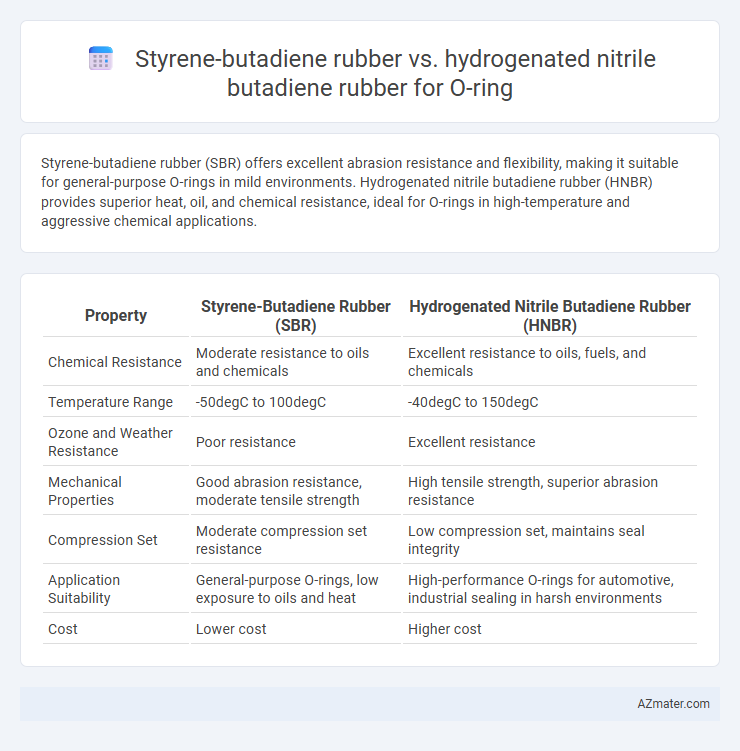
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility, making it suitable for general-purpose O-rings in mild environments. Hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR) provides superior heat, oil, and chemical resistance, ideal for O-rings in high-temperature and aggressive chemical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to oils and chemicals | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 100degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Poor resistance | Excellent resistance |
| Mechanical Properties | Good abrasion resistance, moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength, superior abrasion resistance |
| Compression Set | Moderate compression set resistance | Low compression set, maintains seal integrity |
| Application Suitability | General-purpose O-rings, low exposure to oils and heat | High-performance O-rings for automotive, industrial sealing in harsh environments |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to O-Ring Material Selection
Selecting the optimal O-ring material is crucial for ensuring sealing performance, durability, and chemical resistance. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and moderate heat and oil resistance, making it suitable for general-purpose applications. In contrast, hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR) provides superior resistance to heat, oils, and chemicals, along with enhanced mechanical properties, ideal for demanding environments requiring extended service life.
Overview of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a synthetic copolymer mainly composed of styrene and butadiene, widely used for its good abrasion resistance and aging stability. SBR offers excellent performance in applications requiring resilience and flexibility under moderate temperatures but has limited resistance to oils and chemicals compared to hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR). Its cost-effectiveness and good mechanical properties make SBR a popular choice for O-rings in general-purpose sealing applications where oil and chemical exposure is minimal.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (HNBR) is a high-performance elastomer known for its superior resistance to heat, oil, and chemical degradation compared to Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR). HNBR exhibits enhanced mechanical properties, including excellent tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and low gas permeability, making it ideal for demanding O-ring applications in automotive and industrial sectors. Its hydrogenation process reduces unsaturation in the polymer chain, significantly improving thermal stability and resistance to ozone and weathering.
Chemical Resistance: SBR vs HNBR in O-Ring Applications
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate chemical resistance but tends to degrade when exposed to oils, fuels, and ozone, limiting its effectiveness in aggressive chemical environments for O-ring applications. Hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior chemical resistance to hydrocarbons, oils, and oxidation, making it highly suitable for dynamic sealing in automotive and industrial O-rings. The enhanced saturation of HNBR's polymer backbone provides exceptional durability and aging resistance compared to the unsaturated structure of SBR, ensuring longer service life in harsh chemical conditions.
Temperature Performance Comparison
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) typically operates within a temperature range of -50degC to 100degC, making it suitable for standard O ring applications with moderate thermal demands. Hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR) displays superior temperature resistance, maintaining flexibility and sealing performance from -40degC up to 150degC, and even higher with special grades. This enhanced thermal stability of HNBR makes it ideal for O rings in automotive, oil, and gas industries where exposure to elevated temperatures is common.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and tensile strength, making it suitable for dynamic O-ring applications requiring moderate mechanical durability. Hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior mechanical properties, including higher tensile strength, enhanced elongation, and improved resistance to heat, oil, and ozone, resulting in significantly increased durability for O-rings in harsh environments. While SBR is cost-effective with good wear resistance, HNBR outperforms in long-term mechanical stability and chemical resistance, essential for industrial sealing under demanding conditions.
Cost Considerations for SBR and HNBR O-Rings
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) O-rings generally offer a lower initial cost due to their widespread availability and simpler manufacturing processes, making them suitable for budget-conscious applications with moderate chemical exposure. In contrast, hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR) O-rings command a higher price owing to their enhanced chemical resistance, thermal stability, and durability, which reduce long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Cost considerations between SBR and HNBR O-rings should weigh upfront purchase price against performance longevity and operational conditions.
Typical Industrial Applications
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is commonly used in automotive seals, conveyor belts, and general-purpose gaskets due to its good abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness. Hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR) is preferred for O-rings in oil and gas, chemical processing, and automotive fuel systems because of its superior heat, oil, and chemical resistance. HNBR O-rings perform well in high-temperature and aggressive environments, while SBR suits less demanding sealing applications requiring moderate durability.
Longevity and Maintenance Requirements
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate longevity and requires regular maintenance due to its susceptibility to ozone, heat, and oil degradation, making it less ideal for high-stress O-ring applications. Hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior durability with excellent resistance to heat, ozone, chemicals, and abrasion, significantly extending O-ring service life and reducing maintenance frequency. In industrial environments demanding reliable sealing performance and minimal downtime, HNBR O-rings provide better long-term value despite higher initial costs.
Choosing the Right Material for Your O-Ring Needs
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for general-purpose O-rings in dry environments. Hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR) provides superior chemical resistance, heat tolerance up to 150degC, and enhanced durability against oils and fuels, ideal for demanding automotive and industrial sealing applications. Selecting HNBR over SBR ensures long-term performance in harsh conditions, while SBR remains advantageous for budget-conscious projects with moderate mechanical stresses.
Infographic: Styrene-butadiene rubber vs Hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber for O ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com