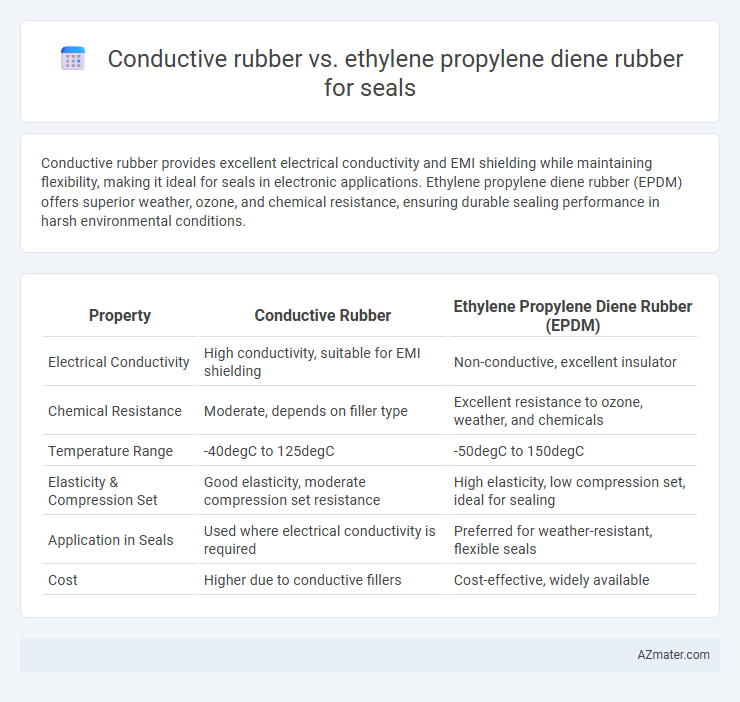
Conductive rubber provides excellent electrical conductivity and EMI shielding while maintaining flexibility, making it ideal for seals in electronic applications. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers superior weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, ensuring durable sealing performance in harsh environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Conductive Rubber | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High conductivity, suitable for EMI shielding | Non-conductive, excellent insulator |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate, depends on filler type | Excellent resistance to ozone, weather, and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 125degC | -50degC to 150degC |
| Elasticity & Compression Set | Good elasticity, moderate compression set resistance | High elasticity, low compression set, ideal for sealing |
| Application in Seals | Used where electrical conductivity is required | Preferred for weather-resistant, flexible seals |
| Cost | Higher due to conductive fillers | Cost-effective, widely available |
Introduction to Rubber Materials for Seals
Conductive rubber and ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber represent two key materials used in sealing applications, each offering distinct properties tailored to specific requirements. Conductive rubber integrates carbon or metal particles to provide electrical conductivity, making it essential for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and grounding seals, whereas EPDM is prized for its excellent weather resistance, ozone resistance, and consistent performance in extreme temperatures, making it ideal for outdoor and automotive seals. The selection between conductive rubber and EPDM depends on the primary functional demands such as electrical conductivity versus environmental durability in seal material applications.
Overview of Conductive Rubber
Conductive rubber, composed of elastomeric materials embedded with conductive fillers like carbon black or metal particles, offers excellent electrical conductivity and flexibility essential for sealing applications in electronic devices. Its ability to maintain consistent conductivity under compression makes it ideal for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and grounding seals. Compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, conductive rubber provides superior electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection while maintaining durability and environmental resistance.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) is a synthetic elastomer widely used in sealing applications due to its excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, UV radiation, and a broad range of temperatures from -40degC to 150degC. EPDM offers superior chemical resistance to acids, alkalis, and polar solvents, making it ideal for automotive seals, roofing membranes, and industrial gaskets. Its high elasticity and durability ensure long-term performance in dynamic and static seal environments, outperforming many materials including conductive rubber in non-conductive sealing tasks.
Key Properties: Conductivity vs. Insulation
Conductive rubber exhibits excellent electrical conductivity due to the integration of conductive fillers like carbon or metal particles, making it ideal for applications requiring electromagnetic interference shielding or static dissipation in seals. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) is valued for its superior electrical insulation properties, outstanding chemical resistance, and weatherability, making it suitable for seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions. The choice between conductive rubber and EPDM hinges on the specific sealing requirement for either electrical conductivity or high dielectric strength and environmental resilience.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Conductive rubber exhibits moderate chemical resistance but can degrade when exposed to strong acids, bases, and solvents, limiting its use in aggressive chemical environments. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and oxygenated solvents, making it ideal for seals in harsh chemical applications. EPDM's robust chemical stability enhances seal longevity and performance where chemical exposure is a critical factor.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Conductive rubber seals are extensively used in electronics and automotive industries for EMI shielding and static dissipation, offering excellent electrical conductivity and durability in harsh environments. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) seals excel in automotive weatherstripping, roofing, and HVAC systems due to superior resistance to heat, ozone, UV exposure, and weathering. While conductive rubber is ideal for applications requiring electrical performance, EPDM is preferred in industries demanding chemical and environmental resilience for sealing solutions.
Environmental Performance and Durability
Conductive rubber offers superior electrical conductivity and environmental resistance, making it ideal for seals in electronic and automotive applications where exposure to moisture and chemicals is common. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in UV, ozone, and weather resistance, providing exceptional durability for outdoor and automotive sealing solutions subject to temperature variations and harsh environmental conditions. EPDM generally demonstrates longer lifespan in extreme weather, while conductive rubber is preferred for applications requiring both environmental resilience and electrical functionality.
Cost Analysis: Conductive Rubber vs. EPDM
Conductive rubber typically incurs higher initial costs than Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) due to its specialized formulation with conductive fillers such as carbon black or metal powders. EPDM offers a cost-effective solution for sealing applications with excellent weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, making it a preferred choice for large-scale industrial use where electrical conductivity is not required. When factoring in total cost of ownership, conductive rubber's premium price can be justified in applications demanding electrical conductivity, whereas EPDM provides significant savings in general sealing tasks.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Conductive rubber seals offer superior electrical conductivity and are ideal for environments requiring static dissipation, but they often demand careful handling during installation to maintain their conductive properties. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber seals provide exceptional resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemicals, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and longer service life in outdoor or industrial settings. Installation of EPDM seals is generally more straightforward due to their flexibility and durability, reducing the risk of damage and the frequency of replacement compared to conductive rubber options.
Choosing the Right Rubber Seal Material
Conductive rubber offers excellent electrical conductivity and EMI shielding capabilities, making it ideal for sealing applications requiring static dissipation and electromagnetic interference protection. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in resistance to weathering, ozone, and a broad range of chemicals, providing superior durability for outdoor and automotive seals. Choosing the right rubber seal material depends on application-specific factors such as electrical requirements, environmental exposure, and chemical compatibility to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Conductive rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com