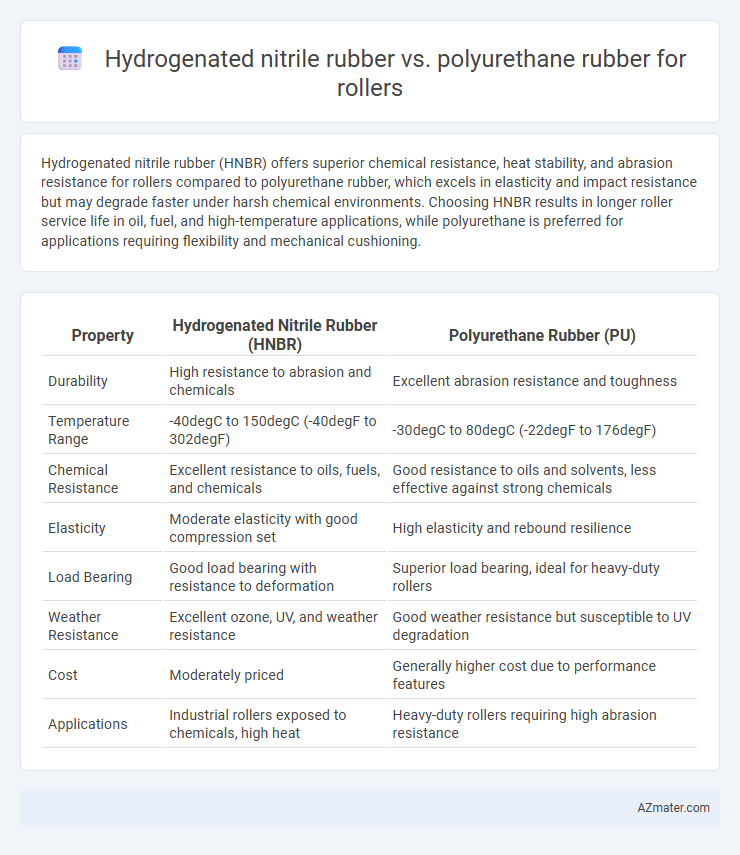
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, heat stability, and abrasion resistance for rollers compared to polyurethane rubber, which excels in elasticity and impact resistance but may degrade faster under harsh chemical environments. Choosing HNBR results in longer roller service life in oil, fuel, and high-temperature applications, while polyurethane is preferred for applications requiring flexibility and mechanical cushioning.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to abrasion and chemicals | Excellent abrasion resistance and toughness |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC (-40degF to 302degF) | -30degC to 80degC (-22degF to 176degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Good resistance to oils and solvents, less effective against strong chemicals |
| Elasticity | Moderate elasticity with good compression set | High elasticity and rebound resilience |
| Load Bearing | Good load bearing with resistance to deformation | Superior load bearing, ideal for heavy-duty rollers |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent ozone, UV, and weather resistance | Good weather resistance but susceptible to UV degradation |
| Cost | Moderately priced | Generally higher cost due to performance features |
| Applications | Industrial rollers exposed to chemicals, high heat | Heavy-duty rollers requiring high abrasion resistance |
Introduction to Roller Materials: HNBR vs Polyurethane
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion, making it ideal for rollers in demanding industrial environments. Polyurethane rubber excels in load-bearing capacity and abrasion resistance, providing excellent durability and flexibility for high-performance roller applications. Comparing HNBR and polyurethane, selection depends on factors like temperature tolerance, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress in the roller's operating conditions.
Chemical Structure Comparison: HNBR and Polyurethane Rubber
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) features a saturated nitrile polymer backbone with hydrogenated olefinic bonds, providing enhanced resistance to heat, oil, and chemical degradation compared to traditional nitrile rubber. Polyurethane rubber consists of segmented copolymers with alternating soft polyol segments and hard urethane linkages, offering superior elasticity, abrasion resistance, and mechanical strength. The chemical structure of HNBR delivers stability in harsh chemical environments, while polyurethane's urethane linkages contribute to its toughness and flexibility, making the choice dependent on specific roller application requirements.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior tensile strength and excellent resistance to abrasion, heat, and chemicals, making it highly durable for roller applications in harsh environments. Polyurethane rubber exhibits exceptional tear resistance, high load-bearing capacity, and outstanding elasticity, contributing to prolonged roller life under dynamic mechanical stress. HNBR's enhanced thermal stability contrasts with polyurethane's superior flexibility, influencing the choice based on specific strength and durability requirements in industrial rollers.
Temperature Resistance Performance
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) outperforms polyurethane rubber in temperature resistance, maintaining stability from -40degC up to 150degC, making it ideal for high-heat roller applications. Polyurethane rubber, while offering excellent abrasion resistance, generally operates effectively between -30degC and 90degC, limiting its use in extreme thermal environments. HNBR's superior thermal endurance ensures consistent roller performance in automotive and industrial settings exposed to fluctuating or elevated temperatures.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance Analysis
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior abrasion and wear resistance compared to polyurethane rubber due to its enhanced chemical stability and higher tensile strength, making it particularly suitable for roller applications in harsh environments. Polyurethane rubber offers excellent wear resistance with superior elasticity and impact resistance but generally falls short of HNBR in withstanding aggressive mechanical abrasion over extended periods. The comparative analysis shows that HNBR rollers typically outperform polyurethane in durability and longevity under continuous abrasive stress, optimizing maintenance intervals and operational efficiency.
Chemical and Oil Resistance Capabilities
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior chemical and oil resistance compared to polyurethane rubber, especially in environments involving hydrocarbons, oils, and fuels. HNBR maintains its mechanical properties and resists swelling or degradation when exposed to aggressive chemicals, making it ideal for applications requiring resilience against petroleum-based fluids. Polyurethane rubber offers good abrasion resistance but generally shows lower resistance to mineral oils and certain solvents, limiting its effectiveness in chemically harsh conditions.
Applications in Industries: Suitability for Rollers
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, heat stability, and abrasion resistance, making it highly suitable for rollers used in automotive, oil and gas, and heavy machinery industries where exposure to oils, solvents, and high temperatures is common. Polyurethane rubber (PU) excels in applications requiring high load-bearing capacity, excellent flexibility, and wear resistance, often preferred for conveyor rollers, printing presses, and material handling equipment due to its durability under mechanical stress and impact. Both materials provide tailored performance for rollers, with HNBR favored in chemically aggressive environments and PU optimized for dynamic, high-wear industrial conditions.
Longevity and Maintenance Requirements
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, resulting in enhanced longevity for rollers operating in harsh environments compared to polyurethane rubber. Polyurethane rubber excels in abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity but typically requires more frequent maintenance due to its susceptibility to UV degradation and hydrolysis. For applications demanding minimal downtime and extended service life, HNBR rollers provide a more durable and low-maintenance solution.
Cost Effectiveness and Economic Considerations
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical and abrasion resistance, making it more durable for rollers in harsh environments, which translates to lower maintenance costs over time despite a higher initial price compared to polyurethane rubber. Polyurethane rubber provides excellent wear resistance and flexibility at a lower upfront cost, making it a cost-effective choice for less demanding applications with moderate operational stress. Evaluating total lifecycle costs, including replacement frequency and downtime, is crucial to determining the most economically viable option for roller materials.
Summary Table: HNBR vs Polyurethane for Roller Selection
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers excellent heat resistance, chemical stability, and durability, making it suitable for high-temperature and aggressive chemical roller applications. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance, high load-bearing capacity, and flexibility, ideal for rollers exposed to heavy mechanical wear and impact. Selection depends on operating conditions, with HNBR preferred for thermal and chemical stress and polyurethane favored for durability under mechanical strain.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Roller
 azmater.com
azmater.com