Synthetic rubber offers superior resistance to chemicals, temperature extremes, and aging, making it ideal for seals in harsh industrial environments. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and resilience but degrades faster under UV exposure and harsh chemicals, limiting its use in demanding sealing applications.
Table of Comparison
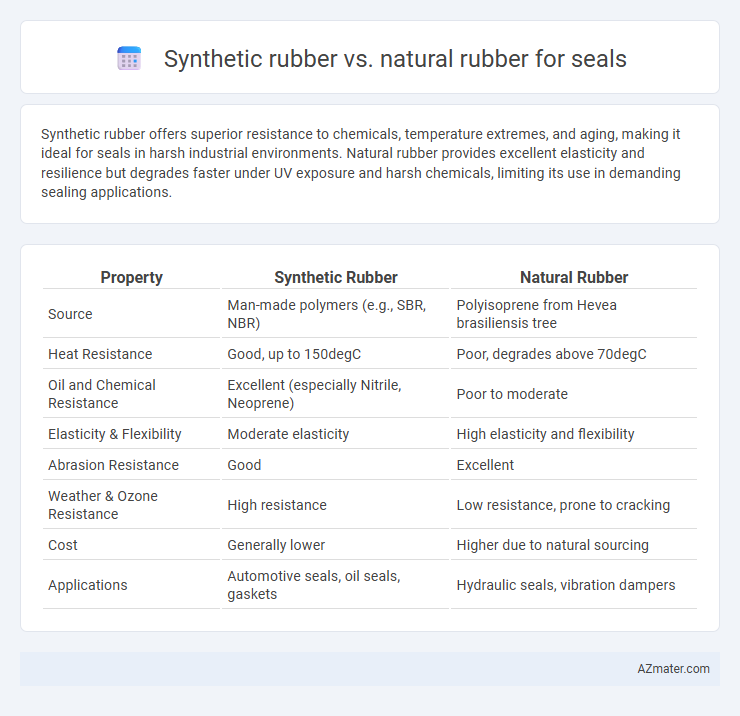
| Property | Synthetic Rubber | Natural Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Man-made polymers (e.g., SBR, NBR) | Polyisoprene from Hevea brasiliensis tree |
| Heat Resistance | Good, up to 150degC | Poor, degrades above 70degC |
| Oil and Chemical Resistance | Excellent (especially Nitrile, Neoprene) | Poor to moderate |
| Elasticity & Flexibility | Moderate elasticity | High elasticity and flexibility |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | High resistance | Low resistance, prone to cracking |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to natural sourcing |
| Applications | Automotive seals, oil seals, gaskets | Hydraulic seals, vibration dampers |
Introduction to Rubber Seals
Rubber seals are essential components in various industries, designed to prevent fluid leakage and maintain airtight or watertight environments. Synthetic rubber, such as nitrile, EPDM, and silicone, offers superior resistance to chemicals, temperature extremes, and aging compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for harsh industrial applications. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and tensile strength but is less resistant to oils, ozone, and heat, limiting its use to less demanding sealing environments.
Overview: Synthetic Rubber vs Natural Rubber
Synthetic rubber offers enhanced resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion, making it ideal for seals in harsh environments, while natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and tensile strength, favored for applications requiring flexibility and resilience. Natural rubber exhibits superior tear resistance and good dynamic properties, suitable for seals in less aggressive conditions. The selection between synthetic and natural rubber depends on specific operating temperatures, chemical exposures, and mechanical demands of the sealing application.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Synthetic rubber, primarily composed of polymers such as styrene-butadiene (SBR) or nitrile butadiene (NBR), features a tailored chemical structure with uniform polymer chains that enhance resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals, making it ideal for seals in harsh environments. Natural rubber consists of polyisoprene with a cis-1,4 configuration, providing high elasticity and tensile strength but lower chemical resistance compared to synthetic variants. The cross-linked molecular structure in both types determines flexibility and durability, with synthetic rubber offering greater customization to meet specific sealing requirements.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Synthetic rubber offers superior mechanical properties for seals, including enhanced tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and elasticity, making it ideal for high-stress applications. Natural rubber provides excellent resilience, high tear strength, and good flexibility, but it often degrades faster under heat, ozone, and chemical exposure. The choice between synthetic and natural rubber seals depends on specific performance requirements such as durability, environmental resistance, and mechanical load conditions.
Temperature and Weather Resistance
Synthetic rubber seals exhibit superior temperature resistance, maintaining flexibility and performance in extreme heat and cold, often ranging from -60degC to 200degC depending on the compound. Natural rubber seals offer excellent elasticity but degrade faster under prolonged exposure to UV light, ozone, and harsh weather conditions, limiting their durability outdoors. For applications requiring long-term weather resistance and stable performance across wide temperature variations, synthetic rubber is the optimal choice.
Compatibility with Fluids and Chemicals
Synthetic rubber, such as nitrile (NBR) and fluoroelastomer (FKM), offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, and a wide range of chemicals, making it highly compatible for seals in harsh industrial environments. Natural rubber exhibits excellent flexibility and tensile strength but is less resistant to petroleum-based fluids, acids, and solvents, limiting its use in aggressive chemical applications. Selecting synthetic rubber seals ensures enhanced durability and longer service life when exposed to diverse fluids and chemicals compared to natural rubber.
Longevity and Durability
Synthetic rubber seals exhibit superior longevity and durability compared to natural rubber due to their enhanced resistance to heat, chemicals, and aging. Materials like nitrile, EPDM, and silicone maintain elasticity and structural integrity under extreme conditions, reducing the risk of cracks and deformation over time. Natural rubber seals, while flexible, tend to degrade faster when exposed to ozone, UV light, and oils, leading to shorter service life in demanding environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Synthetic rubber for seals, produced from petrochemicals, often generates higher greenhouse gas emissions and relies on non-renewable resources, contributing to environmental degradation. Natural rubber, harvested from rubber trees, is a renewable resource with a lower carbon footprint and promotes biodiversity when sourced from well-managed plantations. Choosing natural rubber over synthetic alternatives supports sustainability goals by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and enhancing ecosystem health.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Synthetic rubber offers greater cost efficiency for seals due to lower raw material price volatility and mass production scalability, making it ideal for large-volume applications. Natural rubber, derived from latex sap of rubber trees, can be more expensive and less consistent in supply because it depends on agricultural conditions and seasonal harvesting. Availability of synthetic rubber remains more reliable year-round, supporting continuous manufacturing demands without interruption.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Seals
Synthetic rubber, including materials like nitrile (NBR), silicone, and EPDM, offers superior resistance to chemicals, oils, and extreme temperatures, making it ideal for seals in industrial and automotive applications exposed to harsh environments. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity, resilience, and mechanical strength, suitable for seals in dynamic applications requiring flexibility and high abrasion resistance, such as in hydraulic systems. Selecting the right rubber for seals depends on factors like chemical compatibility, temperature range, mechanical stress, and exposure conditions to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Synthetic rubber vs Natural rubber for Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com