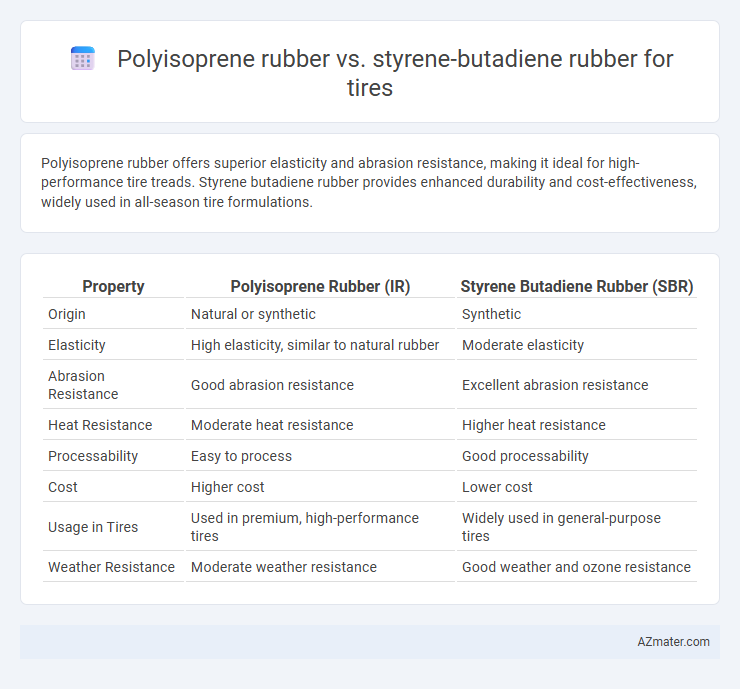
Polyisoprene rubber offers superior elasticity and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for high-performance tire treads. Styrene butadiene rubber provides enhanced durability and cost-effectiveness, widely used in all-season tire formulations.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyisoprene Rubber (IR) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural or synthetic | Synthetic |
| Elasticity | High elasticity, similar to natural rubber | Moderate elasticity |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good abrasion resistance | Excellent abrasion resistance |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat resistance | Higher heat resistance |
| Processability | Easy to process | Good processability |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Usage in Tires | Used in premium, high-performance tires | Widely used in general-purpose tires |
| Weather Resistance | Moderate weather resistance | Good weather and ozone resistance |
Introduction to Polyisoprene Rubber and Styrene Butadiene Rubber
Polyisoprene rubber, closely resembling natural rubber, is prized for its excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and resilience, making it ideal for high-performance tire applications requiring superior wear resistance and grip. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), a synthetic copolymer of styrene and butadiene, offers enhanced abrasion resistance, aging stability, and cost-effectiveness, which are critical for mass-produced tires with reliable durability under diverse road conditions. The combination of these properties influences tire performance characteristics such as traction, rolling resistance, and lifespan, guiding material selection in tire manufacturing.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Polyisoprene rubber (IR) consists mainly of cis-1,4-polyisoprene units that provide high elasticity and resilience due to its natural rubber-like structure, while Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a copolymer composed of styrene and butadiene monomers, with varying styrene content typically between 15-30%, which affects its abrasion resistance and aging properties. The chemical structure of IR features almost pure isoprene units leading to superior tensile strength and flexibility, whereas SBR's alternating styrene and butadiene units create a more amorphous polymer chain, enhancing durability and resistance to heat and oxidation. This difference in molecular architecture directly influences tire performance, where IR offers better tread elasticity and grip, and SBR provides enhanced wear resistance and weathering stability.
Manufacturing Processes of Polyisoprene vs Styrene Butadiene Rubber
Polyisoprene rubber, primarily natural rubber, undergoes a coagulation process after latex extraction followed by drying, milling, and vulcanization, ensuring high elasticity and resilience essential for tire manufacturing. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), a synthetic polymer, is produced through emulsion polymerization of styrene and butadiene monomers, resulting in a more controlled and consistent material. The manufacturing of SBR allows for customization of polymer properties and reduces reliance on natural sources, whereas polyisoprene maintains superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance vital for tire durability.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Analysis
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits superior tensile strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber, making it ideal for high-performance tire treads requiring durability and flexibility. Styrene butadiene rubber offers better aging resistance and lower heat buildup, enhancing tire longevity and fuel efficiency under varied driving conditions. Both rubbers present distinct advantages in mechanical and physical properties, with polyisoprene favoring grip and wear performance while styrene butadiene optimizes resilience and energy dissipation in tire applications.
Tread Performance in Different Road Conditions
Polyisoprene rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength, enhancing tire tread durability on rough, uneven surfaces compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR). SBR provides better heat resistance and traction on wet roads, making it optimal for performance in rainy or slippery conditions. Combining Polyisoprene's wear resistance with SBR's wet grip properties results in a balanced tread performance across diverse road environments.
Durability and Wear Resistance Comparison
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits superior elasticity and resilience, contributing to enhanced tire durability by reducing crack formation and improving flexibility under stress. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance, making it highly wear-resistant but generally less resilient than polyisoprene in extreme conditions. Tires combining polyisoprene and SBR materials often achieve an optimal balance between durability and wear resistance, extending tire life in various driving environments.
Rolling Resistance and Fuel Efficiency
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits lower hysteresis compared to Styrene butadiene rubber, resulting in reduced rolling resistance and enhanced fuel efficiency for tires. The molecular structure of polyisoprene provides better elasticity and energy return, minimizing energy loss during tire deformation. Tires made with styrene butadiene rubber typically offer higher wear resistance but at the cost of increased rolling resistance, leading to decreased fuel economy.
Wet and Dry Traction Performance
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits superior wet traction performance due to its excellent elasticity and higher hysteresis, enhancing tire grip on slippery surfaces. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) offers better dry traction through improved abrasion resistance and stiffness, contributing to durability and handling on dry roads. Combining polyisoprene with SBR can optimize overall tire performance by balancing wet and dry traction capabilities.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyisoprene rubber, a natural polymer derived from rubber trees, offers better biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint compared to synthetic Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), which is petroleum-based and relies on non-renewable resources. SBR production generates higher greenhouse gas emissions and involves more energy-intensive processes, whereas polyisoprene supports sustainable forestry practices and reduces dependence on fossil fuels. Recycling and end-of-life management of polyisoprene tires pose fewer environmental challenges, enhancing overall sustainability in tire manufacturing.
Cost Considerations and Market Applications
Polyisoprene rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and elasticity but generally incurs higher production costs compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making SBR the more cost-effective choice for mass-market tire manufacturing. SBR dominates tire applications due to its balanced performance and affordability, especially in passenger car and light truck tires where budget constraints are critical. Polyisoprene rubber finds niche applications in high-performance or specialty tires where enhanced durability justifies the premium price.
Infographic: Polyisoprene rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com