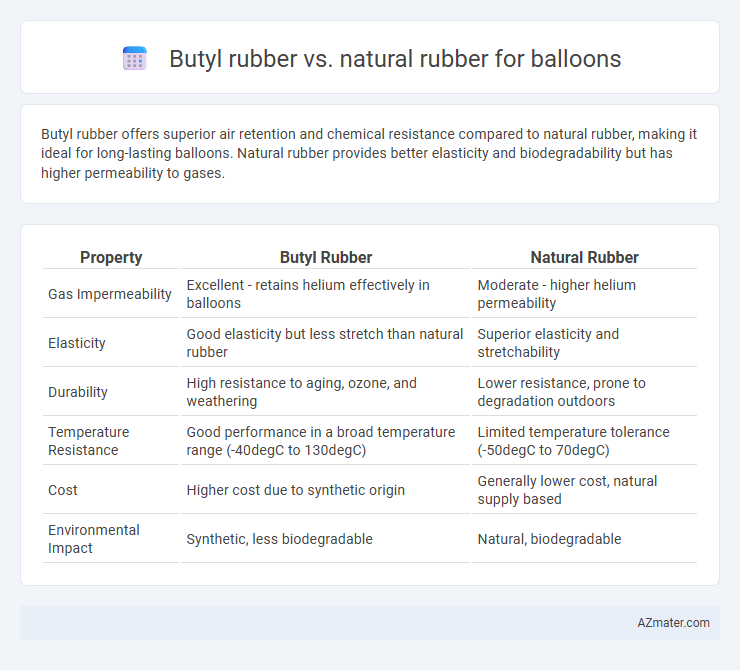
Butyl rubber offers superior air retention and chemical resistance compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for long-lasting balloons. Natural rubber provides better elasticity and biodegradability but has higher permeability to gases.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Butyl Rubber | Natural Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Impermeability | Excellent - retains helium effectively in balloons | Moderate - higher helium permeability |
| Elasticity | Good elasticity but less stretch than natural rubber | Superior elasticity and stretchability |
| Durability | High resistance to aging, ozone, and weathering | Lower resistance, prone to degradation outdoors |
| Temperature Resistance | Good performance in a broad temperature range (-40degC to 130degC) | Limited temperature tolerance (-50degC to 70degC) |
| Cost | Higher cost due to synthetic origin | Generally lower cost, natural supply based |
| Environmental Impact | Synthetic, less biodegradable | Natural, biodegradable |
Introduction: Butyl Rubber vs Natural Rubber for Balloons
Butyl rubber offers superior air retention and excellent resistance to ozone and weathering, making it ideal for long-lasting balloons. Natural rubber provides exceptional elasticity and tensile strength, creating highly stretchable and resilient balloons but with faster air permeability. Choosing between butyl and natural rubber depends on the balloon's required durability and flexibility in various environmental conditions.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Butyl rubber, composed primarily of isobutylene with small amounts of isoprene, exhibits a saturated polymer structure that provides excellent impermeability and resistance to gases, making it ideal for balloons requiring slow gas diffusion. In contrast, natural rubber consists mainly of cis-1,4-polyisoprene, an unsaturated polymer with a highly elastic and flexible molecular chain, offering superior tensile strength and resilience but higher gas permeability. The chemical saturation in butyl rubber's backbone reduces oxidation and ozone degradation compared to the unsaturated double bonds in natural rubber, influencing the balloon's durability and air retention properties.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Butyl rubber is synthesized through the copolymerization of isobutylene and isoprene, involving a controlled chemical reaction that results in a highly impermeable and elastic polymer, ideal for balloon manufacturing. Natural rubber, derived from latex tapping of rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis), undergoes processes such as coagulation, drying, and vulcanization to transform raw latex into elastic balloon material. The manufacturing process of butyl rubber emphasizes chemical synthesis and refining, whereas natural rubber production focuses on harvesting and processing natural latex, impacting the elasticity, durability, and air retention properties of balloons made from each type.
Air Retention Capabilities
Butyl rubber offers superior air retention capabilities compared to natural rubber due to its low permeability to gases, making it ideal for balloons that require long-lasting inflation. Natural rubber, while flexible and elastic, tends to allow air molecules to escape more readily, resulting in faster deflation. The molecular structure of butyl rubber, characterized by its saturated copolymer chains, significantly limits air diffusion, enhancing the balloon's durability and maintaining shape over extended periods.
Elasticity and Flexibility Comparison
Butyl rubber exhibits superior elasticity and low gas permeability, making it ideal for balloons requiring long-lasting inflation and resistance to sudden bursts. Natural rubber offers greater flexibility and tensile strength, allowing for easier stretching and higher elasticity but tends to degrade faster under UV exposure and ozone. Choosing between Butyl and Natural rubber depends on whether durability and airtightness or enhanced stretchability and natural resilience are prioritized for balloon applications.
Durability and Resistance to Degradation
Butyl rubber exhibits superior durability and resistance to degradation compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for balloons that require long-lasting elasticity and protection against air permeability. Its synthetic composition ensures excellent resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and chemical exposure, significantly reducing the risk of cracking and brittleness over time. Natural rubber, while highly elastic and flexible, tends to degrade faster when exposed to environmental factors, limiting its lifespan in balloon applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Butyl rubber exhibits superior resistance to air permeability, making it a preferred material for balloons requiring longer inflation retention, though it is derived from synthetic sources with significant reliance on petrochemicals, impacting carbon footprint and non-renewability. Natural rubber, harvested from Hevea brasiliensis trees, offers biodegradability and renewable sourcing but poses challenges due to deforestation practices and land use concerns in rubber plantations. Evaluating the environmental impact and sustainability, natural rubber presents a lower long-term ecological burden if sourced responsibly, while butyl rubber's synthetic nature necessitates enhanced recycling and waste management efforts to improve its environmental profile.
Safety and Allergen Concerns
Butyl rubber offers superior safety for balloons due to its hypoallergenic properties, making it ideal for individuals with latex allergies that are commonly triggered by natural rubber. Natural rubber contains proteins that can cause allergic reactions such as skin irritation or respiratory issues. Choosing butyl rubber balloons minimizes allergen exposure while maintaining elastic performance and durability.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Butyl rubber offers superior cost efficiency for balloons due to its lower production costs and enhanced durability compared to natural rubber, reducing overall material expenses. Availability of butyl rubber is generally more stable as it is synthetic and less dependent on agricultural factors, unlike natural rubber, which can face supply fluctuations due to climate and geopolitical issues. This makes butyl rubber a more cost-effective and reliably sourced option for balloon manufacturing in large-scale production.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Rubber for Balloons
Butyl rubber excels in balloon applications requiring superior airtightness and chemical resistance, making it ideal for long-lasting helium balloons and industrial uses. Natural rubber offers exceptional elasticity and biodegradability, preferred for standard party balloons and applications demanding high stretchability. Selecting the right rubber depends on the balloon's intended use, balancing durability, flexibility, and environmental impact.
Infographic: Butyl rubber vs Natural rubber for Ballon
 azmater.com
azmater.com