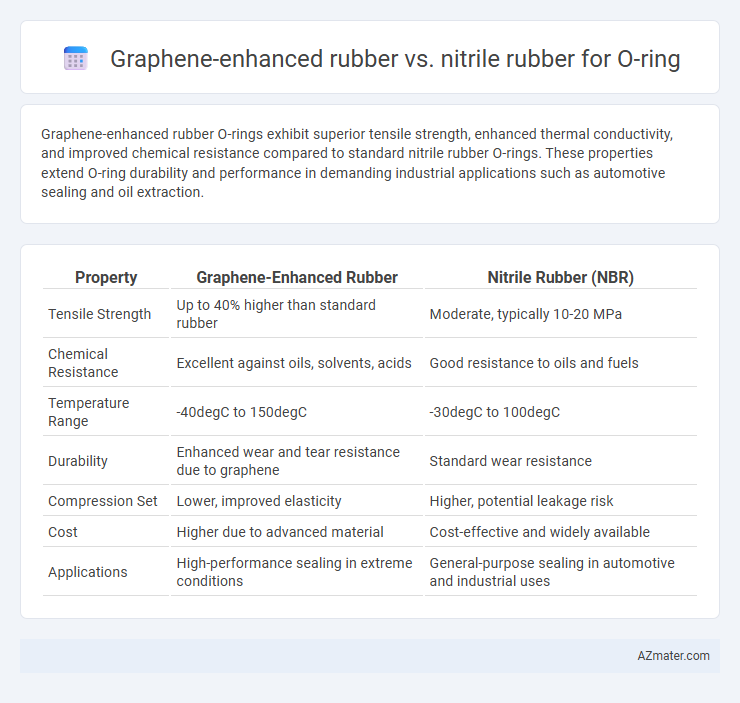
Graphene-enhanced rubber O-rings exhibit superior tensile strength, enhanced thermal conductivity, and improved chemical resistance compared to standard nitrile rubber O-rings. These properties extend O-ring durability and performance in demanding industrial applications such as automotive sealing and oil extraction.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Graphene-Enhanced Rubber | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Up to 40% higher than standard rubber | Moderate, typically 10-20 MPa |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against oils, solvents, acids | Good resistance to oils and fuels |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -30degC to 100degC |
| Durability | Enhanced wear and tear resistance due to graphene | Standard wear resistance |
| Compression Set | Lower, improved elasticity | Higher, potential leakage risk |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced material | Cost-effective and widely available |
| Applications | High-performance sealing in extreme conditions | General-purpose sealing in automotive and industrial uses |
Introduction to O-Ring Materials
Graphene-enhanced rubber offers superior mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and chemical resistance compared to traditional nitrile rubber, making it a promising material for O-ring applications requiring enhanced durability. Nitrile rubber, known for its excellent oil and fuel resistance, remains a standard choice in automotive and industrial sealing due to its balanced performance and cost-effectiveness. Emerging graphene nanocomposites in O-ring manufacturing aim to improve wear resistance and longevity, addressing the limitations of conventional nitrile elastomers in harsh environments.
Overview of Nitrile Rubber Properties
Nitrile rubber (NBR) exhibits excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and abrasion, making it highly suitable for O-ring applications in automotive and industrial sectors. Its high tensile strength and low gas permeability provide reliable sealing performance under various temperatures ranging from -40degC to 120degC. Compared to graphene-enhanced rubber, nitrile rubber offers well-established chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness, though it may lack the enhanced mechanical properties and thermal stability graphene additives provide.
Advancements in Graphene-Enhanced Rubber
Graphene-enhanced rubber significantly improves O-ring performance by increasing tensile strength, elasticity, and chemical resistance compared to traditional nitrile rubber, which is widely used for its oil and abrasion resistance. The incorporation of graphene nanosheets provides superior mechanical reinforcement and thermal stability, extending the O-ring's lifespan in demanding environments such as automotive and aerospace industries. Recent advancements in graphene dispersion techniques have optimized the uniformity of composite materials, enhancing sealing efficiency and durability under high pressure and extreme temperatures.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength than nitrile rubber when used in O-ring applications, improving tensile strength by up to 30-40% and enhancing abrasion resistance. The incorporation of graphene nanosheets increases the material's elasticity and durability, resulting in superior tear resistance and prolonged service life under dynamic stress conditions. In contrast, standard nitrile rubber typically offers moderate mechanical performance but lacks the reinforcement benefits provided by graphene, making it less suitable for high-load or high-wear sealing environments.
Chemical Resistance Performance
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to standard nitrile rubber, especially in aggressive environments involving oils, fuels, and solvents. The addition of graphene provides improved barrier properties and molecular stability, reducing permeation and degradation in hostile chemical exposures. This enhancement extends the service life of O-rings used in automotive, aerospace, and industrial sealing applications where chemical resistance is critical.
Temperature Resistance and Stability
Graphene-enhanced rubber O-rings exhibit superior temperature resistance and thermal stability compared to nitrile rubber, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 200degC. The incorporation of graphene enhances heat dissipation and reduces thermal degradation, enabling prolonged performance under extreme thermal cycles. Nitrile rubber typically withstands temperatures up to 120degC but shows decreased stability and flexibility at higher temperatures, limiting its use in high-heat applications.
Durability and Lifespan
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits superior durability and a longer lifespan compared to traditional nitrile rubber for O-ring applications, owing to graphene's exceptional tensile strength and resistance to wear and tear. The incorporation of graphene significantly improves the material's thermal stability and chemical resistance, reducing degradation under harsh operational conditions. Consequently, graphene-enhanced O-rings maintain their sealing integrity over extended periods, making them ideal for demanding industrial environments.
Applications in Industrial Settings
Graphene-enhanced rubber O-rings exhibit superior mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and chemical resistance compared to conventional nitrile rubber, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications such as aerospace, automotive, and oil and gas sectors. Their enhanced durability under high temperature and aggressive chemical environments ensures prolonged service life and reduced maintenance costs in sealing systems. Nitrile rubber remains a cost-effective solution for moderate conditions but lacks the advanced performance characteristics required in extreme industrial settings.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Graphene-enhanced rubber O-rings offer superior durability and chemical resistance but come with higher production costs due to the expensive raw graphene material and limited large-scale availability. Nitrile rubber O-rings remain more cost-effective and widely accessible, benefiting from established manufacturing processes and abundant supply chains. Budget constraints and supply reliability often make nitrile the preferred choice for standard sealing applications despite graphene's enhanced performance.
Future Trends in O-Ring Material Technology
Graphene-enhanced rubber O-rings exhibit superior mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance compared to traditional nitrile rubber, positioning them as a promising material for high-performance sealing applications. Emerging trends highlight the integration of nanomaterials like graphene to improve durability, reduce wear, and extend service life in extreme environments. Research continues to explore scalable production methods and cost-efficiency to enable widespread adoption of graphene-enhanced O-rings in automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors.
Infographic: Graphene-enhanced rubber vs Nitrile rubber for O-ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com