more frequent maintenance and shorter lifespan.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Fluorocarbon rubber diaphragms generally incur higher costs due to their complex manufacturing processes and superior chemical resistance, making them less economical than natural rubber options. Natural rubber is more widely available and cost-effective, benefiting from abundant raw materials and simpler production techniques. Cost considerations favor natural rubber for budget-sensitive applications, while availability of fluorocarbon rubber can be limited by supplier capacity and global market demand.
Choosing the Best Rubber for Diaphragm Applications
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 200degC, and excellent durability for diaphragm applications exposed to harsh environments such as fuels, oils, and aggressive chemicals. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity, high tensile strength, and better performance in dynamic sealing under moderate temperatures but lacks resistance to oils and solvents. Selecting the best rubber depends on the application's specific requirements, with fluorocarbon rubber preferred for chemical and thermal resilience, while natural rubber suits flexible, abrasion-resistant sealing in milder conditions.
Infographic: Fluorocarbon rubber vs Natural rubber for Diaphragm
 azmater.com
azmater.com