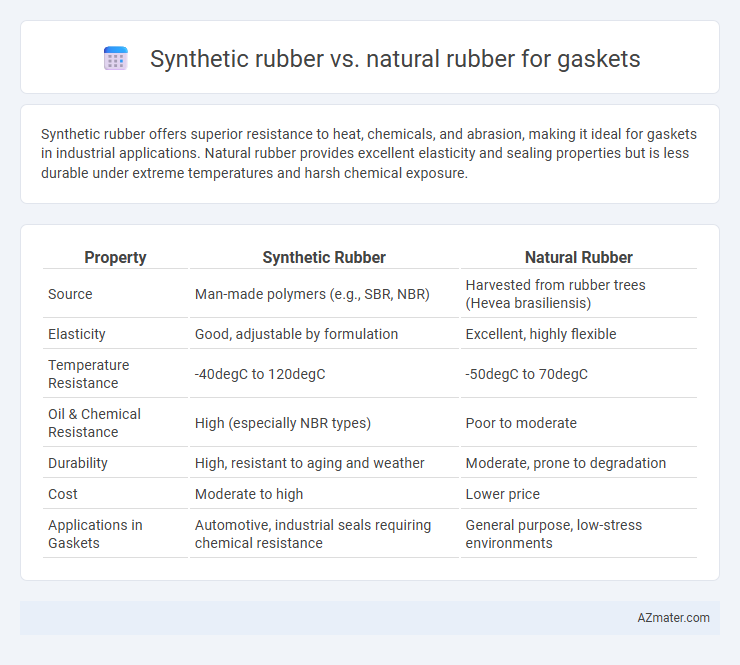
Synthetic rubber offers superior resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion, making it ideal for gaskets in industrial applications. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and sealing properties but is less durable under extreme temperatures and harsh chemical exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Synthetic Rubber | Natural Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Man-made polymers (e.g., SBR, NBR) | Harvested from rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis) |
| Elasticity | Good, adjustable by formulation | Excellent, highly flexible |
| Temperature Resistance | -40degC to 120degC | -50degC to 70degC |
| Oil & Chemical Resistance | High (especially NBR types) | Poor to moderate |
| Durability | High, resistant to aging and weather | Moderate, prone to degradation |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Lower price |
| Applications in Gaskets | Automotive, industrial seals requiring chemical resistance | General purpose, low-stress environments |
Introduction to Rubber Gaskets
Rubber gaskets serve as essential sealing components in various industrial applications, offering flexibility and resistance to pressure, chemicals, and temperature. Synthetic rubber gaskets, made from polymers like neoprene, nitrile, and EPDM, provide enhanced durability, chemical resistance, and temperature tolerance compared to natural rubber gaskets derived from latex. Selection between synthetic and natural rubber depends on specific operational requirements such as exposure to oils, heat, and environmental conditions.
Overview of Natural Rubber
Natural rubber, derived from the latex sap of Hevea brasiliensis trees, offers excellent elasticity, abrasion resistance, and tensile strength, making it an ideal material for gaskets in dynamic applications. Its high resilience and superior sealing capabilities ensure effective performance in environments requiring flexibility and resistance to water and various chemicals. However, natural rubber's vulnerability to oils, solvents, and extreme temperatures limits its use compared to synthetic alternatives in demanding industrial settings.
Overview of Synthetic Rubber
Synthetic rubber, such as nitrile, neoprene, and EPDM, offers superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and temperature extremes compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for gasket applications in automotive and industrial sectors. Its engineered molecular structure provides enhanced durability, flexibility, and aging resistance, ensuring longer service life and consistent sealing performance under harsh conditions. Synthetic rubber gaskets excel in environments requiring specific chemical compatibility and mechanical properties that natural rubber cannot reliably provide.
Key Differences Between Synthetic and Natural Rubber
Synthetic rubber offers superior resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion, making it ideal for gaskets in harsh industrial environments. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and tensile strength but is less durable against oil, solvents, and extreme temperatures. The key differences lie in synthetic rubber's enhanced weather resistance and stability compared to natural rubber's biodegradability and softer texture.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Synthetic rubber gaskets exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to natural rubber, particularly against oils, acids, and solvents commonly encountered in industrial applications. Natural rubber tends to degrade when exposed to hydrocarbons and strong chemicals, limiting its effectiveness in harsh environments. Key synthetic variants like nitrile, neoprene, and EPDM offer enhanced durability and long-term performance, making them ideal for gaskets requiring reliable chemical resistance.
Temperature Tolerance and Performance
Synthetic rubber gaskets, such as those made from nitrile (NBR) or silicone, offer superior temperature tolerance ranging from -40degC to 200degC, making them ideal for applications involving extreme heat or cold. Natural rubber gaskets typically withstand temperatures between -30degC and 70degC but excel in flexibility, resilience, and resistance to wear under moderate conditions. Performance-wise, synthetic rubber provides enhanced chemical resistance and durability in harsh environments, whereas natural rubber delivers excellent sealing and elasticity in less demanding temperature ranges.
Durability and Lifespan Factors
Synthetic rubber gaskets offer enhanced durability compared to natural rubber due to superior resistance to heat, chemicals, and ozone exposure, making them ideal for harsh industrial environments. Natural rubber gaskets provide excellent elasticity and resilience but tend to degrade faster when exposed to UV radiation, oils, and extreme temperatures, limiting their lifespan in demanding applications. The choice between synthetic and natural rubber significantly impacts gasket lifespan, with synthetic variants typically lasting longer under aggressive conditions.
Cost Analysis: Synthetic vs. Natural Rubber Gaskets
Synthetic rubber gaskets typically offer lower production costs due to consistent material availability and scalable manufacturing processes, whereas natural rubber gaskets may incur higher expenses linked to raw material variability and seasonal supply fluctuations. The durability and chemical resistance of synthetic rubber often reduce long-term maintenance and replacement costs compared to natural rubber gaskets, despite slightly higher initial prices in some cases. Cost optimization analysis favors synthetic rubber for industrial gasket applications where performance consistency and lifecycle expenses are critical factors.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Synthetic rubber gaskets, often derived from petroleum-based polymers like neoprene and nitrile, exhibit longer durability but entail higher environmental footprints due to non-renewable resource extraction and complex chemical processing. Natural rubber gaskets, sourced from Hevea brasiliensis, offer biodegradability and renewable origin, reducing ecological impact but may face challenges in consistent performance and susceptibility to degradation under certain conditions. Life cycle assessments highlight that incorporating recycled synthetic rubber or sustainably harvested natural rubber enhances gasket sustainability without compromising functional integrity.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Gasket Application
Synthetic rubber offers superior resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion, making it ideal for gaskets in automotive, industrial, and chemical processing applications. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity, resilience, and tensile strength, which is beneficial for gaskets requiring flexibility and sealing under dynamic conditions. Selecting the right rubber depends on the operating environment, exposure to chemicals, temperature range, and mechanical stress to ensure gasket durability and performance.
Infographic: Synthetic rubber vs Natural rubber for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com