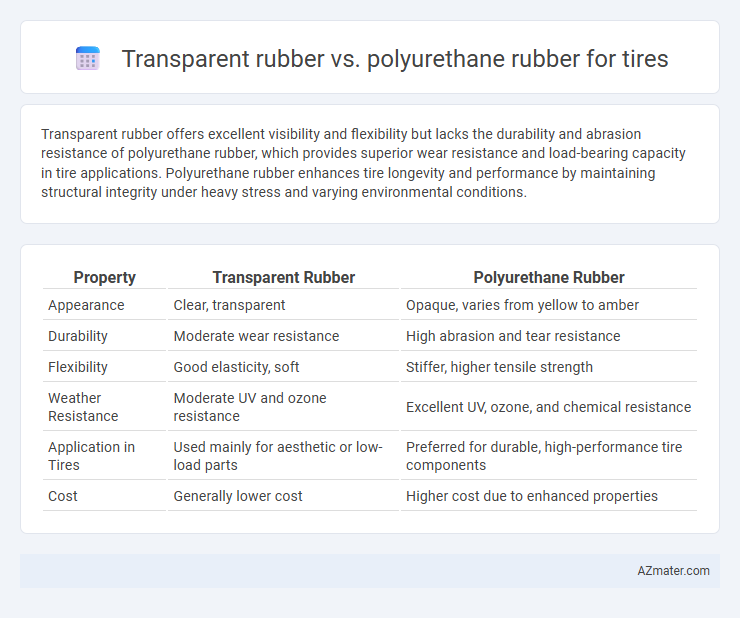
Transparent rubber offers excellent visibility and flexibility but lacks the durability and abrasion resistance of polyurethane rubber, which provides superior wear resistance and load-bearing capacity in tire applications. Polyurethane rubber enhances tire longevity and performance by maintaining structural integrity under heavy stress and varying environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Transparent Rubber | Polyurethane Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear, transparent | Opaque, varies from yellow to amber |
| Durability | Moderate wear resistance | High abrasion and tear resistance |
| Flexibility | Good elasticity, soft | Stiffer, higher tensile strength |
| Weather Resistance | Moderate UV and ozone resistance | Excellent UV, ozone, and chemical resistance |
| Application in Tires | Used mainly for aesthetic or low-load parts | Preferred for durable, high-performance tire components |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to enhanced properties |
Introduction to Transparent Rubber and Polyurethane Rubber
Transparent rubber is a flexible, clear elastomer known for its excellent optical clarity, making it ideal for applications where visibility and aesthetics are crucial. Polyurethane rubber is a durable, abrasion-resistant elastomer widely used in tire manufacturing for its superior toughness, load-bearing capacity, and resistance to oil and chemicals. Both materials offer distinct properties, with transparent rubber emphasizing clarity and flexibility, while polyurethane provides enhanced durability and performance in demanding tire environments.
Chemical Composition and Material Properties
Transparent rubber typically consists of silicone or polyurethane-based compounds with reduced fillers and additives to maintain clarity, while polyurethane rubber for tires is formulated with polyether or polyester segments and higher crosslink density for enhanced durability and abrasion resistance. The chemical composition of transparent rubber emphasizes optical transparency and flexibility, often containing siloxane chains or clear polymers, in contrast to the robust molecular structure of polyurethane rubber that offers superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and elasticity. Material properties such as tensile strength, hardness, and wear resistance are significantly higher in polyurethane rubber, making it ideal for tire applications demanding resilience and longevity, whereas transparent rubber prioritizes clarity and flexibility over toughness.
Transparency and Optical Clarity Comparison
Transparent rubber offers superior optical clarity compared to polyurethane rubber, making it ideal for applications requiring high visibility and light transmission. Polyurethane rubber, while durable and flexible, typically exhibits lower transparency due to its chemical composition and molecular structure, resulting in a more opaque appearance. The advanced formulation of transparent rubber enhances light passage and reduces distortion, providing clearer visibility in tire applications where transparency is critical.
Durability and Wear Resistance in Tire Applications
Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior durability and wear resistance compared to transparent rubber in tire applications due to its higher abrasion resistance and enhanced mechanical strength. Transparent rubber, while offering aesthetic advantages, tends to wear faster under friction and heavy load conditions typical in tire use. The chemical structure of polyurethane rubber provides greater resilience against environmental factors, extending tire lifespan and performance consistency.
Performance Under Different Weather Conditions
Transparent rubber exhibits excellent flexibility and clarity but tends to harden and lose grip in cold temperatures, making it less ideal for winter tire applications. Polyurethane rubber maintains superior abrasion resistance and elasticity across a wide temperature range, offering consistent traction and durability in both hot and cold weather conditions. Its enhanced resistance to UV and chemical exposure also ensures sustained performance and longer tire lifespan under varied environmental stresses.
Flexibility and Elasticity Factors
Transparent rubber exhibits lower elasticity and flexibility compared to polyurethane rubber, which offers superior stretchability and resilience under varying pressures. Polyurethane rubber demonstrates enhanced elastic recovery and maintains flexibility across a wider temperature range, making it ideal for tire applications requiring durability and consistent performance. The molecular structure of polyurethane, with its segmented copolymers, contributes significantly to its higher flexibility and elastic modulus relative to transparent rubber compounds.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Transparent rubber for tires is typically produced using a specialized silicone-based formulation that requires low-temperature curing and UV stabilization to maintain clarity, whereas polyurethane rubber involves a chemical reaction between polyols and diisocyanates, cured at higher temperatures to achieve durability and elasticity. The manufacturing process of transparent rubber emphasizes purity and controlled environment to prevent contamination and discoloration, contrasting with polyurethane's focus on precise mixing ratios and thermal curing cycles for robust performance. These process differences impact equipment choice, production speed, and final tire properties, with transparent rubber demanding more delicate handling to preserve transparency.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Transparent rubber, often made from silicone or specialized elastomers, offers lower environmental impact due to its chemical stability and potential for non-toxic degradation, yet its recyclability remains limited compared to polyurethane rubber. Polyurethane rubber demonstrates superior recyclability through chemical and mechanical reprocessing methods, reducing landfill waste and supporting circular economy initiatives in tire manufacturing. The environmental footprint of polyurethane tires benefits from lower emissions during production and enhanced durability, contributing to resource efficiency despite challenges in biodegradability.
Cost Analysis: Transparent vs. Polyurethane Rubber
Transparent rubber generally incurs higher material costs compared to polyurethane rubber due to its clarity and specialized formulation requirements. Polyurethane rubber offers a cost-effective alternative with superior durability and abrasion resistance, leading to lower long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. The overall cost analysis favors polyurethane rubber for tire applications where budget constraints and performance longevity are critical factors.
Future Prospects in Tire Technology
Transparent rubber offers unique opportunities in tire technology by enabling innovative visual designs and real-time wear monitoring, while polyurethane rubber provides enhanced durability, abrasion resistance, and improved performance in extreme temperatures. The future prospects for transparent rubber include integration with smart sensors for predictive maintenance, whereas polyurethane continues to dominate high-performance tires in electric and autonomous vehicles due to its superior mechanical properties. Advances in composite materials combining both rubbers could lead to next-generation tires that balance aesthetics, longevity, and functionality for evolving automotive demands.
Infographic: Transparent rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com