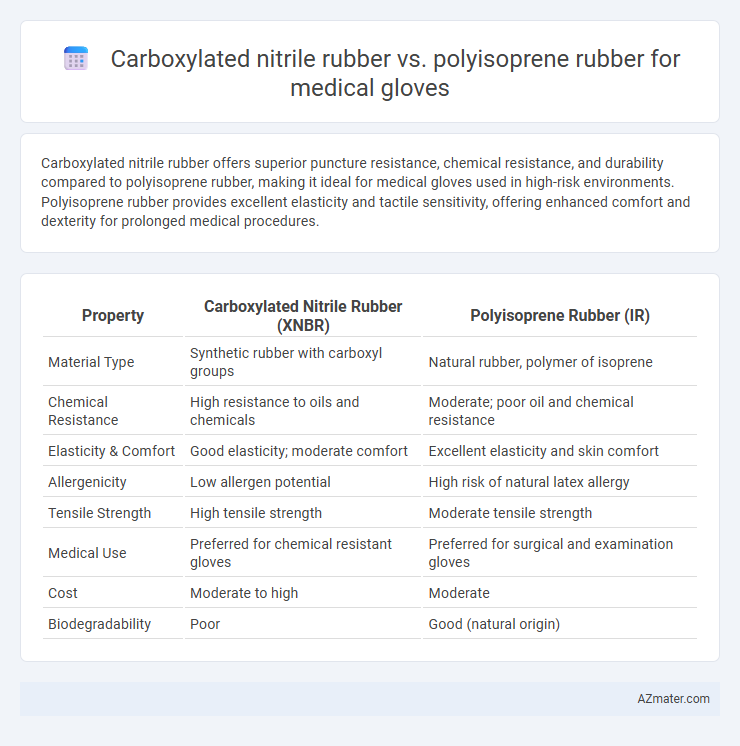
Carboxylated nitrile rubber offers superior puncture resistance, chemical resistance, and durability compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it ideal for medical gloves used in high-risk environments. Polyisoprene rubber provides excellent elasticity and tactile sensitivity, offering enhanced comfort and dexterity for prolonged medical procedures.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Polyisoprene Rubber (IR) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic rubber with carboxyl groups | Natural rubber, polymer of isoprene |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to oils and chemicals | Moderate; poor oil and chemical resistance |
| Elasticity & Comfort | Good elasticity; moderate comfort | Excellent elasticity and skin comfort |
| Allergenicity | Low allergen potential | High risk of natural latex allergy |
| Tensile Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Medical Use | Preferred for chemical resistant gloves | Preferred for surgical and examination gloves |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
| Biodegradability | Poor | Good (natural origin) |
Overview of Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR)
Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) enhances the chemical resistance and abrasion durability of medical gloves compared to traditional Polyisoprene rubber, making it ideal for high-risk healthcare environments. XNBR gloves exhibit superior tensile strength and puncture resistance while maintaining excellent flexibility and tactile sensitivity, crucial for precise medical procedures. The unique carboxyl groups in XNBR improve compatibility with various compounding ingredients, resulting in gloves that offer better resistance to oils, fuels, and disinfectants than Polyisoprene counterparts.
Properties of Polyisoprene Rubber (IR)
Polyisoprene rubber (IR) used in medical gloves exhibits excellent elasticity and tensile strength, closely mimicking natural rubber latex while offering superior barrier protection against pathogens. Its high resilience and lower protein content reduce allergic reactions, making IR gloves suitable for sensitive applications. Furthermore, IR demonstrates good chemical resistance and tactile sensitivity, ensuring optimal performance for medical professionals during precision tasks.
Key Differences in Chemical Composition
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) contains acrylonitrile, butadiene, and carboxylic acid groups, which enhance its chemical resistance and tensile strength, making it suitable for medical gloves requiring durability and protection against oils and solvents. Polyisoprene rubber is a natural polymer composed primarily of isoprene monomers, offering superior elasticity and tactile sensitivity but lower resistance to chemicals compared to XNBR. The presence of carboxyl groups in XNBR introduces ionic crosslinking sites, improving mechanical properties and chemical resistance, whereas polyisoprene's hydrocarbon backbone provides excellent flexibility and comfort without enhanced chemical protection.
Barrier Protection Performance
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and puncture strength compared to polyisoprene rubber, making XNBR gloves ideal for higher-risk medical environments requiring enhanced barrier protection. Polyisoprene rubber, while providing excellent elasticity and tactile sensitivity, has lower resistance to oils, solvents, and certain chemicals, which may compromise protection against hazardous substances. In terms of barrier performance, carboxylated nitrile gloves demonstrate longer durability under exposure to harsh chemicals, reducing the risk of glove degradation and ensuring reliable protection for medical personnel.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) medical gloves exhibit superior mechanical strength and enhanced durability compared to polyisoprene rubber gloves, owing to the presence of carboxyl groups that improve polymer crosslinking and abrasion resistance. XNBR gloves demonstrate higher tensile strength, greater puncture resistance, and better chemical stability, making them well-suited for demanding healthcare environments. Polyisoprene gloves offer excellent elasticity and tactile sensitivity but generally have lower tear resistance and reduced lifespan under mechanical stress compared to XNBR alternatives.
Comfort and Tactile Sensitivity
Carboxylated nitrile rubber offers superior chemical resistance and durability but tends to be less elastic, impacting overall comfort and tactile sensitivity compared to polyisoprene rubber. Polyisoprene rubber closely mimics natural latex, providing enhanced elasticity and a soft, flexible fit that improves wearer comfort and fine tactile sensitivity critical for delicate medical procedures. The low modulus and high elongation of polyisoprene gloves contribute to better touch precision, making them preferred in environments requiring high dexterity and sensitivity.
Allergenicity and Skin Compatibility
Carboxylated nitrile rubber exhibits lower allergenicity compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it a preferable choice for individuals with latex allergies or sensitive skin. Its chemical composition reduces the presence of natural proteins associated with allergic reactions, enhancing skin compatibility. Polyisoprene rubber, while offering excellent elasticity and tactile sensitivity, contains natural latex proteins that may trigger allergic responses in susceptible users.
Cost-Effectiveness in Medical Glove Production
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced chemical resistance and durability compared to polyisoprene rubber, contributing to longer glove lifespan and reduced replacement frequency in medical settings. Although XNBR gloves might have a higher initial material cost, their superior puncture resistance and extended usability result in lower overall expenses for healthcare providers. Polyisoprene gloves are generally less expensive upfront but may require more frequent replacement due to lower durability, affecting cost-effectiveness in large-scale medical glove production.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced durability and chemical resistance compared to polyisoprene rubber, leading to longer glove lifespan and reduced waste generation. Polyisoprene rubber is biodegradable and derived from natural latex, making it more environmentally sustainable but prone to causing latex allergies. Choosing carboxylated nitrile rubber can reduce environmental impact through extended use and lower allergy risks, while polyisoprene prioritizes biodegradability and renewable resource use in medical glove applications.
Applications and Recommendations for Healthcare Settings
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and tensile strength, making it ideal for medical gloves used in high-risk environments requiring protection against oils, fats, and certain chemicals. Polyisoprene rubber, known for its excellent elasticity and natural latex-like feel, provides enhanced comfort and dexterity, preferred in surgical gloves and procedures demanding tactile sensitivity. Healthcare settings involving exposure to harsh chemicals or extended glove use benefit from XNBR gloves, while polyisoprene gloves are recommended for allergy-sensitive patients and tasks requiring precision.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Polyisoprene rubber for Medical glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com