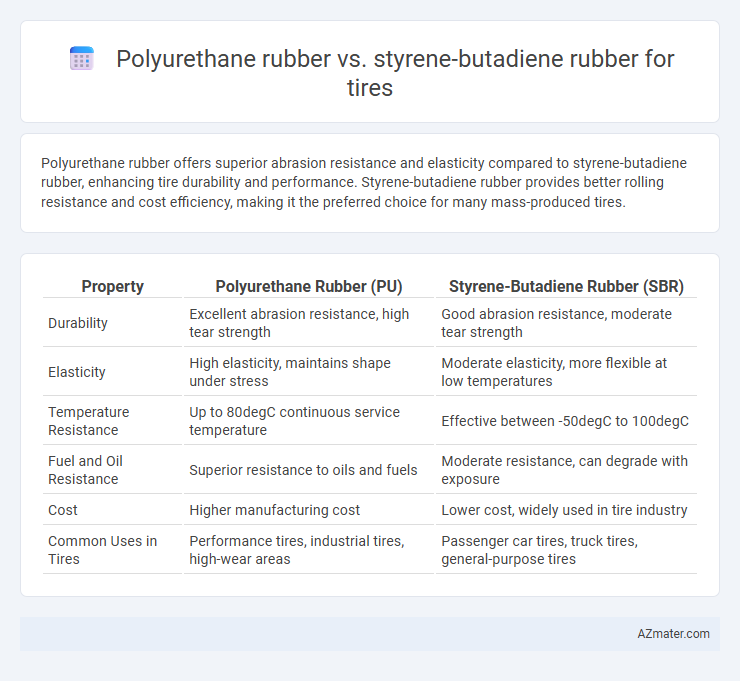
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and elasticity compared to styrene-butadiene rubber, enhancing tire durability and performance. Styrene-butadiene rubber provides better rolling resistance and cost efficiency, making it the preferred choice for many mass-produced tires.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Excellent abrasion resistance, high tear strength | Good abrasion resistance, moderate tear strength |
| Elasticity | High elasticity, maintains shape under stress | Moderate elasticity, more flexible at low temperatures |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 80degC continuous service temperature | Effective between -50degC to 100degC |
| Fuel and Oil Resistance | Superior resistance to oils and fuels | Moderate resistance, can degrade with exposure |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower cost, widely used in tire industry |
| Common Uses in Tires | Performance tires, industrial tires, high-wear areas | Passenger car tires, truck tires, general-purpose tires |
Introduction to Tire Rubber Materials
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and elasticity compared to Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), which is commonly used in tire treads for its cost-effectiveness and balanced performance. SBR provides good wear resistance and traction but falls short in durability and fuel efficiency relative to polyurethane compounds. In tire manufacturing, the choice between polyurethane and SBR impacts ride comfort, tread life, and overall tire performance under varying road conditions.
Overview of Polyurethane Rubber
Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior abrasion resistance and flexibility compared to styrene-butadiene rubber, making it ideal for high-performance tire applications requiring enhanced durability. Its molecular structure offers excellent tensile strength and resilience, contributing to extended tire life and improved traction under varying road conditions. Manufacturers favor polyurethane for specialty tires where low rolling resistance and resistance to oils and chemicals are critical performance factors.
Overview of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a synthetic rubber widely used in tire manufacturing due to its excellent abrasion resistance, good aging stability, and cost-effectiveness. SBR is typically blended with natural rubber to enhance tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for passenger car and truck tires. Compared to Polyurethane rubber, SBR offers better resilience and is easier to process, contributing to its dominant position in the tire industry.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Polyurethane rubber manufacturing involves a chemical reaction between polyols and isocyanates, enabling precise control over hardness and abrasion resistance, which enhances tire durability and performance. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is produced through emulsion polymerization of styrene and butadiene monomers, resulting in excellent aging stability and cost-effective mass production. The manufacturing process of polyurethane offers customizable mechanical properties but requires more complex chemical handling compared to the relatively straightforward polymerization and compounding of SBR for tire applications.
Performance Characteristics: Grip and Traction
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and maintains better grip on wet surfaces compared to Styrene-butadiene rubber, enhancing overall traction performance. Styrene-butadiene rubber provides excellent flexibility and resilience, contributing to improved grip on dry roads but tends to wear faster under harsh conditions. The combination of polyurethane's durability with reliable traction characteristics makes it ideal for tires requiring long-lasting performance in diverse driving environments.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Polyurethane rubber offers superior durability and exceptional wear resistance compared to styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for high-performance tire applications. Its molecular structure provides enhanced abrasion resistance and resists deformation under stress, extending tire lifespan in demanding conditions. While SBR is cost-effective and widely used for standard tires, polyurethane's advanced toughness delivers improved longevity and reliability in heavy-duty and industrial tire uses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane rubber offers superior resistance to abrasion and chemical degradation, extending tire lifespan and reducing waste generation compared to styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR). SBR, commonly derived from non-renewable petrochemical sources, typically exhibits lower recyclability and higher environmental footprints due to its energy-intensive production processes. Choosing polyurethane rubber for tires supports sustainability goals through enhanced durability and potential for recycling, contributing to reduced resource consumption and waste in the automotive industry.
Cost Analysis: Polyurethane vs SBR
Polyurethane rubber typically incurs higher material costs compared to Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) due to its complex synthesis and superior performance characteristics in abrasion resistance and durability. SBR offers a more cost-effective solution for tire manufacturing, benefiting from large-scale production and lower raw material expenses while providing adequate wear resistance and grip. The choice between polyurethane and SBR for tires often hinges on balancing initial material investment with long-term performance benefits and maintenance costs.
Applications in Different Types of Tires
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for high-performance tires used in racing and heavy-duty industrial vehicles. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) exhibits excellent aging stability and good wet traction, commonly utilized in passenger car tires and commercial truck tires for enhanced durability and safety. The selection between polyurethane rubber and SBR depends on specific tire application requirements such as wear resistance, elasticity, and environmental conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Tires
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and higher load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for heavy-duty tires requiring durability and performance under harsh conditions. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) provides excellent flexibility, good wear resistance, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for passenger car tires with balanced performance and comfort. Selecting the right rubber depends on specific tire application, prioritizing polyurethane for rugged, industrial use and SBR for general automotive purposes.
Infographic: Polyurethane rubber vs Styrene-butadiene rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com