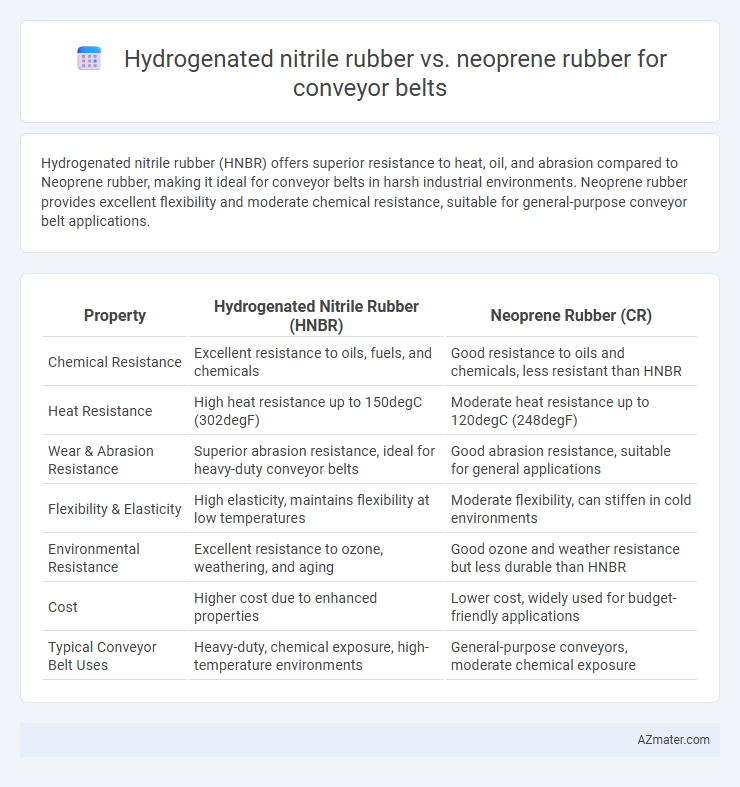
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion compared to Neoprene rubber, making it ideal for conveyor belts in harsh industrial environments. Neoprene rubber provides excellent flexibility and moderate chemical resistance, suitable for general-purpose conveyor belt applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Neoprene Rubber (CR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Good resistance to oils and chemicals, less resistant than HNBR |
| Heat Resistance | High heat resistance up to 150degC (302degF) | Moderate heat resistance up to 120degC (248degF) |
| Wear & Abrasion Resistance | Superior abrasion resistance, ideal for heavy-duty conveyor belts | Good abrasion resistance, suitable for general applications |
| Flexibility & Elasticity | High elasticity, maintains flexibility at low temperatures | Moderate flexibility, can stiffen in cold environments |
| Environmental Resistance | Excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and aging | Good ozone and weather resistance but less durable than HNBR |
| Cost | Higher cost due to enhanced properties | Lower cost, widely used for budget-friendly applications |
| Typical Conveyor Belt Uses | Heavy-duty, chemical exposure, high-temperature environments | General-purpose conveyors, moderate chemical exposure |
Introduction to Conveyor Belt Materials
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) and neoprene rubber are prominent materials used in conveyor belts due to their distinct chemical and physical properties. HNBR offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion, making it ideal for heavy-duty conveyor applications in harsh industrial environments. Neoprene rubber provides excellent weathering and ozone resistance, along with good mechanical properties, suitable for general-purpose conveyor belts exposed to moderate environmental stresses.
What is Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)?
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its exceptional resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals, making it ideal for heavy-duty conveyor belts in harsh industrial environments. Compared to Neoprene rubber, HNBR offers superior abrasion resistance and durability under high temperatures, extending conveyor belt lifespan and reducing maintenance costs. Its enhanced mechanical properties and chemical stability provide reliable performance in automotive, mining, and manufacturing applications where conveyor belts face aggressive conditions.
Overview of Neoprene Rubber
Neoprene rubber, known for its excellent chemical stability and flexibility over a wide temperature range, is widely used in conveyor belts for its resistance to oils, heat, and weathering. This synthetic rubber provides superior durability and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for industrial environments where exposure to harsh conditions is common. Its ability to maintain performance in extreme temperatures and resist environmental degradation ensures reliable conveyor belt operation and longevity.
Key Chemical Properties: HNBR vs Neoprene
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior chemical resistance due to its saturated polymer backbone, providing enhanced resistance to oil, heat, and oxidation compared to neoprene rubber. Neoprene contains chlorine atoms in its polymer chain, contributing to moderate resistance against chemicals, ozone, and weathering but lower thermal stability than HNBR. HNBR's molecular structure results in better tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it more suitable for demanding conveyor belt applications where chemical exposure is significant.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior mechanical strength compared to neoprene rubber, exhibiting higher tensile strength and enhanced abrasion resistance, which makes it more suitable for conveyor belts operating under heavy loads and harsh conditions. HNBR's improved heat and chemical resistance further contribute to its durability and longevity in industrial conveyor applications. Neoprene rubber, while durable, generally has lower tensile strength and is more prone to wear, limiting its performance where mechanical stress is significant.
Temperature Resistance: HNBR vs Neoprene
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior temperature resistance for conveyor belts, maintaining performance in continuous temperatures up to 150degC and intermittent exposure up to 165degC. Neoprene rubber typically withstands lower maximum temperatures around 120degC, making HNBR more suitable for high-heat environments. The enhanced thermal stability of HNBR extends conveyor belt lifespan in demanding industrial applications compared to neoprene.
Oil and Chemical Resistance
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior oil and chemical resistance compared to neoprene rubber, making it ideal for conveyor belts exposed to harsh petroleum-based fluids and aggressive chemicals. HNBR maintains its mechanical properties and resists swelling and degradation in oils, fuels, and solvents, extending conveyor belt lifespan in industrial environments. Neoprene rubber provides moderate chemical resistance but is less effective against petroleum oils and aggressive chemicals, limiting its suitability for demanding oil-rich conveyor applications.
Cost Analysis: HNBR vs Neoprene Rubber
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) generally incurs higher upfront costs compared to neoprene rubber due to its superior chemical resistance and durability, which can lead to longer conveyor belt lifespan and reduced maintenance expenses. Neoprene rubber offers a more cost-effective solution for applications with less demanding environmental conditions, providing a balance between performance and initial investment. When evaluating conveyor belt materials, total cost of ownership favors HNBR in harsh environments where frequent replacements and downtime are costly.
Application Suitability for Conveyor Belts
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior oil, heat, and abrasion resistance, making it highly suitable for conveyor belts in harsh industrial environments such as automotive and chemical processing plants. Neoprene rubber provides excellent weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, ideal for conveyor belts exposed to outdoor conditions or moderate chemical exposure. When selecting a conveyor belt material, HNBR excels in heavy-duty applications requiring durability against hydrocarbons, while neoprene is preferred for applications demanding flexibility and resistance to environmental aging.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Conveyor Belt Durability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oils, and abrasion, making it ideal for conveyor belts in harsh industrial environments. Neoprene rubber provides excellent weather and ozone resistance but falls short in high-temperature and chemical exposure compared to HNBR. Selecting HNBR enhances conveyor belt durability where chemical and thermal stability are critical, while neoprene suits moderate environments with good flexibility.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Neoprene rubber for Conveyor belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com