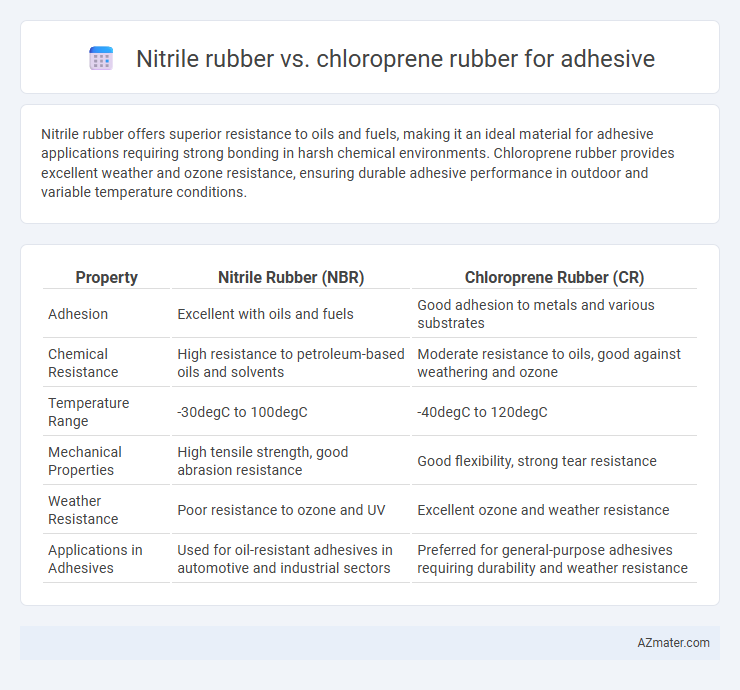
Nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to oils and fuels, making it an ideal material for adhesive applications requiring strong bonding in harsh chemical environments. Chloroprene rubber provides excellent weather and ozone resistance, ensuring durable adhesive performance in outdoor and variable temperature conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) |
|---|---|---|
| Adhesion | Excellent with oils and fuels | Good adhesion to metals and various substrates |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to petroleum-based oils and solvents | Moderate resistance to oils, good against weathering and ozone |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 100degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Mechanical Properties | High tensile strength, good abrasion resistance | Good flexibility, strong tear resistance |
| Weather Resistance | Poor resistance to ozone and UV | Excellent ozone and weather resistance |
| Applications in Adhesives | Used for oil-resistant adhesives in automotive and industrial sectors | Preferred for general-purpose adhesives requiring durability and weather resistance |
Introduction to Nitrile and Chloroprene Rubber
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a synthetic polymer known for its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for adhesive applications requiring durability and chemical stability. Chloroprene rubber (CR), also called neoprene, offers superior weathering, ozone, and flame resistance, alongside good mechanical properties, which enhances the adhesive's performance in outdoor and harsh environments. Both elastomers provide unique benefits, with NBR favored for oil resistance and CR valued for environmental resilience in adhesive formulations.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, characterized by its polar nitrile groups which provide strong resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for adhesive applications requiring chemical resistance. Chloroprene rubber (CR), composed of polychloroprene, exhibits a balanced molecular structure with chlorine atoms that enhance weather, ozone, and flame resistance, contributing to durable adhesive bonds under harsh environmental conditions. The chemical composition difference results in NBR adhesives offering superior oil and solvent resistance, while CR adhesives provide enhanced physical durability and environmental stability.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Nitrile rubber exhibits superior oil and fuel resistance, making it ideal for adhesives exposed to hydrocarbons, while chloroprene rubber offers excellent weathering and ozone resistance with good flexibility over a wide temperature range. Nitrile rubber typically has higher tensile strength and abrasion resistance, enhancing the durability of adhesive bonds under mechanical stress compared to chloroprene. Chloroprene's better resilience and aging stability contribute to long-lasting adhesive performance in outdoor or harsh environmental conditions.
Adhesion Performance and Strength
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior adhesion performance to polar substrates such as metals and rubbers due to its excellent oil and chemical resistance, making it ideal for industrial adhesive applications requiring strong bonding under harsh conditions. Chloroprene rubber (CR), known for its balanced adhesion properties and good weather and ozone resistance, provides reliable bonding strength on non-polar surfaces like plastics and wood, with higher tensile strength and elongation contributing to durable adhesive joints. Both elastomers exhibit strong cohesive strength, but NBR excels in adhesive durability against hydrocarbons while CR delivers enhanced mechanical stability and aging resistance in diverse environments.
Resistance to Chemicals and Solvents
Nitrile rubber (NBR) exhibits superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals and solvents including oils, fuels, and alcohols, making it ideal for adhesive applications exposed to harsh environments. Chloroprene rubber (CR), while offering good resistance to weathering and ozone, shows moderate resistance to chemicals but can degrade when exposed to strong acids or alkalis. Selecting NBR ensures enhanced durability and chemical resistance in adhesives used in industrial and automotive sectors.
Flexibility and Mechanical Durability
Nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to oils and fuels, providing excellent mechanical durability in adhesive applications exposed to harsh environments, while maintaining moderate flexibility. Chloroprene rubber (Neoprene) excels in flexibility and weather resistance, making it ideal for adhesives requiring elasticity and resilience against UV exposure and ozone. Choosing between nitrile and chloroprene depends on the specific balance needed between mechanical strength and flexible performance in the adhesive's operating conditions.
Temperature and Weather Resistance
Nitrile rubber exhibits superior resistance to heat and oil, maintaining its adhesive strength effectively between -40degC and 120degC, making it ideal for applications exposed to fluctuating temperatures. Chloroprene rubber offers enhanced weather resistance, including ozone, sunlight, and UV stability, with a usable temperature range from -40degC to 100degC, ensuring long-lasting durability in outdoor environments. Both elastomers provide robust adhesion properties, but nitrile excels in high-temperature oily conditions while chloroprene is preferred for exposure to harsh weather elements.
Applications in Adhesive Formulations
Nitrile rubber offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for adhesive formulations used in automotive and industrial applications where strong bonding to metal and rubber surfaces is critical. Chloroprene rubber provides superior weather, ozone, and heat resistance, enhancing adhesives for outdoor, marine, and construction uses that require durability under harsh environmental conditions. Both elastomers contribute distinct mechanical and chemical properties to pressure-sensitive adhesives, sealants, and bonding agents, optimizing performance based on specific application requirements.
Cost and Availability Factors
Nitrile rubber offers a cost-effective solution for adhesives due to its widespread availability and lower raw material expenses compared to chloroprene rubber. Chloroprene rubber, while generally more expensive, provides consistent supply chains predominantly sourced from established producers in Asia and North America. The cost differential often influences manufacturers to choose nitrile rubber for large-scale adhesive production where budget and material accessibility are critical.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Adhesive Use
Nitrile rubber offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for adhesives requiring strong bonding in harsh environments and industrial applications. Chloroprene rubber provides superior weather, ozone, and aging resistance, suitable for outdoor adhesives exposed to variable conditions and UV light. Selecting the right rubber depends on the adhesive's exposure to chemicals versus environmental factors, where nitrile excels in chemical resistance and chloroprene in durability and flexibility.
Infographic: Nitrile rubber vs Chloroprene rubber for Adhesive
 azmater.com
azmater.com