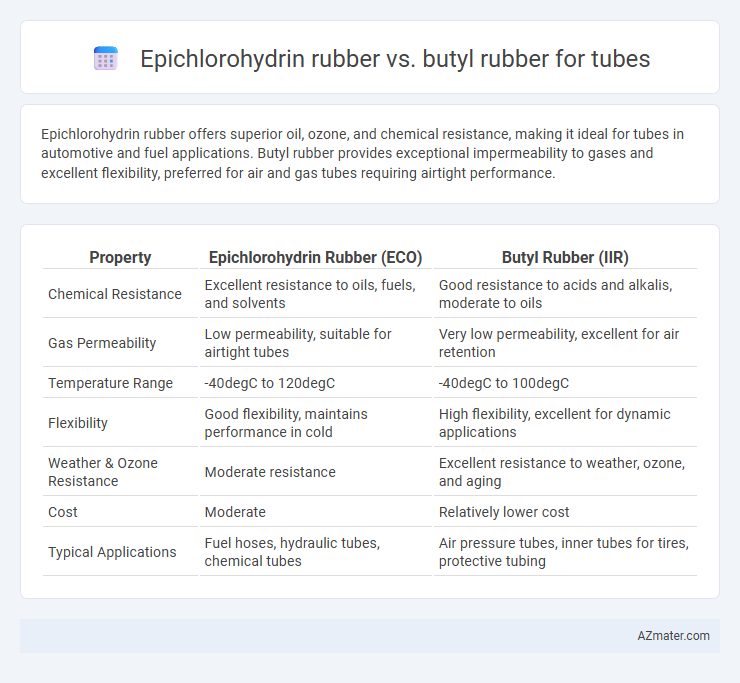
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil, ozone, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for tubes in automotive and fuel applications. Butyl rubber provides exceptional impermeability to gases and excellent flexibility, preferred for air and gas tubes requiring airtight performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) | Butyl Rubber (IIR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents | Good resistance to acids and alkalis, moderate to oils |
| Gas Permeability | Low permeability, suitable for airtight tubes | Very low permeability, excellent for air retention |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -40degC to 100degC |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility, maintains performance in cold | High flexibility, excellent for dynamic applications |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Moderate resistance | Excellent resistance to weather, ozone, and aging |
| Cost | Moderate | Relatively lower cost |
| Typical Applications | Fuel hoses, hydraulic tubes, chemical tubes | Air pressure tubes, inner tubes for tires, protective tubing |
Introduction to Epichlorohydrin Rubber and Butyl Rubber
Epichlorohydrin rubber, known for its excellent resistance to oil, chemicals, and ozone, is widely used in applications requiring flexibility and durability, particularly in fuel lines and industrial hoses. Butyl rubber offers superior air impermeability and weather resistance, making it ideal for inner tubes and tire applications where airtightness and longevity are crucial. Both materials provide unique advantages for tube manufacturing depending on the required chemical resistance and elasticity.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) features a saturated polymer backbone with pendant chloromethyl groups, providing excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and ozone due to its polar epichlorohydrin units. Butyl rubber (IIR) is a copolymer of isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, characterized by a saturated hydrocarbon backbone that imparts exceptional impermeability and resistance to weathering and chemicals. The presence of chloromethyl groups in ECO enhances chemical resistance and adhesion properties, while the unique isobutylene structure in Butyl rubber offers superior air retention and flexibility for tube applications.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) exhibits superior resistance to oil, ozone, and weathering compared to butyl rubber, making it ideal for tube applications exposed to harsh environments. Butyl rubber offers exceptional impermeability to gases and excellent flex fatigue resistance, ensuring durability in pneumatic tube systems. Both rubbers provide good abrasion resistance, but ECO typically offers better tensile strength and elongation, while butyl rubber excels in low gas permeability and heat stability.
Performance in Tube Applications
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits excellent resistance to oil, ozone, and weathering, making it suitable for tubes exposed to harsh chemical environments and outdoor conditions. Butyl rubber offers superior impermeability to gases and exceptional flexibility at low temperatures, making it ideal for airtight tube applications requiring sustained elasticity. While Epichlorohydrin excels in chemical durability, Butyl rubber outperforms in gas retention and low-temperature performance, influencing tube material selection based on specific operational demands.
Resistance to Heat and Ozone
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits excellent resistance to heat and ozone, maintaining flexibility and integrity at temperatures up to 150degC, making it suitable for high-heat environments. Butyl rubber provides outstanding resistance to ozone degradation but typically withstands heat only up to 120degC, limiting its use in higher temperature applications. For tube applications demanding superior heat resistance combined with ozone durability, epichlorohydrin rubber offers a balanced performance advantage over butyl rubber.
Air Permeability and Retention
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior air impermeability and retention compared to butyl rubber, making it ideal for applications requiring minimal gas permeability. Butyl rubber offers good air retention but is generally more permeable to gases than epichlorohydrin rubber, resulting in faster air loss over time. The chemical structure of epichlorohydrin creates a more effective barrier against air molecules, enhancing its performance in tube applications demanding long-term air retention.
Flexibility and Elasticity
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent resistance to oils and chemicals, making it ideal for tubes exposed to harsh environments. Butyl rubber provides exceptional elasticity and air impermeability, ensuring durable sealing and vibration damping in tubes. For applications requiring both flexibility and elasticity, epichlorohydrin rubber excels in dynamic performance, whereas butyl rubber is preferred for static sealing and insulation.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil resistance and flexibility for tube applications but involves higher raw material costs and more complex manufacturing processes compared to butyl rubber. Butyl rubber is cost-effective with simpler curing techniques, making it advantageous for large-scale production where chemical resistance requirements are moderate. Selecting between these elastomers depends on balancing production budgets against performance needs in oil-exposure environments.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to ozone and chemicals, resulting in less frequent replacements and reduced environmental waste compared to butyl rubber. Butyl rubber, known for its excellent impermeability to gases, poses lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during manufacturing, enhancing workplace safety. Both materials require careful handling to prevent exposure to hazardous substances, but epichlorohydrin rubber's potential release of chlorinated byproducts may present greater environmental risks.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Tubes
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, and ozone, making it ideal for fuel and hydraulic tubes exposed to harsh chemicals, while butyl rubber excels in gas impermeability and weather resistance, perfect for air and water tubes requiring airtight seals. Epichlorohydrin's tensile strength and flexibility withstand mechanical stress, whereas butyl rubber's low permeability ensures minimal gas loss and excellent aging stability. Selecting the right rubber depends on tube application requirements, chemical exposure, and environmental durability to maximize performance and lifespan.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Butyl rubber for Tube
 azmater.com
azmater.com