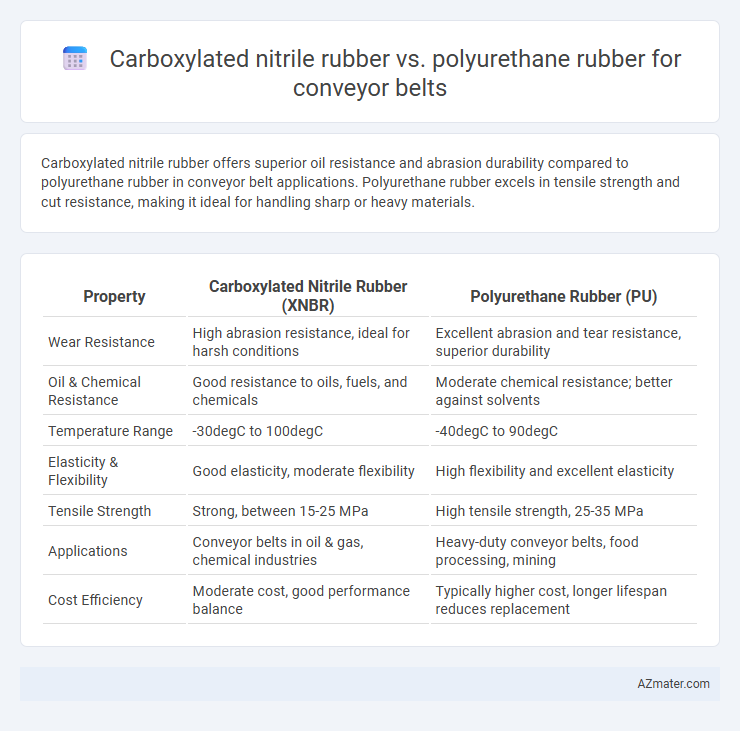
Carboxylated nitrile rubber offers superior oil resistance and abrasion durability compared to polyurethane rubber in conveyor belt applications. Polyurethane rubber excels in tensile strength and cut resistance, making it ideal for handling sharp or heavy materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Wear Resistance | High abrasion resistance, ideal for harsh conditions | Excellent abrasion and tear resistance, superior durability |
| Oil & Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Moderate chemical resistance; better against solvents |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 100degC | -40degC to 90degC |
| Elasticity & Flexibility | Good elasticity, moderate flexibility | High flexibility and excellent elasticity |
| Tensile Strength | Strong, between 15-25 MPa | High tensile strength, 25-35 MPa |
| Applications | Conveyor belts in oil & gas, chemical industries | Heavy-duty conveyor belts, food processing, mining |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate cost, good performance balance | Typically higher cost, longer lifespan reduces replacement |
Introduction to Conveyor Belt Materials
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) and polyurethane rubber are widely used materials in conveyor belts, each offering distinct advantages based on their chemical properties and mechanical performance. XNBR provides excellent oil and chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications that involve exposure to harsh substances, while polyurethane rubber delivers superior abrasion resistance and elasticity, suitable for heavy-duty and high-impact conveyor systems. Selecting the appropriate material depends on the operational environment and specific requirements such as durability, flexibility, and resistance to wear and chemicals.
Overview of Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR)
Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) exhibits enhanced tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and chemical stability compared to standard nitrile rubber, making it ideal for conveyor belt applications that require durability under harsh conditions. XNBR's carboxyl groups improve cross-linking density, resulting in superior mechanical properties and resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents. Its ability to maintain flexibility at low temperatures alongside excellent wear resistance outperforms polyurethane rubber in many industrial conveyor systems, especially those exposed to aggressive chemicals and fluctuating temperatures.
Overview of Polyurethane Rubber (PU)
Polyurethane rubber (PU) offers superior abrasion resistance and elasticity compared to carboxylated nitrile rubber, making it ideal for conveyor belts subjected to heavy loads and sharp-edged materials. PU exhibits excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and temperature variations, which enhances the durability and lifespan of conveyor belts in harsh industrial environments. Its high tensile strength and flexibility ensure efficient material handling with minimal downtime and maintenance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength compared to polyurethane rubber, making it highly suitable for heavy-duty conveyor belts exposed to harsh conditions. Polyurethane rubber offers greater elasticity and tear resistance, providing enhanced flexibility and durability under dynamic loads and repeated impact. Mechanical properties such as tensile strength for XNBR typically range from 15 to 30 MPa, while polyurethane rubber ranges from 25 to 35 MPa, with elongation at break favoring polyurethane at approximately 400-600% versus XNBR's 300-500%.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior abrasion resistance compared to polyurethane rubber, making it highly effective in heavy-duty conveyor belt applications where abrasive materials are handled. XNBR's enhanced cross-linking and polar functional groups provide excellent wear resistance, extending the service life of conveyor belts in harsh environments. Polyurethane rubber, while flexible and resistant to impact, generally exhibits lower abrasion resistance, leading to faster degradation under continuous abrasive stress.
Chemical Resistance and Compatibility
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, and certain chemicals, making it highly suitable for conveyor belts exposed to aggressive substances. Polyurethane rubber exhibits excellent resistance to abrasion, fats, and solvents, but its chemical resistance is generally lower against concentrated acids and oils compared to XNBR. Compatibility depends on the conveyor belt's specific application environment, with XNBR preferred for chemical-laden contexts and polyurethane favored for wear resistance and mechanical durability.
Temperature and Environmental Performance
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior resistance to a wide temperature range from -40degC to 120degC, maintaining flexibility and wear resistance under thermal stress, making it ideal for conveyor belts exposed to fluctuating temperatures. Polyurethane rubber withstands higher mechanical abrasion and performs well in temperatures ranging from -30degC to 80degC, but it may degrade faster under prolonged heat exposure compared to XNBR. Environmentally, XNBR exhibits excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and oxidation, while polyurethane is more vulnerable to UV radiation and hydrolysis, impacting the conveyor belt's longevity in outdoor or harsh industrial environments.
Cost Considerations and Longevity
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) generally offers a lower initial cost compared to polyurethane rubber, making it a budget-friendly option for conveyor belts in environments with moderate abrasion and chemical exposure. Polyurethane rubber, while more expensive upfront, provides superior longevity and resistance to wear, abrasion, and tearing, resulting in lower total cost of ownership over extended service periods. When evaluating conveyor belt materials, balancing the upfront cost of XNBR against the enhanced durability and reduced replacement frequency of polyurethane is critical for optimizing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Application Suitability in Conveyor Belting
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) demonstrates superior oil and chemical resistance, making it ideal for conveyor belts in industries handling petroleum products or aggressive chemicals. Polyurethane rubber offers exceptional abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, suited for conveyor systems transporting heavy or abrasive materials like coal or ore. Selection depends on specific operational demands, where XNBR excels in chemical exposure environments and polyurethane provides durability under high wear conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Ideal Material
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil and chemical resistance, making it ideal for conveyor belts in harsh industrial environments where exposure to oils and solvents is frequent. Polyurethane rubber excels in abrasion resistance and tensile strength, providing extended durability in applications with heavy mechanical stress and sharp materials. Selecting the ideal conveyor belt material depends on balancing chemical exposure and mechanical wear, with XNBR preferred for chemical resistance and polyurethane for abrasion-heavy operations.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Conveyor belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com