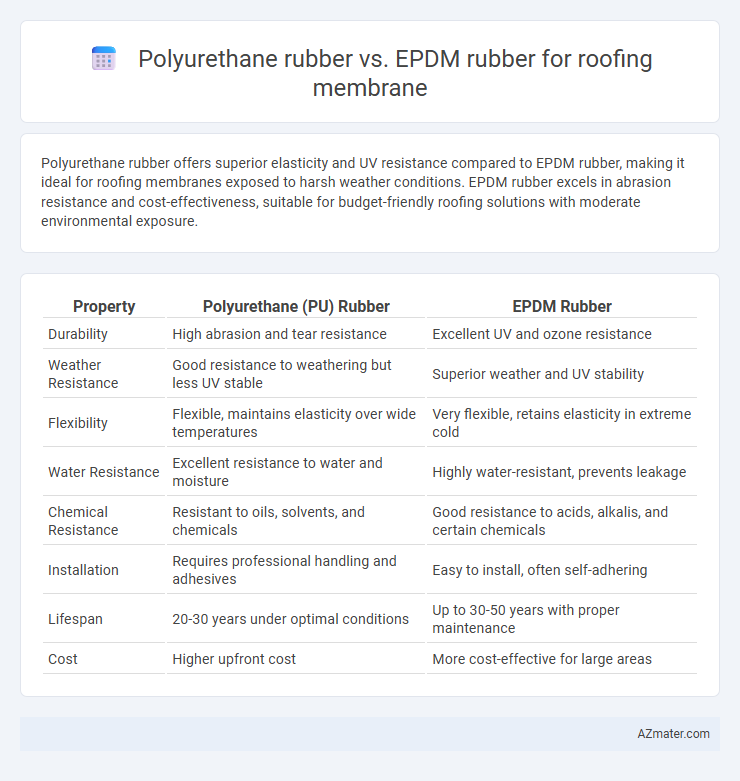
Polyurethane rubber offers superior elasticity and UV resistance compared to EPDM rubber, making it ideal for roofing membranes exposed to harsh weather conditions. EPDM rubber excels in abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, suitable for budget-friendly roofing solutions with moderate environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) Rubber | EPDM Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High abrasion and tear resistance | Excellent UV and ozone resistance |
| Weather Resistance | Good resistance to weathering but less UV stable | Superior weather and UV stability |
| Flexibility | Flexible, maintains elasticity over wide temperatures | Very flexible, retains elasticity in extreme cold |
| Water Resistance | Excellent resistance to water and moisture | Highly water-resistant, prevents leakage |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils, solvents, and chemicals | Good resistance to acids, alkalis, and certain chemicals |
| Installation | Requires professional handling and adhesives | Easy to install, often self-adhering |
| Lifespan | 20-30 years under optimal conditions | Up to 30-50 years with proper maintenance |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost | More cost-effective for large areas |
Introduction to Roofing Membranes
Polyurethane rubber and EPDM rubber are popular materials used in roofing membranes, each offering distinct advantages for waterproofing and durability. Polyurethane membranes provide excellent resistance to UV rays, chemicals, and abrasion, making them ideal for flat or low-slope roofs exposed to harsh environmental conditions. EPDM rubber membranes excel in flexibility, weather resistance, and ease of installation, commonly applied in both commercial and residential roofing systems for long-lasting protection.
What is Polyurethane Rubber?
Polyurethane rubber is a highly durable, flexible polymer used in roofing membranes for its excellent resistance to weathering, UV radiation, and chemical exposure. Its superior elasticity and waterproofing capabilities make it ideal for protecting roofs against leaks and structural damage. Unlike EPDM rubber, polyurethane offers enhanced tensile strength and longevity, especially in harsh environmental conditions.
What is EPDM Rubber?
EPDM rubber, or Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer, is a synthetic rubber commonly used for roofing membranes due to its excellent weather resistance and flexibility. It offers superior durability against UV rays, ozone, and extreme temperatures, making it ideal for long-lasting waterproof roofing applications. EPDM's seamless installation and resistance to cracking and abrasion provide a reliable solution for commercial and residential roofs.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Polyurethane rubber offers superior elasticity and weather resistance, making it ideal for roofing membranes exposed to harsh UV radiation and fluctuating temperatures. EPDM rubber provides excellent ozone and chemical resistance, with greater durability against water absorption and thermal aging. Both materials excel in flexibility and waterproofing, but polyurethane typically delivers higher tensile strength and abrasion resistance, enhancing roof longevity under mechanical stress.
Durability and Longevity
Polyurethane rubber roofing membranes offer superior durability with excellent resistance to abrasion, impact, and weathering, making them ideal for long-term applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. EPDM rubber membranes provide strong UV and ozone resistance, maintaining flexibility over time, but may exhibit slightly lower abrasion resistance compared to polyurethane. The longevity of polyurethane membranes often surpasses 20 years under optimal maintenance, whereas EPDM membranes typically last 15 to 25 years depending on thickness and exposure factors.
Weather and UV Resistance
Polyurethane rubber roofing membranes exhibit superior weather and UV resistance due to their dense, elastomeric structure that prevents degradation from prolonged sun exposure and extreme temperature fluctuations. EPDM rubber also offers excellent resistance to UV rays and weathering but tends to perform better in colder climates as its rubber composition is less prone to hardening and cracking. For long-term durability and minimal maintenance in high UV index regions, polyurethane membranes provide enhanced protection against ozone, oxidation, and chemical exposure compared to EPDM.
Installation Methods and Ease
Polyurethane rubber roofing membranes typically require professional installation involving heat welding or adhesives, offering strong seams that enhance durability and weather resistance, though this process demands skilled labor and precise equipment. EPDM rubber membranes are often installed using simpler methods such as mechanical fasteners, ballasting, or adhesive bonding, making the installation more straightforward and faster, particularly suitable for DIY projects or quick applications. The ease of installation with EPDM often translates to lower labor costs, while polyurethane's more complex installation generally yields longer-lasting, seamless results beneficial for high-performance roofing systems.
Cost Factors and Value for Money
Polyurethane rubber roofing membranes generally have higher upfront costs due to advanced chemical composition and enhanced durability compared to EPDM rubber, which is more affordable but may have a shorter lifespan. EPDM offers cost-effective installation and maintenance, making it a budget-friendly option for large-scale or temporary projects. Polyurethane provides superior resistance to weathering and chemical exposure, delivering better long-term value despite its initial higher expense.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
Polyurethane rubber roofing membranes typically require less frequent maintenance due to their superior resistance to UV rays, chemicals, and abrasion, ensuring extended durability with minimal repair needs. EPDM rubber, while highly flexible and easy to repair with readily available patches and adhesives, may demand more regular inspections to address potential seam failures and weather-related degradation. Maintenance strategies for polyurethane emphasize proactive surface cleaning and protective coatings, whereas EPDM maintenance prioritizes sealing seams and promptly repairing punctures to maintain waterproof integrity.
Choosing the Right Roofing Membrane for Your Project
Polyurethane rubber offers excellent elasticity and superior resistance to weathering, UV radiation, and chemical exposure, making it ideal for roofs requiring long-term durability and flexibility. EPDM rubber is highly valued for its exceptional resistance to ozone, UV rays, and water, along with its ease of installation and cost-effectiveness, suitable for a variety of commercial and residential roofing projects. Choosing the right roofing membrane depends on project-specific factors such as climate conditions, expected lifespan, budget constraints, and the roof's structural requirements.
Infographic: Polyurethane rubber vs EPDM rubber for Roofing membrane
 azmater.com
azmater.com