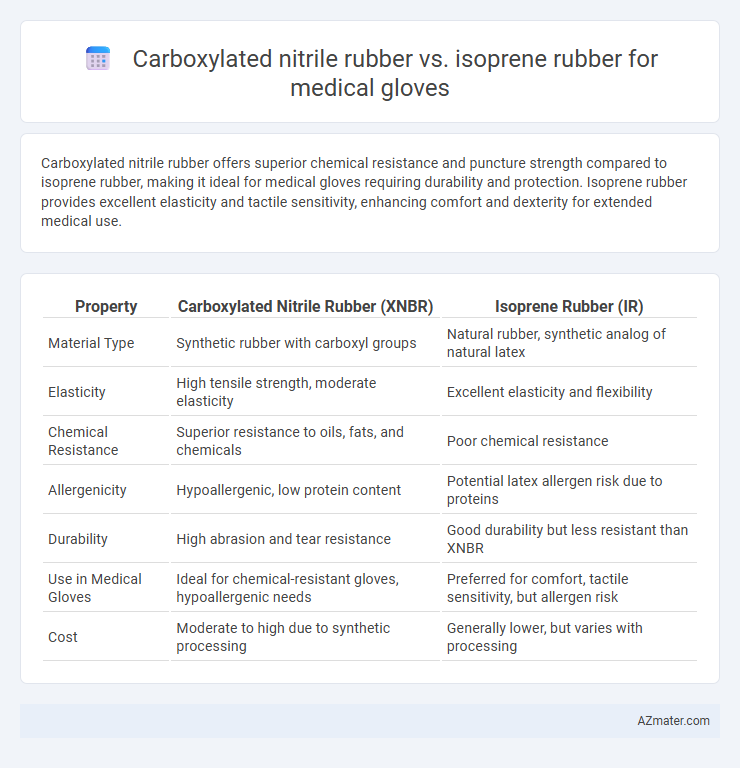
Carboxylated nitrile rubber offers superior chemical resistance and puncture strength compared to isoprene rubber, making it ideal for medical gloves requiring durability and protection. Isoprene rubber provides excellent elasticity and tactile sensitivity, enhancing comfort and dexterity for extended medical use.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Isoprene Rubber (IR) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic rubber with carboxyl groups | Natural rubber, synthetic analog of natural latex |
| Elasticity | High tensile strength, moderate elasticity | Excellent elasticity and flexibility |
| Chemical Resistance | Superior resistance to oils, fats, and chemicals | Poor chemical resistance |
| Allergenicity | Hypoallergenic, low protein content | Potential latex allergen risk due to proteins |
| Durability | High abrasion and tear resistance | Good durability but less resistant than XNBR |
| Use in Medical Gloves | Ideal for chemical-resistant gloves, hypoallergenic needs | Preferred for comfort, tactile sensitivity, but allergen risk |
| Cost | Moderate to high due to synthetic processing | Generally lower, but varies with processing |
Introduction to Medical Glove Materials
Carboxylated nitrile rubber offers enhanced chemical resistance and puncture durability, making it highly suitable for medical gloves used in environments requiring protection against harsh chemicals and oils. Isoprene rubber provides excellent elasticity and tactile sensitivity, closely mimicking natural latex while reducing allergy risks associated with latex proteins. Both materials balance critical performance factors such as barrier protection, comfort, and hypoallergenic properties essential for medical glove applications.
Overview of Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR)
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) features enhanced tensile strength, improved elasticity, and superior chemical resistance, making it highly suitable for medical glove applications. Its carboxyl groups facilitate stronger cross-linking, resulting in better puncture resistance and durability compared to non-carboxylated nitrile variants. XNBR gloves also offer excellent protection against oils, solvents, and many disinfectants, ensuring safety and comfort for healthcare professionals.
Key Properties of Isoprene Rubber (IR)
Isoprene Rubber (IR) offers superior elasticity, softness, and resilience compared to Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber, making it highly suitable for medical gloves requiring high tactile sensitivity and comfort. Its excellent conformability and low protein content reduce the risk of allergic reactions, enhancing patient safety during medical procedures. IR also exhibits strong puncture resistance and biocompatibility, essential for durable and reliable protection in healthcare environments.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to isoprene rubber in medical gloves, offering higher tensile strength and enhanced tear resistance essential for durability in clinical settings. The presence of carboxyl groups in XNBR facilitates stronger crosslinking, resulting in improved abrasion resistance and elongation at break compared to natural isoprene rubber. Isoprene rubber, while providing excellent elasticity and comfort, generally falls short in mechanical resilience, making XNBR a preferred choice for gloves requiring enhanced protection and durability.
Chemical Resistance and Protection
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior chemical resistance compared to isoprene rubber, making it more effective in protecting against a wide range of acids, oils, and solvents commonly encountered in medical environments. Isoprene rubber provides excellent elasticity and comfort but has limited resistance to degradation by chemicals and oils, reducing its protective efficacy in chemical exposure scenarios. For medical gloves requiring robust chemical resistance and barrier protection, carboxylated nitrile rubber is the preferable material due to its enhanced durability and chemical inertness.
Allergy and Sensitization Risks
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers significantly lower allergy and sensitization risks compared to isoprene rubber due to its synthetic composition, which lacks natural latex proteins known to cause Type I hypersensitivity reactions. Isoprene rubber, derived from natural latex, contains residual proteins that can trigger allergic responses in sensitive individuals, making it less suitable for medical gloves in allergy-prone environments. The reduced allergenic potential of XNBR medical gloves enhances patient and healthcare worker safety by minimizing immune sensitization and contact dermatitis occurrences.
Comfort, Fit, and Tactile Sensitivity
Carboxylated nitrile rubber offers greater chemical resistance and durability compared to Isoprene rubber, enhancing glove longevity in medical settings, but Isoprene rubber provides superior elasticity and softness, resulting in better comfort and fit. Isoprene gloves closely mimic natural latex in tactile sensitivity, ideal for precise medical procedures, while carboxylated nitrile gloves, though less sensitive, offer improved puncture resistance. Medical professionals prioritizing tactile sensitivity and a natural feel often prefer isoprene rubber, whereas those requiring enhanced barrier protection choose carboxylated nitrile rubber gloves.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Carboxylated nitrile rubber offers higher resistance to punctures and chemicals compared to isoprene rubber, often justifying a slightly higher raw material cost in medical glove production. Manufacturing carboxylated nitrile gloves typically requires advanced curing and processing techniques that can increase production time but improve consistent quality and durability. Isoprene rubber, while generally less expensive and easier to process, may lead to higher overall costs due to lower resistance properties and increased waste during manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) for medical gloves offers enhanced chemical resistance and durability but involves synthetic production processes with significant reliance on petrochemical resources, leading to higher environmental impact compared to natural rubber alternatives. Isoprene rubber, derived from renewable sources through sustainable cultivation of rubber trees, provides biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint in medical glove manufacturing. Sustainable sourcing and end-of-life degradation make isoprene rubber gloves more environmentally friendly, while carboxylated nitrile gloves present challenges in waste management and resource renewability.
Choosing the Right Glove Material for Healthcare Applications
Carboxylated nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to punctures, chemicals, and oils compared to isoprene rubber, making it ideal for healthcare environments requiring high durability and protection. Isoprene rubber provides excellent elasticity and a natural latex-like feel, reducing the risk of latex allergies while maintaining comfort and sensitivity for prolonged medical use. Selecting the right glove material involves balancing protection, tactile sensitivity, and allergy considerations to ensure safe and effective healthcare applications.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Isoprene rubber for Medical glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com