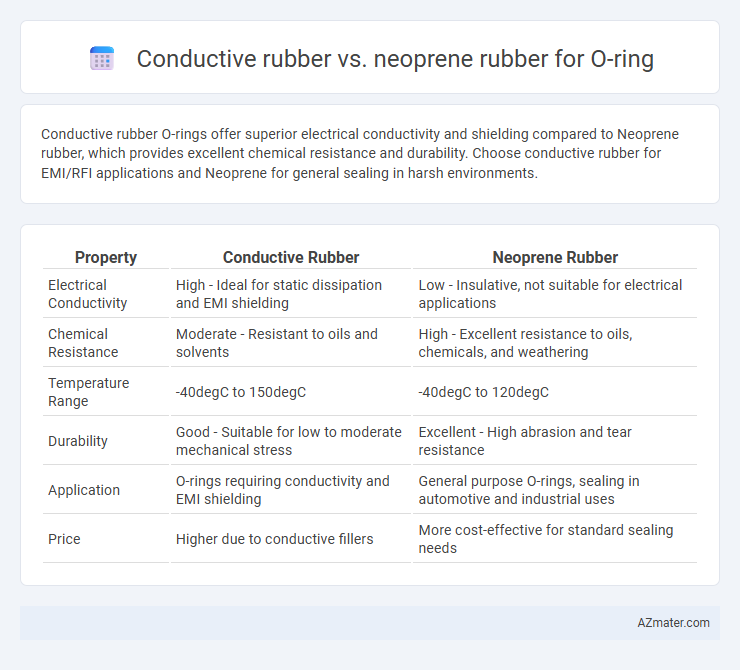
Conductive rubber O-rings offer superior electrical conductivity and shielding compared to Neoprene rubber, which provides excellent chemical resistance and durability. Choose conductive rubber for EMI/RFI applications and Neoprene for general sealing in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Conductive Rubber | Neoprene Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High - Ideal for static dissipation and EMI shielding | Low - Insulative, not suitable for electrical applications |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate - Resistant to oils and solvents | High - Excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Durability | Good - Suitable for low to moderate mechanical stress | Excellent - High abrasion and tear resistance |
| Application | O-rings requiring conductivity and EMI shielding | General purpose O-rings, sealing in automotive and industrial uses |
| Price | Higher due to conductive fillers | More cost-effective for standard sealing needs |
Introduction to O-Ring Materials
Conductive rubber and neoprene rubber serve distinct purposes in O-ring applications, with conductive rubber offering electrical conductivity essential for electromagnetic shielding and static dissipation. Neoprene rubber provides excellent chemical resistance, weather durability, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for general sealing and industrial environments. Choosing between conductive and neoprene rubbers for O-rings depends on specific requirements such as conductivity needs, chemical exposure, and environmental stress.
Overview of Conductive Rubber
Conductive rubber for O-rings is engineered with carbon or metallic fillers to provide excellent electrical conductivity and dissipation of static electricity, making it ideal for electronic and anti-static applications. This material offers robust resistance to compression set and vibration, ensuring long-term sealing performance in sensitive environments. In contrast, neoprene rubber primarily delivers strong chemical and weather resistance but lacks the electrical conductivity essential for ESD protection.
Overview of Neoprene Rubber
Neoprene rubber is a versatile synthetic elastomer widely used for O-rings due to its excellent chemical stability and resistance to oils, solvents, and weathering. It offers moderate conductivity when combined with additives but is predominantly valued for its durability, flexibility, and resistance to abrasion and ozone. Compared to conductive rubber, Neoprene provides superior sealing reliability in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications where environmental resistance and mechanical strength are critical.
Key Properties Comparison
Conductive rubber O-rings provide excellent electrical conductivity and static dissipation, making them ideal for electronic sealing applications, while Neoprene rubber O-rings offer superior chemical resistance and durability in harsh environments. Conductive rubber typically contains carbon or metal fillers that enhance conductivity but may compromise flexibility compared to Neoprene's balanced elasticity and resilience. Both materials provide robust sealing performance, but the choice depends on the application requirements for electrical conductivity versus chemical and weather resistance.
Electrical Conductivity Differences
Conductive rubber O-rings utilize embedded conductive fillers such as carbon or metal particles to provide low electrical resistance, enabling effective dissipation of static electricity and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding. Neoprene rubber O-rings, composed primarily of chloroprene polymers, exhibit excellent chemical and weather resistance but lack inherent electrical conductivity, making them unsuitable for applications requiring electrical grounding or signal transmission. The electrical conductivity of conductive rubber significantly outperforms neoprene, making it the preferred material in electronic, automotive, and aerospace sealing applications where EMI mitigation is critical.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Conductive rubber O-rings exhibit superior resistance to static electricity and are highly effective in environments requiring electrostatic discharge protection, but their chemical resistance can vary widely depending on the specific conductive filler used. Neoprene rubber O-rings offer excellent resistance to a broad spectrum of chemicals including oils, fuels, and mild acids, and display robust performance under harsh environmental conditions such as ozone, weathering, and temperature extremes. For applications demanding high chemical inertness combined with environmental durability, neoprene is often preferred due to its well-documented stability and resistance to degradation.
Common Applications in Industry
Conductive rubber O-rings are widely used in electronic enclosures, medical devices, and aerospace applications due to their ability to dissipate static electricity and provide electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding. Neoprene rubber O-rings are favored in automotive, refrigeration, and oil and gas industries for their excellent chemical resistance, weathering durability, and resistance to oils and temperature extremes. Both materials serve critical sealing functions but are chosen based on specific industry requirements for electrical conductivity or chemical resilience.
Durability and Longevity
Conductive rubber O-rings offer superior durability in applications requiring resistance to electrical interference and static discharge, maintaining performance under frequent compression. Neoprene rubber O-rings exhibit excellent longevity due to their resistance to weathering, ozone, and moderate chemical exposure, making them ideal for outdoor and industrial environments. Both materials provide reliable sealing performance, but conductive rubber excels in electrically sensitive settings, while neoprene ensures extended service life in harsh physical conditions.
Cost and Availability
Conductive rubber O-rings typically cost more than neoprene rubber due to specialized conductive fillers and limited manufacturing sources, whereas neoprene rubber is widely available and more affordable because of its broader industrial use. Neoprene offers reliable sealing properties and moderate chemical resistance, making it a cost-effective choice for general applications, while conductive rubber is essential for static dissipation in electronics but comes with higher procurement expenses. Availability of neoprene is global and consistent, whereas conductive rubber may experience longer lead times and regional supply constraints.
Choosing the Right Rubber for O-Rings
Conductive rubber O-rings offer superior electrical conductivity and static dissipation, making them ideal for electronic and EMI shielding applications, while neoprene rubber provides excellent chemical resistance and durability in industrial environments. Selecting the right rubber for O-rings depends on specific requirements such as conductivity, chemical exposure, temperature range, and mechanical stress. Evaluating the performance characteristics of conductive rubber versus neoprene ensures optimal sealing, longevity, and functionality in the intended application.
Infographic: Conductive rubber vs Neoprene rubber for O-ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com