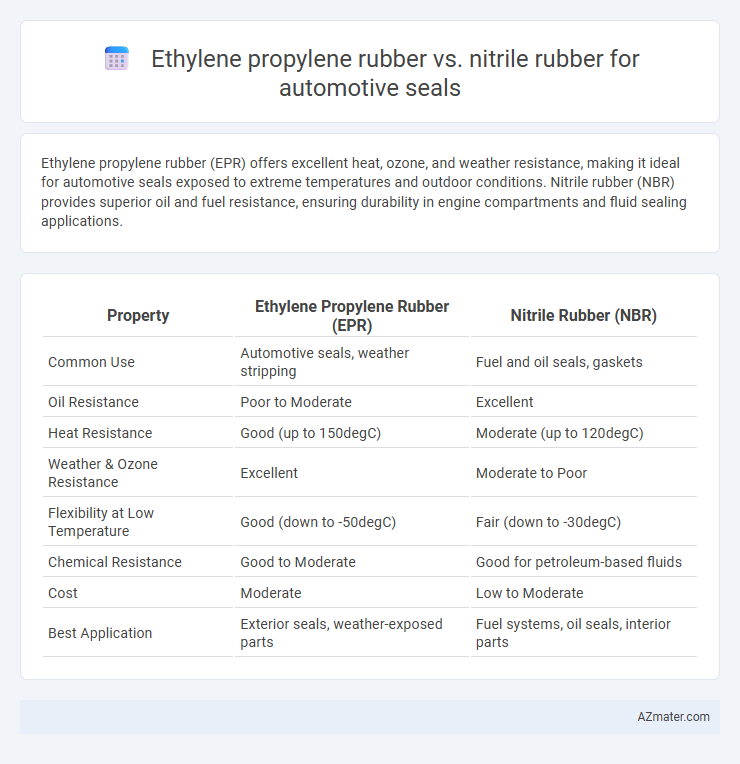
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent heat, ozone, and weather resistance, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to extreme temperatures and outdoor conditions. Nitrile rubber (NBR) provides superior oil and fuel resistance, ensuring durability in engine compartments and fluid sealing applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Common Use | Automotive seals, weather stripping | Fuel and oil seals, gaskets |
| Oil Resistance | Poor to Moderate | Excellent |
| Heat Resistance | Good (up to 150degC) | Moderate (up to 120degC) |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Moderate to Poor |
| Flexibility at Low Temperature | Good (down to -50degC) | Fair (down to -30degC) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good to Moderate | Good for petroleum-based fluids |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to Moderate |
| Best Application | Exterior seals, weather-exposed parts | Fuel systems, oil seals, interior parts |
Introduction to Automotive Rubber Seals
Automotive rubber seals require materials with excellent resistance to heat, oils, and weathering, making Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) and Nitrile Rubber (NBR) top choices. EPR provides superior resistance to ozone, UV, and aging, ensuring long-lasting performance in engine compartments and exterior sealing. NBR excels in oil and fuel resistance, making it ideal for seals exposed to petroleum-based fluids in fuel systems and hydraulic components.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR/EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR/EPDM) is a synthetic elastomer widely used in automotive seals due to its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for under-the-hood applications. Its superior flexibility and durability at low temperatures enhance sealing performance, preventing leaks and maintaining integrity under harsh conditions. Compared to Nitrile Rubber (NBR), EPR/EPDM offers better resistance to oxidation and environmental factors but has lower resistance to oil and fuel exposure.
Overview of Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Nitrile Rubber (NBR) is a synthetic elastomer renowned for its exceptional resistance to oils, fuels, and other hydrocarbons, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh chemical environments. It offers superior abrasion resistance and excellent mechanical properties over a wide temperature range, typically from -40degC to 120degC. Compared to Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR), NBR provides enhanced durability and sealing performance in fuel systems, hydraulic components, and engine gaskets, where resistance to petroleum-based fluids is critical.
Chemical Resistance: EPDM vs NBR
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPDM) exhibits superior resistance to polar solvents, weathering, ozone, and aging, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to brake fluids, water, and steam. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers excellent resistance to hydrocarbons, oils, fuels, and grease, ensuring durability in engine and fuel system seals. Selecting EPDM over NBR ensures enhanced chemical stability in harsh weather and aqueous environments, while NBR excels in oil and fuel resistance applications.
Temperature Tolerance Comparison
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) exhibits superior temperature tolerance for automotive seals, maintaining flexibility and performance in extreme temperatures ranging from -50degC to 150degC. Nitrile rubber (NBR) operates effectively between -40degC and 120degC but tends to harden and lose elasticity at the lower and upper temperature thresholds. For high-temperature engine environments and cold weather conditions, EPR provides enhanced durability and resistance to thermal degradation compared to NBR.
Durability and Ageing in Automotive Applications
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) demonstrates superior durability and resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it highly suitable for automotive seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers excellent oil, fuel, and chemical resistance but tends to degrade faster under prolonged heat and UV exposure, reducing its lifespan in high-temperature engine compartments. For automotive sealing applications, EPR outperforms NBR in ageing resistance, providing longer service life and enhanced reliability in dynamic and static seals.
Resistance to Oils and Fluids
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) exhibits excellent resistance to water, steam, and many polar solvents but has limited compatibility with petroleum-based oils and fuels, making it less suitable for automotive seals exposed to hydrocarbons. Nitrile rubber (NBR), on the other hand, offers superior resistance to a broad range of oils, fuels, and automotive fluids due to its acrylonitrile content, which enhances its oil and fuel resistance properties. For automotive seals requiring durability against aggressive oils and fluids, nitrile rubber is generally the preferred choice over ethylene propylene rubber.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPDM) offers cost advantages and excellent weather resistance for automotive seals, often priced lower than nitrile rubber (NBR) due to simpler manufacturing processes. NBR provides superior oil and fuel resistance but typically comes at a higher cost and can have limited availability in large quantities compared to EPDM. Automotive manufacturers prioritize EPDM for cost-effective sealing applications exposed to heat and water, while NBR is chosen when chemical resistance justifies the premium price.
Application Suitability in Automotive Sealing
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) excels in automotive sealing applications requiring superior resistance to heat, weathering, and ozone exposure, making it ideal for exterior seals and weatherstripping. Nitrile rubber (NBR) is preferred for oil-resistant seals within engines and fuel systems due to its excellent resistance to petroleum-based fluids and erosion from hydraulic fluids. Selecting EPR or NBR depends on specific automotive sealing requirements such as temperature range, fluid exposure, and environmental durability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Automotive Seals
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) excels in heat resistance, ozone durability, and flexibility, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to extreme temperatures and weathering. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, enhancing seal performance in engine compartments and fuel systems. Selecting the right rubber depends on the specific automotive application requirements, with EPR favored for external and high-temperature seals, while NBR is optimal for oil and fuel-exposed environments.
Infographic: Ethylene propylene rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Automotive seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com