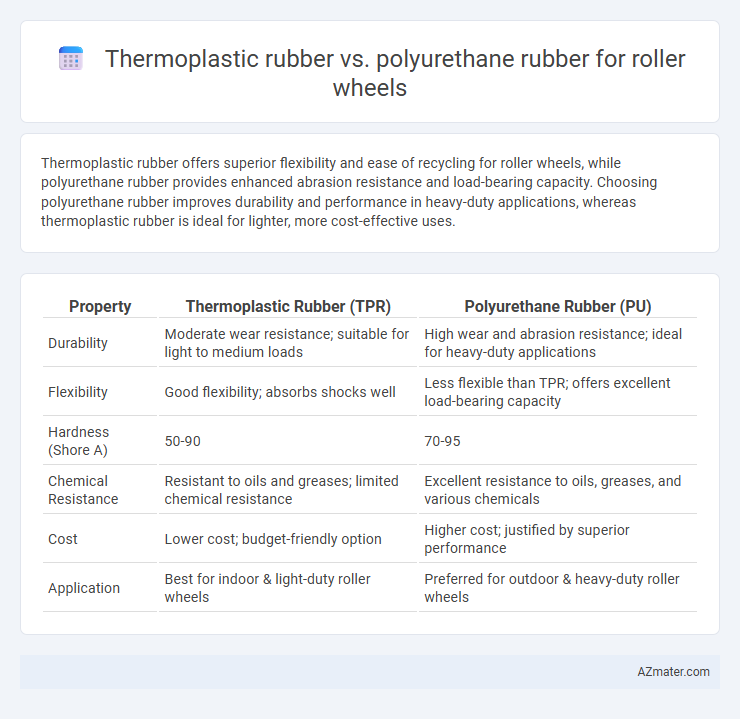
Thermoplastic rubber offers superior flexibility and ease of recycling for roller wheels, while polyurethane rubber provides enhanced abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity. Choosing polyurethane rubber improves durability and performance in heavy-duty applications, whereas thermoplastic rubber is ideal for lighter, more cost-effective uses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR) | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Moderate wear resistance; suitable for light to medium loads | High wear and abrasion resistance; ideal for heavy-duty applications |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility; absorbs shocks well | Less flexible than TPR; offers excellent load-bearing capacity |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 50-90 | 70-95 |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils and greases; limited chemical resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, greases, and various chemicals |
| Cost | Lower cost; budget-friendly option | Higher cost; justified by superior performance |
| Application | Best for indoor & light-duty roller wheels | Preferred for outdoor & heavy-duty roller wheels |
Introduction to Roller Wheel Materials
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) and polyurethane (PU) are the leading materials used in roller wheel manufacturing due to their distinct mechanical properties. TPR offers excellent flexibility and shock absorption, making it suitable for smooth and quiet operation on diverse surfaces. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, enhancing durability and performance in heavy-duty industrial applications.
Overview of Thermoplastic Rubber
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) combines the elasticity of rubber with the recyclability of plastics, making it ideal for roller wheel applications requiring flexibility and durability. TPR offers excellent abrasion resistance, good grip, and softer ride comfort compared to polyurethane rubber, which tends to be harder and more wear-resistant. Its ability to withstand varying temperatures and impact loads enhances performance in environments demanding both resilience and flexibility.
Overview of Polyurethane Rubber
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity compared to thermoplastic rubber, making it ideal for roller wheel applications requiring durability and resilience. Its excellent elasticity and resistance to oils, greases, and chemicals enhance performance in demanding industrial environments. Polyurethane rubber also provides better noise reduction and ride comfort due to its unique molecular structure and flexibility.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers excellent elasticity and good abrasion resistance, making it suitable for roller wheels requiring flexibility and moderate durability. Polyurethane rubber (PU) exhibits superior tensile strength, higher load-bearing capacity, and exceptional wear resistance, ideal for heavy-duty roller wheels subjected to harsh mechanical stress. PU's enhanced mechanical properties ensure longer lifespan and better performance under repetitive impact and heavy loads compared to TPR.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers excellent flexibility and moderate wear resistance, making it suitable for roller wheels in applications with light to medium loads. Polyurethane rubber significantly outperforms TPR in durability and abrasion resistance, providing superior longevity under heavy loads and harsh conditions. The enhanced mechanical properties of polyurethane contribute to less frequent replacements and lower maintenance costs in industrial roller wheel applications.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers excellent resistance to oils, greases, and many chemicals, making it suitable for roller wheels in environments exposed to automotive fluids or mild solvents. Polyurethane rubber (PU) excels in resistance to abrasion, hydrocarbons, and harsh chemicals, providing superior durability in industrial settings with exposure to fuels and aggressive solvents. Both materials are environmentally resistant, but polyurethane demonstrates enhanced resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and extreme temperatures, extending roller wheel lifespan in outdoor or chemically aggressive conditions.
Load-Bearing Capacity and Performance
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers moderate load-bearing capacity with good flexibility and shock absorption, making it suitable for light to medium-duty roller wheels. Polyurethane rubber, known for its high load-bearing strength and superior abrasion resistance, excels in heavy-duty applications where durability and performance under stress are critical. The performance of polyurethane wheels generally surpasses TPR in terms of wear resistance, load capacity, and longevity, especially in industrial environments demanding sustained heavy loads.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers a lower upfront cost compared to polyurethane rubber, making it a cost-effective choice for roller wheels in budget-sensitive applications. Polyurethane rubber, priced higher due to superior durability and load-bearing capabilities, provides longer service life, reducing replacement frequency and total cost of ownership. Both materials are widely available globally, but polyurethane has a broader range of specialized suppliers and formulations tailored for high-performance roller wheels.
Application Suitability for Different Industries
Thermoplastic rubber offers excellent flexibility and chemical resistance, making it ideal for roller wheels in automotive, consumer goods, and packaging industries where impact absorption and durability are crucial. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, suited for heavy-duty applications in industries such as logistics, manufacturing, and material handling that demand long-lasting performance under high stress. Selecting the appropriate material depends on specific operational conditions, including load requirements, environmental exposure, and desired lifespan.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Roller Wheels
Thermoplastic rubber offers excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for lighter loads and applications requiring frequent cleaning. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance, load-bearing capacity, and durability, ideal for heavy-duty roller wheels subject to harsh environments and high impact. Selecting the right material depends on specific operational demands, where polyurethane is preferred for longevity and toughness, while thermoplastic rubber fits budget-friendly, versatile uses.
Infographic: Thermoplastic rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Roller wheel
 azmater.com
azmater.com